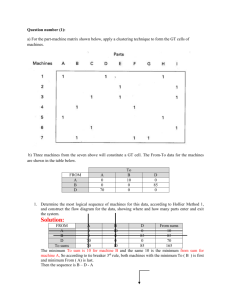
Question number (1): a) For the part
advertisement
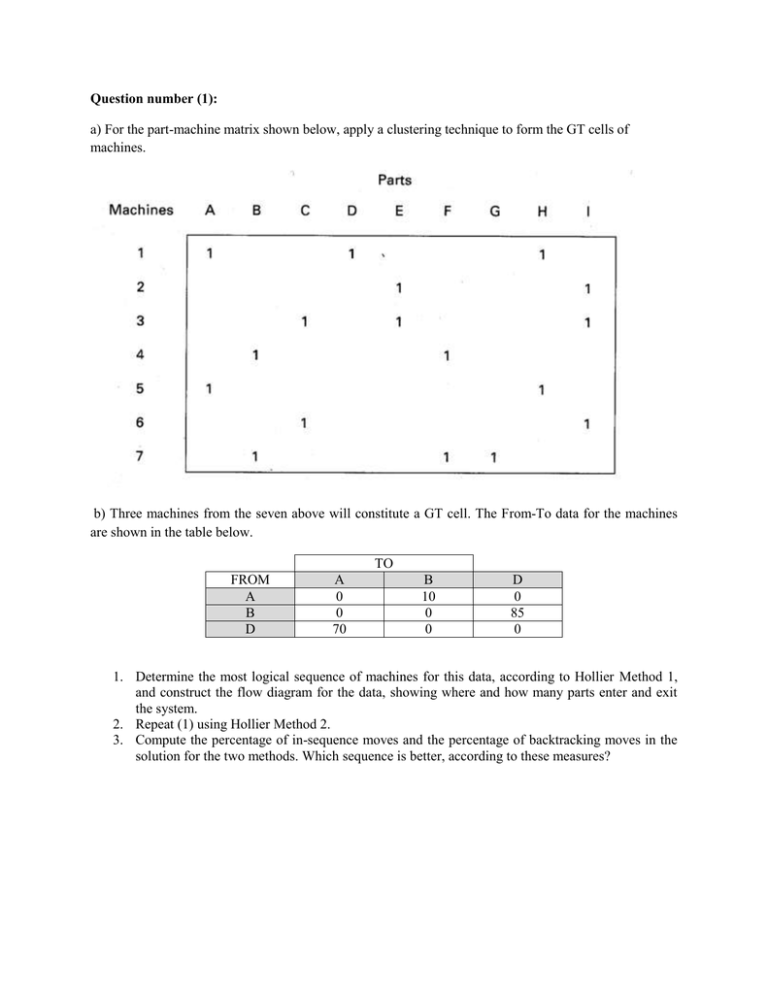
Question number (1): a) For the part-machine matrix shown below, apply a clustering technique to form the GT cells of machines. b) Three machines from the seven above will constitute a GT cell. The From-To data for the machines are shown in the table below. TO FROM A B D A 0 0 70 B 10 0 0 D 0 85 0 1. Determine the most logical sequence of machines for this data, according to Hollier Method 1, and construct the flow diagram for the data, showing where and how many parts enter and exit the system. 2. Repeat (1) using Hollier Method 2. 3. Compute the percentage of in-sequence moves and the percentage of backtracking moves in the solution for the two methods. Which sequence is better, according to these measures? Question number (2): a) For the part-machine matrix shown below, apply the rank order clustering technique to form the GT cells of machines. Parts ‘Number’ 1 2 A Machines 1 5 6 1 1 1 1 D E 4 1 B C 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 b) If we suppose that the previous five machines will constitute a GT cell. The From-To data for the machines are shown in the table below. FROM 1 2 3 4 5 1 0 0 0 100 0 2 40 0 0 0 105 TO 3 110 0 0 50 0 4 0 115 0 0 50 5 0 0 0 0 0 1. Determine the most logical sequence of machines for this data, according to Hollier Method 1, and construct the flow diagram for the data, showing where and how many parts enter and exit the system. 2. Repeat (1) using Hollier Method 2. 3. Compute the percentage of in-sequence moves and the percentage of backtracking moves in the solution for the two methods. Which sequence is better, according to these measures?