GAC Physics Topic 5: Electric Currents Ch 17
advertisement

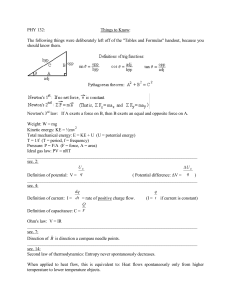
Name ________________ Date ________ Block ___ GAC Physics Topic 5: Electric Currents Ch 17 5.1 Electric potential difference, current and resistance Electric Potential difference and Capacitance 5.1.1 Sec 1, Define electric potential difference. Practice A, 5.1.2 Determine the change in potential energy when a charge moves between two points at different SR pg 601 potentials. 5.1.4 Solve problems involving electric potential difference. 5.1.12 Sec 2, Relate capacitance to the storage of electrical potential energy in the form of separated charges. 5.1.13 Practice B, Calculate the capacitance of various devices. 5.1.14 SR pg 607 Calculate the energy stored in a capacitor. Electric Current and resistance Assessment statement 5.1.5 Sec 3, Define electric current. Practice C, SR pg 616 5.1.6 Sec 3, Practice D, SR pg 616 5.1.7 Teacher’s notes It is sufficient for students to know that current is defined in terms of the force per unit length between parallel current-carrying conductors. Define resistance. Apply the equation for resistance in the form: where ρ is the resistivity of the material of the resistor. State Ohm’s law Solve problems involving potential difference, capacitance, current and resistance. 5.1.8 5.1.11 Students should be aware that R = V/I is a general definition of resistance. It is not a statement of Ohm’s law. Students should understand what is meant by resistor. For example, students should be able to draw I– V characteristics of an ohmic resistor and a filament lamp. 5.2 Electric Circuits 5.2.1 5.2.2 5.2.3 Ch 18, Sec 2, Practice A, SR pg656 Ch 18, Sec 2, Practice B, SR pg 656 Ch 18 Sec 3, Practice C & D, SR pg 663 5.2.4 Ch 18, Sec 1, SR pg 645 5.2.5 Apply the equations for resistors in series. Apply the equations for resistors in parallel. Apply the equations for combinations of resistors in complete circuits. Draw circuit diagrams. Students should be able to recognize and use the accepted circuits symbols. Describe the use of ideal ammeters and ideal voltmeters.