MARKET OR PLANNED ECONOMY?
advertisement

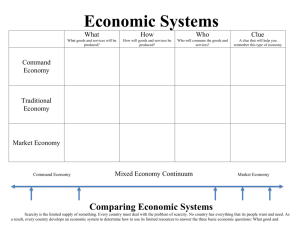
Types of economies ALLOCATION OF LIMITED RESOURCES RESOURCES – scarce WANTS – unlimited The function of an economy is to find ways how to allocate these scarce resources, basically answering the following questions: The main questions an economy should provide answers to: WHAT to produce? WHO to produce for? HOW to produce? WHY to produce? THREE TYPES OF ECONOMIES MARKET ECONOMY PLANNED ECONOMY MIXED ECONOMY IN DIFFERENT ECONOMIES WHO Owns Provides Allocates Distibutes Compete Decides Ensures Passes ...... scarce resources? against each other? fair competition? what to produce, how and who for? laws? means of production? goods and services? police, defence, judiciary ? minimum standard of living? Owns means of production Provides a minimum standard of living Owns scarce resources Allocates scarce resources Distributes goods and services Compete against each other Decides what to produce, how and who for Ensures fair competition Passes laws Ensures police, defence and judiciary PLANNED ECONOMY (command e.) State owns the means of production Decides about the allocation of resources More equal distribution of goods and services No competition among companies RB Read p. 30 (Planned & Market E.) MARKET ECONOMY (capitalist, free enterprise e.) Government intervention at minimum Private individuals and businesses own the means of production The main aim is to make profit and the businesses compete against each other The market mechanism – the law of supply and demand decides what to produce, how to produce and who gets what is produced MARKET OR PLANNED ECONOMY? demand and supply state-owned resources competition production of standardised goods of lower quality profit equal distribution of wealth in society wider choice and better quality of goods production for need, not profit MIXED ECONOMY It is a mixture of the planned and market economy The country’s e. is devided into two parts or sectors according to ownership: PUBLIC SECTOR – owned by the government PRIVATE SECTOR – owned by private individuals and businesses Resources are allocated by the forces of supply and demand The government regulates the market How do mixed economies work? Think about some of the goods and services that you have used in the past few days. Are they part of the public or private sector? When we purchase smth from a private retailer we assume that we are contibuting to the private sector. When, however, we use a government service, we enjoy smth that the public sector provides often mistakenly believing that such a service is free of charge. Let’s examine this idea through the example of taking a ride in a taxi cab. Imagine that you took a taxi on a rainy afternoon. When the ride is over, you paid the driver, who, after subtracting his costs, made a small profit on driving you in his privately owned car. This seems like a transaction that took place exclusively in the private sector. Although it is not obvious at first glance, government plays an important role in regulating traffic in general and the work of cab drivers in particular. The roads that taxis drive on are also public goods paid by the taxes that people – like the cab driver – pay on their income. No private business could exist without public goods and services: they are protected by the police, use streetlights, their employees are educated in the public school system and kept healthy or cured in public hospitals. At the same time, all governments want to encourage the success of private businesses, because without their contribution to the budget, in the form of taxes, public goods and services would not exist. Boglarka Kiss-Kulenović Taken from the Coursebook English for Business 1 MIXED ECONOMY • • • • • Some resources are a_______ by the state (public sector), and some by the market system (private sector). The public sector s______ public goods by local or central government (goods used by general public, paid through _________). The state usually p______ a minimum standard of living for the poor. The government e______ fair competition. In the private sector means of production are o_______ privately. MIXED ECONOMY PRIVATE SECTOR v. PUBLIC SECTOR • private individuals own r________ • firms make d______ •firms allocate r_____ in response to demand →RB, p. 30 • the government (central or local) owns and allocates r _____ • the government supplies p_____ g_____ and s______ •the government ensures a level p____ f___ CE → CAPITALIST OR MARKET ECONOMY PE → PLANNED ECONOMY ME → MIXED ECONOMY BIDDING SENTENCES 1. In CE resources are allocated by the government. 2. Public goods in ME are provided free when used and are paid for by taxes. 3. The role of the government in CE is to pass laws, plans and organises the production process. 4. In ME, in the private sector, production decisions are made by firms in response to the demands of consumers, and individuals are allowed to own the means of production. 5. In PE, production is for need rather than for profit. 6. In ME the state usually provides a minimum standard of living for the poor. 7. In PE there is more equal distribution of income and wealth. 8. In the CE the government doesn’t ensure a level playing field. 9. In ME, the public sector (central or local government) is responsible for the supply of some public goods and services. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. All the countries with PE have a good standard of living. In ME some resources are allocated by the government and some by the market. Private firms are interested in financing national defence and police. Laissez-faire economy is another name for planned economy. Since the only interest of firms in CE is profit and lower costs, they often tend to sacrifice public interest. SPEAKING TASK MAKE A PRESENTATION ON EACH TYPE OF ECONOMY IN GROUPS OF THREE. USE THE INFORMATION IN THE GRID. Student 1: market economy Student 2: planned economy Student 3: mixed economy USE YOUR NOTES TO MAKE A SHORT SUMMARY ON ONE TYPE OF ECONOMY FILL IN THE GAPS. After World War II there were several _________________ economies in the world, _________________ present there are only a few left. Both Croatia and Sweden are _________________ states, Sweden, however, provides a much higher _________________ of living to its citizens. In Croatia some resources are _________________ (e.g., silver) and some are _________________ (e.g., lumber). In the _________________ sector the state _________________ decisions about what to produce. The _________________ of goods and services is more equal in planned economies, the standard of _________________, however, is lower than in _________________ or _________________ economies. The majority of US and Canadian universities require that foreign students provide proof of their _________________ abilities, i.e., that they can support themselves while studying there. CHANGE THESE VERBS INTO NOUNS: VERB need want produce own allocate compete NOUN VERB supply demand disribute plan intervene NOUN WRITE TRUE AND MEANINGFUL THE FOLLOWING TERMS: SENTENCES USING economic system, allocate ____________________________________________________ _____________________ resources, own ____________________________________________________ _____________________ decide, market mechanism, market economy ____________________________________________________ _____________________ mixed economy, two sectors Source of exercises: “English for Business”, Kiss-Kulenović, Lekaj-Lubina, Lumezi Linčir, Planinšek-Čikara