Document
advertisement

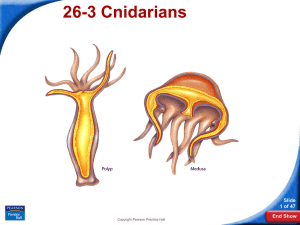
• The mouth opens at one end and leads to a digestive cavity. Every cnidarians has at least two layers of cells that form its body wall. • The body of a cnidarians may be shaped like a cylinder, a bell, or an umbrella • An outer layer makes up the body covering, and an inner layer lines the digestive cavity. • Many cnidarians have a third, or middle, layer consisting of a stiff, jellylike material that helps support the animal. • Jelly fish are cnidarians that has a bell- or umbrella-shaped body • A polyp is a cnidarians that has a body shaped like a hollow cylinder. A polyp lives with one end of its body attached to the sea bottom • some cnidarians to regenerate lost parts or even a complete body • Hydrodtatic Skeleton. This type of skeleton is a skeleton where muscles surround a water-filled body cavity and the muscles are supported by this cavity • Cnidarians have radial symmetry - that means they have symmetry revolving around a center point. • Cnidarians have 2 forms: Polyp (like sea anemone) and medusa (like jellyfish) • The size is 100 ft (30 m) long and more than a ton (910 kg) in weight • The name scyphozoa means cup animals which describes the medusa, the dominant form of life cycle of this class. • • The size they can reach to 40 meters • The habitat is cold artic waters • Their food source is most jellyfishes are passive drifters that feed on living or dead preys: small fish, eggs, zooplankton and other invertebrates that become caught in their tentacles. • The class hydrozoa includes about 3,700 species most of which live as colonial organisms in the ocean. • The size of a hydrozoa is 6 to 9 centimeters (2.4 to 3.5 in) • The habitat is Fern like hydrozoans can be found living on rocks and jetty piles • Food source is mainly feed on daphnia and Cyclops • The name anthozoa means flower animals which is a fitting description for the approximately 6,100 marine species in this class. Over thousands of years, these polyps build up large, rock like formations known as coral reefs. • The size is 200mm in length . • Their habitat less than 150 ft (46 m), where sunlight penetrates. • Their food source is small fishes. Others consume organic debris. • KINGDOM: Animalia • PHYLUM: Cnidarians CLASS: Hydrozoa • ORDER: hydroida • FAMILY: Aequorea • GENUS: Aequorea • SPECIES victoria • COMMON: water jellyfish • • • • • • • • KINGDOM: Animalia PHYLUM: Cnidarians CLASS: Medusozoa ORDER: semaestomeae FAMILY: ulmariadea GENUS: Aurelia SPECIES: aurita COMMON sea jellyfish • KINGDOM: Animalia • PHYLUM: Cnidarians CLASS: Anthozoa • ORDER: actiniaria • FAMILY: actiniidea • GENUS: Anthopleura • SPECIES sola • COMMON corals • http://dai.ly/g7za45 • http://dai.ly/f5S0vQ • Dawkins, R. The Jellyfish’s Tale. In "The Ancestor's Tale." (2004) Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, New York. pp. 388-390 • Dunn, Casey, and Rebecca R. Helm. "Cnidarian." World Book Advanced. World Book, 2011. Web. 22 Mar. 2011. Arai, M.N. (1997). A Functional Biology of Scyphozoa. London: Chapman & Hall [p. 316]. Myers, P., R. Espinosa, C. S. Parr, T. Jones, G. S. Hammond, and T. A. Dewey. 2008. The Animal Diversity Web (online). Accessed April 03, 2011 at http://animaldiversity.org. • • • Mills, C. 2008. "Hydromedusae" (On-line). Accessed July 10, 2009 at http://faculty.washington.edu/cemills/Hydromedusae.html