Krafts_practice_Q_and_bug_table_12.12.09
advertisement
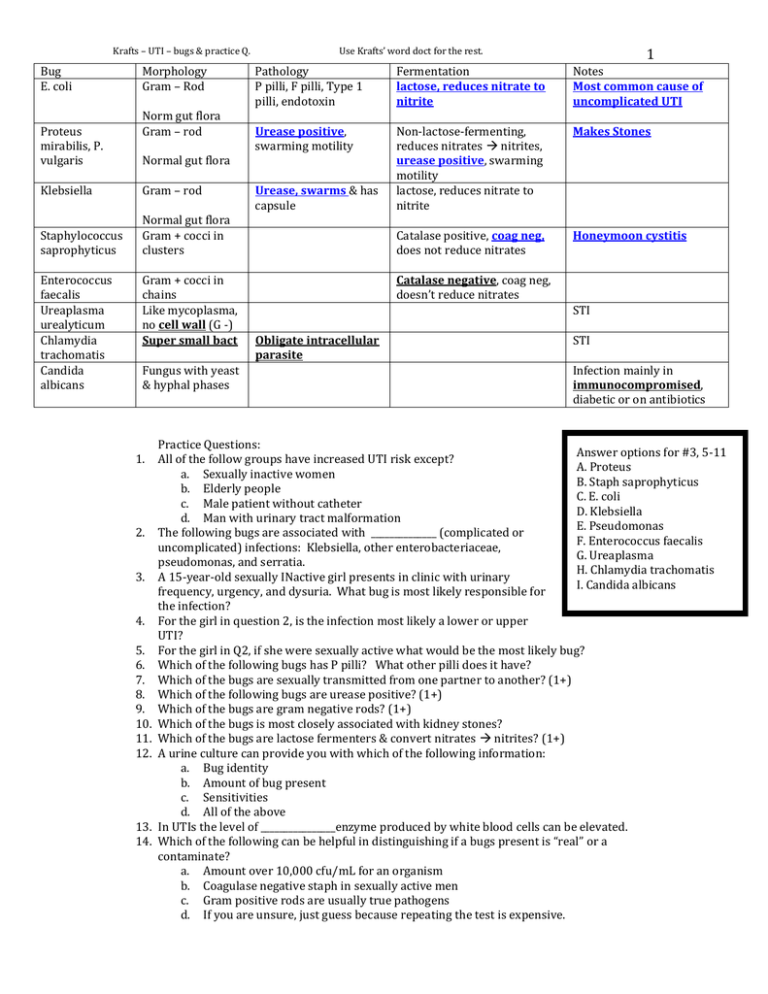
Krafts – UTI – bugs & practice Q. Bug E. coli Proteus mirabilis, P. vulgaris Morphology Gram – Rod Norm gut flora Gram – rod Normal gut flora Klebsiella Gram – rod Staphylococcus saprophyticus Normal gut flora Gram + cocci in clusters Enterococcus faecalis Ureaplasma urealyticum Chlamydia trachomatis Candida albicans Gram + cocci in chains Like mycoplasma, no cell wall (G -) Super small bact Fungus with yeast & hyphal phases 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 1 Use Krafts’ word doct for the rest. Pathology P pilli, F pilli, Type 1 pilli, endotoxin Fermentation lactose, reduces nitrate to nitrite Notes Most common cause of uncomplicated UTI Urease positive, swarming motility Non-lactose-fermenting, reduces nitrates nitrites, urease positive, swarming motility lactose, reduces nitrate to nitrite Makes Stones Catalase positive, coag neg, does not reduce nitrates Honeymoon cystitis Urease, swarms & has capsule Catalase negative, coag neg, doesn’t reduce nitrates STI Obligate intracellular parasite STI Infection mainly in immunocompromised, diabetic or on antibiotics Practice Questions: Answer options for #3, 5-11 All of the follow groups have increased UTI risk except? A. Proteus a. Sexually inactive women B. Staph saprophyticus b. Elderly people C. E. coli c. Male patient without catheter D. Klebsiella d. Man with urinary tract malformation E. Pseudomonas The following bugs are associated with ______________ (complicated or F. Enterococcus faecalis uncomplicated) infections: Klebsiella, other enterobacteriaceae, G. Ureaplasma pseudomonas, and serratia. H. Chlamydia trachomatis A 15-year-old sexually INactive girl presents in clinic with urinary I. Candida albicans frequency, urgency, and dysuria. What bug is most likely responsible for the infection? For the girl in question 2, is the infection most likely a lower or upper UTI? For the girl in Q2, if she were sexually active what would be the most likely bug? Which of the following bugs has P pilli? What other pilli does it have? Which of the bugs are sexually transmitted from one partner to another? (1+) Which of the following bugs are urease positive? (1+) Which of the bugs are gram negative rods? (1+) Which of the bugs is most closely associated with kidney stones? Which of the bugs are lactose fermenters & convert nitrates nitrites? (1+) A urine culture can provide you with which of the following information: a. Bug identity b. Amount of bug present c. Sensitivities d. All of the above In UTIs the level of ________________enzyme produced by white blood cells can be elevated. Which of the following can be helpful in distinguishing if a bugs present is “real” or a contaminate? a. Amount over 10,000 cfu/mL for an organism b. Coagulase negative staph in sexually active men c. Gram positive rods are usually true pathogens d. If you are unsure, just guess because repeating the test is expensive. Krafts – UTI – bugs & practice Q. Use Krafts’ word doct for the rest. Answers: 1. A (not C because even though sexual activity increases a woman’s risk for UTI, by virtue of female genital anatomy, she is still at greater risk than a male patient without a catheter.) 2. Complicated UTI 3. C -E. coli – it is responsible for the majority of uncomplicated UTIs 4. Lower UTI (bladder, urethra) because she lacks symptoms of tissue invasion (flank pain, fever, chills). 5. B (honeymoon cystitis) 6. C. E. coli --- F pilli & type 1 pilli. 7. G & H – although not classified as an STI, you could make an argument for B because is a risk factor. 8. A & D 9. A, C, D 10. A 11. C & D 12. D 13. Leukocytes esterase 14. A 2