Operant Conditioning
advertisement

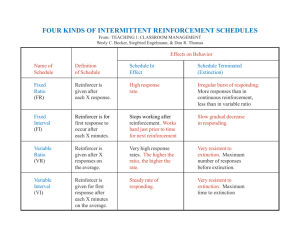
Operant Conditioning The Learner is NOT passive. Learning based on consequence!!! The Law of Effect Click picture to see a better explanation of the Law of Effect. • Edward Thorndike • Locked cats in a cage • Behavior changes because of its consequences. • Rewards strengthen behavior. • If consequences are unpleasant, the StimulusReward connection will weaken. • Called the whole process instrumental learning. B.F. Skinner • Influence of Nurture • Used a Skinner Box (Operant Conditioning Chamber) to prove his concepts. Skinner Box • Cumulative Recorder- attached to the Skinner box and it graphs the organisms response rate – Steep slope- fast response rate – Shallow slope- slow response rate Reinforces • A reinforcer is anything the INCREASES a behavior. Positive Reinforcement: • The addition of something pleasant. Negative Reinforcement: • The removal of something unpleasant. • Two types of NR • Escape Learning • Avoidance Learning (Getting kicked out of class versus cutting class) Positive or Negative? Putting your seatbelt on. Faking sick to avoid AP Psych class. Studying for a test. Having a headache and taking an aspirin. Breaking out of jail. Getting a kiss for doing the dishes. Punishment Meant to decrease a behavior. Positive Punishment • Addition of something unpleasant. Negative Punishment (Omission Training) • Removal of something pleasant. Punishment works best when it is immediately done after behavior and if it is harsh! How do we actually use Operant Conditioning? Do we wait for the subject to deliver the desired behavior? Sometimes, we use a process called shaping. Shaping is reinforcing small steps on the way to the desired behavior. To train a dog to get your slippers, you would have to reinforce him in small steps. First, to find the slippers. Then to put them in his mouth. Then to bring them to you and so on…this is shaping behavior. To get Barry to become a better student, you need to do more than give him a massage when he gets good grades. You have to give him massages when he studies for ten minutes, or for when he completes his homework. Small steps to get to the desired behavior. Chaining Behaviors • Subjects are taught a number of responses successively in order to get a reward. Click picture to see a rat chaining behaviors. Click to see a cool example of chaining behaviors. Big Bang Theory Same Terminology as Classical Conditioning • Acquisition If I wanted to • Extinction reinforce my son’s dancing by giving him • Spontaneous Recovery lollipops when he • Generalization dances. Identify the following…. • Discrimination Primary v. Secondary Reinforcers Primary Reinforcer • Things that are in themselves rewarding. Secondary Reinforcer • Things we have learned to value. • Money is a special secondary reinforcer called a generalized reinforcer (because it can be traded for just about anything) Token Economy • Every time a desired behavior is performed, a token is given. • They can trade tokens in for a variety of prizes (reinforcers) • Used in homes, prisons, mental institutions and schools. Premack Principle Hamburgers might be a great positive reinforcer for some, but it would not work well on a vegetarian. • You have to take into consideration the reinforcers used. • Is the reinforcer wanted….or at least is it more preferable than the targeted behavior. Reinforcement Schedules How often to you give the reinforcer? • Every time or just sometimes you see the behavior. Continuous v. Partial Reinforcement • • • • Continuous Reinforce the behavior EVERYTIME the behavior is exhibited. Usually done when the subject is first learning to make the association. Acquisition comes really fast. But so does extinction. Partial • Reinforce the behavior only SOME of the times it is exhibited. • Acquisition comes more slowly. • But is more resistant to extinction. • FOUR types of Partial Reinforcement schedules. Fixed- set amount Ratio- Variable- random amount FR Based on •FR-15 (reinforcer certain # of every 15th responses response) •Paid by the job Interval FI Based on • FI-15 (reinforcer time after every 15 seconds if 1 correct response is made) •Paid by the hour VR • VR-15 (reinforcer over an average of 15 responses, not every 15 •Gambling •Hardest to extinguish VI • VI- 15 (reinforcer over an average interval of 15 seconds) •Pop quiz Observational Learning • Albert Bandura and his BoBo Doll • We learn through modeling behavior from others. • Observational learning + Operant Conditioning = Social Learning Theory Click pic to see some observational learning. Latent Learning Edward Tolman Three rat experiment. Latent means hidden. Sometimes learning is not immediately evident. • Rats needed a reason to display what they have learned. • Cognitive Maps • • • • Insight Learning • Wolfgang Kohler and his Chimpanzees. • Some animals learn through the “ah ha” experience. Click pic to see insight learning.