Balancing Equations for Redox Reactions
advertisement
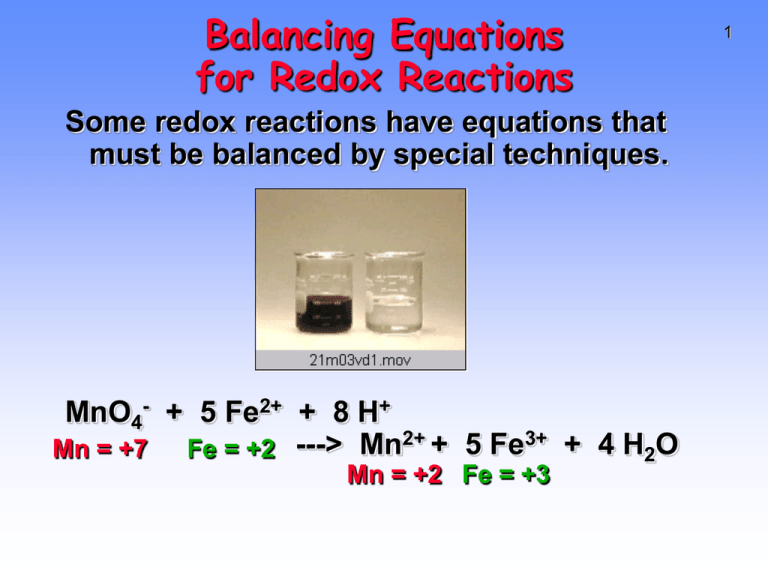
Balancing Equations for Redox Reactions Some redox reactions have equations that must be balanced by special techniques. MnO4- + 5 Fe2+ + 8 H+ Mn = +7 Fe = +2 ---> Mn2+ + 5 Fe3+ + 4 H2O Mn = +2 Fe = +3 1 2 Balancing Equations Consider the reduction of Ag+ ions with copper metal. Cu + Ag+ --give--> Cu2+ + Ag Balancing Equations Step 1: Divide the reaction into halfreactions, one for oxidation and the other for reduction. Ox Cu ---> Cu2+ Red Ag+ ---> Ag Step 2: Balance each for mass. Already done in this case. Step 3: Balance each half-reaction for charge by adding electrons. Ox Cu ---> Cu2+ + 2eRed Ag+ + e- ---> Ag 3 Balancing Equations Step 4: Multiply each half-reaction by a factor so that the reducing agent supplies as many electrons as the oxidizing agent requires. Reducing agent Cu ---> Cu2+ + 2eOxidizing agent 2 Ag+ + 2 e- ---> 2 Ag Step 5: Add half-reactions to give the overall equation. Cu + 2 Ag+ ---> Cu2+ + 2Ag The equation is now balanced for both charge and mass. 4 Reduction of VO2+ with Zn 5 Balancing Equations Balance the following in acid solution— VO2+ + Zn ---> VO2+ + Zn2+ Step 1: Write the half-reactions Ox Zn ---> Zn2+ Red VO2+ ---> VO2+ Step 2: Balance each half-reaction for mass. Ox Zn ---> Zn2+ Red 2 H+ + VO2+ ---> VO2+ + H2O Add H2O on O-deficient side and add H+ on other side for H-balance. 6 Balancing Equations Step 3: Ox Red Step 4: Ox Red 2e- Balance half-reactions for charge. Zn ---> Zn2+ + 2ee- + 2 H+ + VO2+ ---> VO2+ + H2O Multiply by an appropriate factor. Zn ---> Zn2+ + 2e+ 4 H+ + 2 VO2+ ---> 2 VO2+ + 2 H2O Step 5: Add balanced half-reactions Zn + 4 H+ + 2 VO2+ ---> Zn2+ + 2 VO2+ + 2 H2O 7 8 Tips on Balancing Equations • Never add O2, O atoms, or O2- to balance oxygen. • Never add H2 or H atoms to balance hydrogen. • Be sure to write the correct charges on all the ions. • Check your work at the end to make sure mass and charge are balanced. • PRACTICE!