(8) Microclimate
advertisement

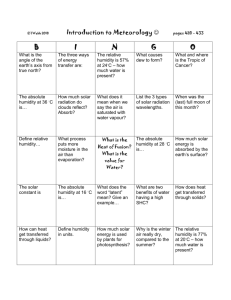
Environmental Controls I/IG Lecture 8 Microclimate Microclimate Immediate local conditions for temperature, humidity, solar radiation, and wind. Microclimate Affected by: Earth Wind Fire Water Earth: Topography The leeward side of a hill can protect from unwanted winds Elevation Temperature changes about -3.6 ºF with each +1000 feet change in altitude Salt Lake City Park City Elevation Temperature 4200’ 6800’ 95º F ~86º F Rain & Snow Shadows Form when moisture precipitates out as air moves up slopes L: p.73 Fig. 5.2d Ground Cover – Vegetation Trees, shrubbery, and grasses provide shade that prevents moisture from evaporating Permeable surfaces reduce temperatures through evaporative cooling Reeves House, Lopez Island, WA Cutler-Anderson, 2002 http://www.greenroofs.com/projects/ pview.php?id=562 Ground Cover Impermeable surfaces reduce evaporative cooling opportunities Surface Color Lighter surfaces reflect radiant heat heat Darker surfaces absorb radiant Urban heat island Large concentrations of thermal masses with darker and/or impermeable surfaces create urban heat islands Wind: Topography Warm air rises Cool air drops Morning and afternoon “diurnal winds” are intensified in canyons and on sloped surfaces and diverted by hills and ridges Convective Air Flow Warm air rises Cool air drops Recognizing air channels can help reduce discomfort or enhance comfort Wind Direction & Speed Confirm mean (average) speed direction Consult a wind rose for prevailing direction L: p. 89 Region 1 Wind Roses January L: p.81 Fig. 5.6d Wind Roses July L: p.83 Fig. 5.6f Sea Breeze Effect Onshore winds occur when water temperature is lower than adjoining air temperature over land. Offshore winds are the reverse process. Bernouli Effect Air flow closer to the ground is slowed by frictional effects of surfaces L: p.270 Fig. 10.5j Venturi Effect Air follows the path of least resistance Wind speeds increase as cross sectional area decreases L: p.318 Fig. 11.8c Wind Breaks/Channeling Terrain and vegetation can block or channel wind Plan Views Solar (Fire): Mean Daily Radiation Confirm how much solar radiation is a available S: p. 1504, T. C.3 Mean Percentage of Possible Sunshine L: p. 89 Region 1 Confirm how frequently the sun shines Solar Orientation South facing slopes get significantly more solar radiation than north facing slopes N Water: Thermal Mass Large bodies of water moderate local temperatures A thermal mass that can act as at thermal buffer/ heat sink Lakes & Oceans Warm temperatures are reduced in summer Cool temperatures are raised in winter 72ºF 35ºF 10ºF 80ºF 30ºF 10ºF Groundwater Groundwater table affects temperature and humidity Rivers & Streams Moving water generates air movement Perspiration Occurs as body core temperature rises In low RH conditions evaporation occurs and cools skin In high RH conditions evaporation is inhibited Insolation Humidity and cloud cover affect the amount of solar radiation entering or leaving the local environment Evapotranspiration Trees and shrubbery give off moisture that increases local humidity