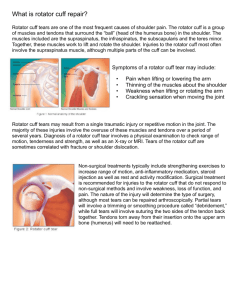
The muscles in the rotator cuff include
advertisement

Shoulder injury prevention Why do these exercises? Muscles of the rotator cuff The rotator cuff is a group of tendons and muscles in the shoulder, connecting the upper arm (humerus) to the shoulder blade (scapula). The rotator cuff tendons provide stability to the shoulder; the muscles allow the shoulder to rotate. The muscles in the rotator cuff include: Teres minor Infraspinatus Supraspinatus Subscapularis Each muscle of the rotator cuff inserts at the scapula, and has a tendon that attaches to the humerus. Together, the tendons and other tissues form a cuff around the humerus. - - Help prevent future injuries May improve posture, which could lead to pulling more water and improving your stroke Can help improve performance by limiting shoulder pain. Internal & External Rotation By: Julia DelNero How can injuries be prevented? What is Internal & External rotation External Rotation Internal rotation Equipment: Light to moderate theraband or resistance tube. Equipment: Light to moderate theraband or resistance tube Movement: Stand perpendicular to your anchor point and pull the tubing directly across the body. Keep elbow tight and leave about a 2-inch space between your waist and elbow. Movement: The opposite of external rotation: Hold the tubing in the hand that is closest to your anchor point and rotate the arm away from the anchor point across the body. Keep elbow tight and leave about a 2-inch space between your waist and elbow Form tip: Keep scapula tight and your shoulder lowered to work the rotator cuff, and not the arm muscles. Reps: One minute for each side, progressing up to two minutes Form tip: Take one lateral step away to add slight resistance Reps: One minute each side, progressing up to two minutes - Communication between athlete, Parent, coach, and medical professional - Good stroke technique - Lessen repetitive strokes that cause overuse injuries - Perform core strengthening and crosstraining exercises in pre and early season routines - Use periods of rest to recover - Consider alternative training techniques rather then training through an injury - Focus rehab efforts on rotator cuff and scapular strengthening - Return to play only when clearance is granted by a health care processional