Chem 30CL_Lecture 5c..
advertisement

Lecture 5c
Introduction
•
1H-NMR
spectroscopy is used to determine the structure of
the epoxide based on characteristic splitting patterns in the
aromatic range and the epoxide range
• When analyzing the spectrum, it will become much more
difficult if the submitted sample is a mixture of many
compounds i.e., epoxide, aldehyde, water (d=1.56 ppm),
ethyl acetate (d=1.26 ppm, 2.05 ppm and 4.12 ppm),
hexane (d=0.88 ppm, 1.26 ppm), etc. (see SKR, p. 284)
• The proton spectrum will exhibit a singlet at d=7.26 ppm
due to the presence of CDCl3 if the concentration of the
epoxide is very low
• The carbon spectrum will show a “triplet” at d=77 ppm
due to the presence of CDCl3
4-Methylstyrene oxide
• 1H-NMR Spectrum (integration in blue)
11.5
11.0
4
5.5
J3
10.5
H1-H2
H1-H3
H2-H3
3.31 Hz
3.30 Hz
5.68 Hz
CH3
5.0
10.0
9.5
4.5
9.0
8.5
4.0
8.0
7.5
3
7.0
3.5
6.5
3.0
6.0
5.5
2.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
1
3.5
2.0
11
3.0
H1, dd
H2, dd H3, dd
1.5
2.5
2.0
1.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.5
0.0
7.0
6.5
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
4-Methylstyrene oxide
•
13C{1H}-NMR
Spectrum
• Seven signals total
• Epoxide carbons at
~ 50-60 ppm
• Four signals in the
aromatic range
• The size of the peak
for CDCl3 depends on
the concentration of
the sample
120
H
115
3a 3
9
110
105
129.60
8
125.78
100
H
2
2b
H
2a
5
6
H3C
90
1
4
7
95
O
10
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
51.46
52.67
21.49
50
45
40
35
CDCl3
30
25
20
15
138.29
77.08
77.28
10
5
0
140
130
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
4-Methylbenzacetaldehyde
• 1H-NMR Spectrum (J3(CH2-CHO)= 2.56 Hz)
CHO, “s”
11
CH3
1
3
10
CH2, “s”
9
8
2
7
6
4
5
4
3
2
1
0
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
4-Methylbenzacetaldehyde
• 13C{1H}-NMR Spectrum
• Aldehyde: ~200 ppm
• Methylene: 45-50 ppm
• Methyl group: ~30 ppm
120
H H
115
(5;3)
(2;6)
105
5
1
H
100
8a
4
95
H3C
90
2
3
10
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
CHO
CH2
(8)
(7)
45
40
35
30
25
CDCl3
20
(4)
(1)
(Sol.)
(Sol.)
(Sol.)
15
10
5
200
150
100
CH3
(10)
50
0
O
7a7 7b 8 9
6
110
50
4-Methylacetophenone
•
1H-NMR
Spectrum
• Two doublets in the
aromatic range, one
of then significantly
shifted downfield due
to the adjacent
carbonyl function
• Two singlets in the
d= 2-2.5 ppm range
due to the two methyl
groups
11.5
3
11.0
10.5
10.0
9.5
9.0
8.5
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3
3.5
3.0
2 2
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
4-Methylacetophenone
•
Spectrum
• Carbonyl: ~195 ppm (small)
• Methyl groups: 20-30 ppm
13C{1H}-NMR
120
115
110
128.31
128.92
105
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
CH3
60
21.41
26.52
55
50
45
40
35
CDCl3
30
25
20
15
CO
197.41
76.28
77.08
77.88
143.46
10
5
0
200
150
100
50
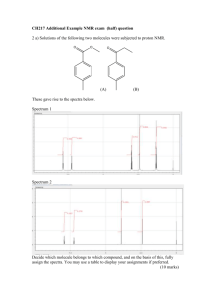
What is that?
• Interpret the following 1H-NMR Spectrum
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
How about that one?
• Interpret the following 13C{1H}-NMR Spectrum
spectrum
120
115
125.78
128.31
129.14
129.60
110
105
31.62
22.70
14.12
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
76.28
77.08
77.88
60
52.67
51.46
55
199.91
60.50
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
197.41
171.38
136.60
143.46
10
5
0
200
150
100
50
0