Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
advertisement

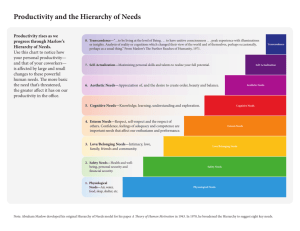
Sandra Cortez P.2 McElmoyl Who Abraham Maslow was a pioneer of humanistic psychology who is best known for his creation of Maslow’s hierarchy of need He believed that all humans need to feel competent in order to win approval and recognition The Hierarchy of Need Hierarchy of need includes five stages Physiological needs, Safety needs, Belonging needs, Esteem needs and Self-actualization needs What is the Theory The lower levels represent the more fundamental needs and the upper levels represent the growth being needs, and the final need for self-actualization According to the theory, the higher needs in the hierarchy become evident only after all the needs that are lower down in the pyramid have been met Physiological needs These are biological needs, they consist of needs for oxygen, food, water, and a normal constant body temperature. They are the strongest needs because if a person lacked these they wouldn’t be able to survive Safety Needs Safety needs may be different for each individual, depending on where he or she is in life. For a child, this need is the need for a safe family environment. There has to be security in the home, with warmth and love. When a family has problems, it makes it hard for that child to move up to the next level of social needs because fear is often present. For adults, this need may be economically wise. If a person looses his or her job, for example fear and anxiety will have a doing on that person’s life. Belonging needs Advancing up the hierarchy pyramid, the next level represents the need to belong on a social level. The social level generally becomes the priority only after the physiological and safety needs have been sufficiently met and maintained. A sense of belonging can be felt when an individual becomes more focused on the desire to build relationships with others. This includes the desire for a romantic partner, to have close friends, and maybe to get married and have children. Esteem need When a person feels a sense of belonging the need to feel important rises. Once the first three classes of needs are met, the need for self-esteem can become dominant because this includes the esteem a person gets from others Self-respect, achievement, attention, recognition, and reputation is what is important for a persons esteem need Self-Actualization Self-Actualization is the highest point of Maslow's hierarchy of need, it is the quest of reaching ones full potential as a person unlike lower level needs this need is never fully satisfied A person's need to do that which he or she feels they are meant to do and as one grows there are always new opportunities to continue to grow According to Maslow only a small percent of the population reach the level of self-actualization Characterizations of Self-Actualization Unusual sense of humor Highly created Need for privacy Strong/normal ethical standards Accept themselves and others for what they are Characterization leading to SelfActualization Experiencing childhood Trying new things not only don’t what you know Being responsible and working hard Standing up for what you believe not jumping on the band wagon What is needed Physiological Air Water Nourishment Sleep Safety • Living in a safe area • Medical insurance • Job security • Financial reserves Belonging Need of friends Need of belonging Need to give and receive love Esteem • Self-respect • Achievements • Attention • Recognition • Reputation • • • • • Self Actualization Truth Justice Wisdom Meaning Maslow’s needs in real life situations Management Physiological Needs: provide lunch breaks, rest breaks and pay minion wage Safety Needs: provide a safe working environment, retirement benefits and job security Social Needs: create a sense of community based on projects and social events Esteem Needs: recognition achievements to make employees feel appreciated and valued Self-Actualization Needs: provide employees a challenge and opportunity to reach their full career potential New Corporation Physiological Need: Employee, product/service, business strategy, small funds, work space, phone computer, internet Safety Needs: Multiple Employees, steady retention rate, office space Belonging Need: Employee relations, investor, clients Esteem Need: Brand recognition, partnership, press coverage Self-Actualization: corporate citizenship, corporate social responsibility Limitations of Maslow’s Hierarchy While Maslow’s hierarchy makes sense there is little evidence to support its point for example some people place social needs before any other, also starving artist neglect lower needs in hopes to pursuit a higher one Maslow's assumption that the lower needs must be satisfied before a person can achieve their esteem need and self-actualize need is not always the case and therefore Maslow's hierarchy of needs in some aspects has been proven wrong Still used today Even though the hierarchy lacks scientific support it is quite well knows and is the first theory of motivation to which many people are exposed It presents an intuitive and potentially useful theory of human motivation Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a popular way of thinking about people's needs this theory contends that as humans strive to meet our most basic needs we also seek to satisfy a higher set of needs Citation Burton, Neel. "Our Hierarchy of Needs." N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Sept. 2013. "Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs." - Simply Psychology. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Sept. 2013. "Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs." Maslow's Hierarchy. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Sept. 2013. "Related Materials." Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs and Diagrams of Maslow's Motivational Theory. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Sept. 2013.