Conditions of Learning
advertisement

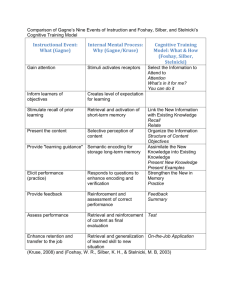
King Saud University College of nursing Master program Objectives At the end of this session the students will be able to: • Identify five major categories of learning. • Synthzies learning tasks for intellectual skills & organized in a hierarchy according to complexity. • Discuss nine instructional events. • Apply principles of conditions of learning. Out lines:• Overview • Major categories of learning • Instructional events & corresponding of the theory. • Application of nine instructional events. • Principles of learning theory • Conclusion Overview: According to Gagne's theory, it is important for teachers to understand the conditions of learning in order to teach new concepts to all different types of learners. This theory stipulates that there are several different types or levels of learning. The significance of these classifications is that each different type requires different types of instruction. Cognitivism • Has its roots in cognitive psychology & Information Processing Theory. Information Processing • Theory emphasizes the identification of the internal processes of learning • The best way to introduce this theory is through Gagne's model which describes the set of factors that influence learning and that collectively may be called the conditions of learning. • They include internal as well as external conditions that shape the learning processes So the focus of the theory is on intellectual skills Gagne identifies five major categories of learning (Conditions of Learning) Attitudes Verbal information Intellectual skills Motor skills Cognitive strategies Verbal information: The kind of information that we are able to state; declarative knowledge. Intellectual skills: Processes that allow the individual to interact with their environment. – These include reading, writing, mathematics, to advanced science and engineering; procedural knowledge. Cognitive strategies: Capabilities that govern the individual’s own learning, remembering, and thinking behavior. – Learning to learn strategies, – For example elaboration strategies, practical strategies, organizational strategies, & comprehension monitoring strategies or what is often referred to as meta-cognition. Metacognition: Students’ knowledge about their own cognitive processes, their ability to control these processes by organizing, monitoring, and modifying them as a function of learning outcomes. Psychomotor skills: Coordinated muscular movements, e.g. walking, drawing, Psychomotor skills must be practiced to be learned. Injection --- Attitudes: • Mental state that predisposes a learner to choose to behave in a certain way. Tasks for intellectual skills can be organized in a hierarchy according to complexity Gagne's nine events of instruction: B) Practical Application Gagne’s nine instructional events and corresponding cognitive processes can serve as the basis for designing instruction and selecting appropriate media. In applying these instructional events, Kearsley . suggests keeping the following principles in mind………..!!!!!! 1. Learning hierarchies define a sequence of instruction. 2. Learning hierarchies define what intellectual skills are to be learned. 3. Different instruction is required for different learning outcomes. Instructions Lesson Example 1. Gaining Attention Shows an example diagram & Asks learners questions about diagramming. 2. Informing the Learner of the Objective Teacher says, "Today I am going to show you how to use a multimedia presentation." 3. Stimulating Recall of Prior Learning For this particular group of learners, they have learned previously about Mind Mapping. Teacher associates this knowledge with lesson at hand. 4. Presenting the Stimulus Teacher gives students step -by-step discussion group 5. Providing Learner Guidance Teacher demonstrates how to create a diagram on the video projection screen/TV monitor. 6. Eliciting Teacher asks students to demonstrate tools Performance 7. Giving Feedback Teacher gives immediate feedback to learners after eliciting responses. 8. Assessing Assign a practice activity Performance 9. Enhancing Teacher asks learners to create activities Retention & Transfer Principles: 1. Different instruction is required for different learning outcomes. 2. Events of learning operate on the learner in ways that constitute the conditions of learning. 3. The specific operations that constitute instructional events are different for each different type of learning outcome. 4. Learning hierarchies define what intellectual skills are to be learned and a sequence of instruction. Conclusion Gagne’s Conditions of Learning Theory is based on a hierarchy of intellectual skills organized according to complexity that can be used to identify prerequisites necessary to facilitate learning at each level. Instruction can be made more efficient by following a sequence of nine instructional events defined by the intellectual skills that the learner is required to learn for the specific task at hand. References: • Gagne, R. (1962). Military training and principles of learning. American Psychologist, 17, 263-276. • Gagne, R. (1985). The Conditions of Learning (4th ed.). New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston. • Gagne, R. (1987). Instructional Technology Foundations. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Assoc. • Gagne, R. & Driscoll, M. (1988). Essentials of Learning for Instruction (2nd Ed.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. • Gagne, R., Briggs, L. & Wager, W. (1992). Principles of Instructional Design (4th Ed.). Fort Worth, TX: HBJ College Publishers. Relevant Web Sites • The following web sites provide further information about Gagne and his work: • http://www.psy.pdx.edu/PsiCafe/KeyTheorist s/Gagne.htm • http://www.ittheory.com/gagne1.htm • Conditions of Learning: Gagne • http://tip.psychology.org/gagne.html • Robert Gagne's Instructional Design Approach • http://www.gsu.edu/~mstswh/courses/it700 0/papers/robert.