ch 2b Nubia _ Ancient Americas
advertisement

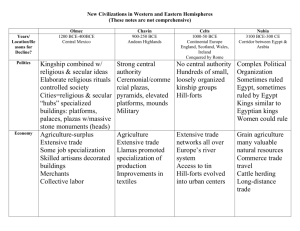
I. Nubia A. Geography 1. developed along the Nile River south of Egypt 2. Nubia (“Land of the Bow”): name of region where the Kush and Meroë Kingdoms developed 3. often at war with Egypt (starting in Middle Kingdom) 4. shared many of the same cultural traits as Egypt (religion, architecture, art) Nubian Pyramids B. Economics 1. Extensively trade in iron & gold 2. ivory, copper, incense, animals, & ebony A frankincense tree. The resin was used to make good smelling incense. C. Nubian Society & Politics 1. mimicked Egypt extensively (ie: Egyptian gods) 2. conquered Egypt until Assyrians invaded 3. matrilineal & women played important role in politics (Candace, title of a Queen of Nubia) Cause of decline? -overrun by nomadic camel traders? -Roman control of Mediterranean? -ENV collapse of iron mines? II. Early Mesoamerica: The Olmec Geography: -hot and humid, with rivers, swamps, jungles; heavy rainfall Mesoamerica: area between central Mexico & Honduras A. Olmec Society: -“mother culture” of Mesoamerica (1500 B.C.E.-200 C.E.) -ruled by wealthy families, instead of kings (theocracy) -cities site of religious ceremonies (bloodletting…) B. Olmec Politics: -called “Cult of the Jaguar” -city-led government -military used to protect trade -dirt & clay pyramids -colossal heads C. Olmec Economy: -mostly corn, beans, & squash farmers Highlands: obsidian, jade, cacao (drink for nobility) Lowlands: sea food, turtle shells, shark teeth III. Early South America: The Chavín • “Mother culture” in Peru (900 B.C.E. to 250 B.C.E.) • Andes mountains (10,000 ft.); capital Chavín de Huántar A. Chavin Economy & Society: 1. farming: maize, potatoes, llamas, coca leaves 2. roads, bridges, irrigation/drainage B. Chavin Society: 1. Chavin de Huantar: religious center w/ pyramids, plazas, & massive mounds 2. Chavín culture spread over coastal Peru