File - Mrs. Maners
advertisement
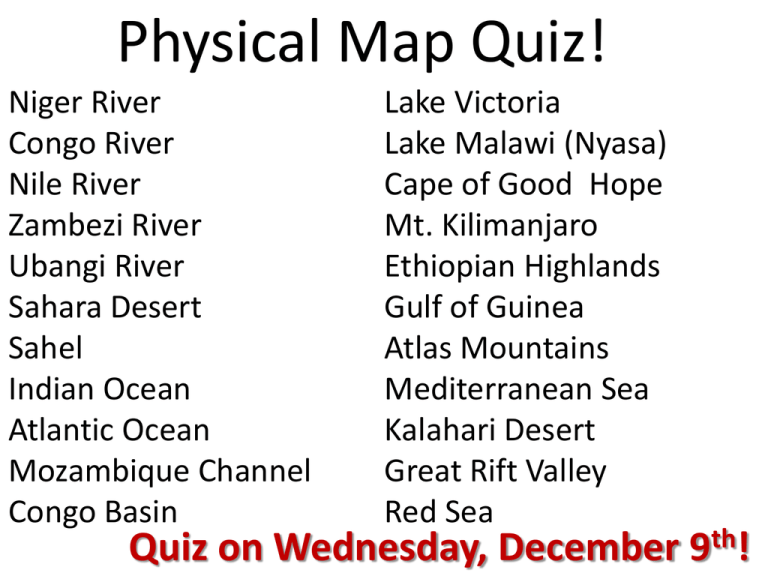
Physical Map Quiz! Niger River Congo River Nile River Zambezi River Ubangi River Sahara Desert Sahel Indian Ocean Atlantic Ocean Mozambique Channel Congo Basin Lake Victoria Lake Malawi (Nyasa) Cape of Good Hope Mt. Kilimanjaro Ethiopian Highlands Gulf of Guinea Atlas Mountains Mediterranean Sea Kalahari Desert Great Rift Valley Red Sea Quiz on Wednesday, December 9th! Africa! –54 Countries –Over 1 billion people –Over 2100 languages –18 of the 20 poorest countries on Earth –50% of Africa’s population born after 1991 –Largest City: Lagos, Nigeria 21 million people Ancient African Kingdoms – Ancient Kingdoms – Traditions of early cultures (oral stories, trading, etc.) – Physical and Political Geography • What technologies did African civilizations have access to? • How did migration and trade affect African history? • What forms of agriculture developed in Africa? Colonialism – European Contact and Exploration – Culture Clash and Ethnocentrism – Berlin Conference – Scramble for Africa – The White Mans Burden • How has colonialism affected Africa? • Why were Europeans able to colonize Africa? • How did Africans resist and then defeat European Colonization? “The Shape of Africa” intro: geography • Why does geography matter? • What can you say about Africa just by looking at it? Mr. Diamond’s Thesis “The Shape of Africa” • What was Jared’s thesis? • Share three pieces of supporting information: 1. 2. 3. Thesis Share • Share verbally with your table. • Each person must share their thesis and one piece of supporting evidence. –Person with next birthday starts –Give feedback for each person • Decide: Person who had the best thesis • Write: Your revised thesis and your reflection about why you changed what you changed Several Quality? Theses • Africa is not doomed to a state of poverty despite geographic realities that almost ensured struggles because geography is not the sole cause but combined with income that it brings. • Geographic luck results in successful or not successful technology and helpful or not helpful resources. Africa as a continent had little luck. Why are some cultures rich, while others are poor? What can the U. S. do to help Africa, and itself? East/West Axis Features of Africa • Sahara Desert – The Sahel • Kalahari Desert • The African Rainforest – Tsetse Flies – Lack of edible vegetation • The Savanna – Mediterranean Climates – Grassy plains – Great agriculture • What problems does this cause? Early Africa • Humans emerge in Rift Valley • Hunter-Gatherer societies • Pastoral Nomads: Nomadic societies based around herds of livestock such as goats, sheep, and cattle • Wealth measure by size of herd • Millions of modern Africans are still pastoral herders in Kenya, Tanzania, & Ethiopia Early African Societies Societies first develop South of the Sahara Religion develops: Generally monotheistic Animism: A religion in which spirits play an important role in regulating daily life and are presents in plants/animals/nature Written languages are rare, stories passed orally Griots: African storytellers What are the advantages of this? Disadvantages? The Iron Age Iron artifacts emerge from around 500 BCE Nok Culture: Modern day Nigeria, earliest known African Civilization Smelted iron into tools and weapons West African Civilizations West African Civilizations 3 Empires emerge by dominating trade across the Sahara - Empire of Ghana - Empire of Mali - Empire of Songhai West African Civilizations Objectives • Understand why gold and salt were important in early Africa. • Describe how the rulers of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai built strong kingdoms. • Summarize how other West African societies developed. West African Civilizations How did the kingdoms of West Africa develop and prosper? • As trade in Africa expanded, cities such as Gao and Timbuktu developed and became wealthy centers of commerce. • Between A.D. 800 and A.D. 1600, several kingdoms gained control of prosperous cities such as these. Salt and Gold Too much or too little salt in the diet can lead to muscle cramps, dizziness which can cause neurological problems, or death. US Department of agriculture West African Civilizations • The Sahara had an abundance of salt, which people needed in their diet to replace salt lost in perspiration. • In the savanna, salt was scarce. A merchant might trade one pound of gold for one pound of salt. • As trade grew, cities developed on the northern edges of the savanna. West African Civilizations • How did the kingdom of Ghana develop? • By A.D. 800, the rulers of the Soninke people united many farming villages to create Ghana. • Rulers of Ghana controlled goldsalt routes across West Africa. • Muslim merchants from North of the Sahara brought Islam to Ghana. West African Civilizations • Ghana fell in around 1050. In time, the new kingdom of Mali replaced Ghana. • Mali was founded in 1235 Sundiata. • The kings of Mali, or mansas, took control of gold-mining regions and the gold-salt trade. Founder of Mali Mansa Musa King of West Africa After a pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324, Mansa Musa brought Muslim scholars and architects to Mali. He built a university at Timbuktu that became a great center of learning. This map shows Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage to Mecca. • Inflation: Mansa Musa’s hajj devalued gold for a decade in Cairo, Medina, and Mecca. In the 1400s, Mali weakened and the new West African kingdom of Songhai arose. The soldier-king Sonni Ali brought trade routes & cities under his control. When he died, the emperor Askia Muhammad expanded Songhai territory, holding court at Gao. He formed strong ties to the Muslim world. The Songhai kingdom experienced disputes over succession in the late 1500s. • In 1591, invaders from Morocco conquered the empire. • Though the invaders couldn’t maintain control, the glory of the Songhai kingdom was over. Great Kingdoms of West Africa Kingdom Notable Cities Years Ghana Kumbi Saleh 800–1050 Mali Timbuktu 1235–1400s Songhai Gao 1464–1591 1. What products did the kingdoms of Ghana, Songhai, and Mali have that the rest of the world wanted? 2. What came across the Sahara to West Africa? In addition to the great kingdoms of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai, there were several smaller societies in the region. • Benin rose on the Guinea Coast during the 1300s. Its people knew how to cast bronze and brass. • The Hausa of West Africa became prominent in the 1300s. They lived in walled city-states. • The Hausa came to dominate many Saharan trade routes. Benin How did the Kingdom of Benin stay rich and powerful? What did they supply? John Green-Mansa Musa Share 1. Share with your table groups the 5 questions you came up with and discuss answers 2. Pick the top three questions at your table and write them on the quarter sheet of paper 1. Just questions, no need to include the answers 3. Turn in your quarter sheet in to me when your table is finished







