lecture 9 ppt
advertisement

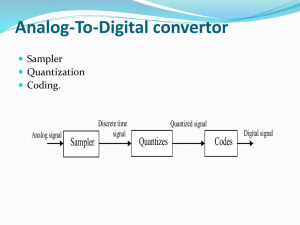
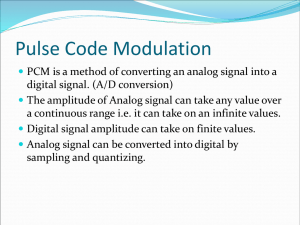
IT-101 Section 001 Introduction to Information Technology Lecture #9 Overview Chapter 12 Digital Audio Digitization of Audio Samples Quantization Reconstruction Quantization error Digitization of Audio Samples Step 2: Quantization Audio signals are continuous in time and amplitude Audio signal must be digitized in both time and amplitude to be represented in binary form. Discrete in time by sampling – Nyquist Discrete in amplitude by quantization Once samples have been captured, they must be made discrete in amplitude. Step 1: Sampling Step 2: Quantization The two step digitization process Quantization Quantization Converts actual sample values (usually voltage measurements) into an integer approximation Process of rounding off a continuous value so that it can be represented by a fixed number of binary digits Tradeoff between number of bits required and error Human perception limitations affect allowable error Specific application affects allowable error Two approaches to quantization Rounding the sample to the closest integer. (e.g. round 3.14 to 3) Create a Quantizer table that generates a staircase pattern of values based on a step size. Consider an audio signal with a voltage range between -10 and +10 Assume the audio waveform has already been time sampled, as shown How can the amplitude also be converted into discrete values? For this example, let’s choose to represent each sample by 4 bits There are an infinite number of voltages between -10 and 10. We will have to assign a range of voltages to each 4-bit codeword. There will be 16 steps. Why? How large will each step be? Reconstruction Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) provides the sampled and quantized binary code. Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) converts the quantized binary code back into an approximation of the analog signal by clocking the code to the same sample rate as the ADC conversion. Quantization and Reconstruction example on next two slides: QUANTIZATION RECONSTRUCTION Quantization Error Quantization is only an approximation. After quantization, some information is lost Errors (noise) introduced The difference between the original sample value and the rounded value is called the quantization error A signal to noise ratio (SNR) is the ratio of the relative sizes of the signal values and the errors. The higher the SNR, the smaller the average error is with respect to the signal value, and the better the fidelity. Comments for next class Chapter 13 The Telephone System: wired and wireless Analog Telephone system Digital telephone system Cellular telephone system Chapters Read So Far Information Technology Inside and Outside Everyone should have read the following chapters thus far: Chapter 1: What is the Information in the Information Revolution? Chapter 3: Representing Information in Bits Chapter 4: The Need and Basis for Data Protocols Chapter 5: From the Real World to Images and Video Chapter 7: Compressing Information Chapter 8: Image Compression Chapter 9: Digital Video Chapter 10: Audio as Information Chapter 11: Sampling of Audio Signals Chapter 12: Digital Audio