Organic Molecules
advertisement

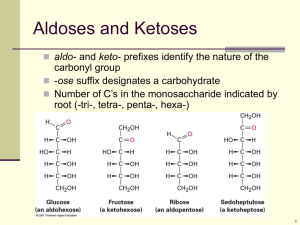
Organic Molecules Bio First Five Compare and contrast monosaccharides and disaccharides. Today’s Announcements • • Cell Structure Unit Exam • Corrections due no later than, Thursday, February 27 Quiz: Carbohydrates & Lipids • Friday, February 28 Table Groups On a whiteboard, draw a Venn diagram to compare and contrast monosaccharides and disaccharides. The many forms of glucose: Straight chain(linear) form (least common/stable) α-Ring form Alpha-ring (“OH” group is below the ring) β-Ring form Beta-ring (“OH” group is above the ring) Cyclic Structure of Glucose: Rotation Straight open-chain glucose is so reactive that almost all molecules quickly rearrange their bonds to form two new structures. These structures are six-membered rings like those below. The beta version is more stable. 6 Other important monosaccharides Fructose • • Fruit sugar E.g. high fructose corn syrup Ribose • Main component of DNA and RNA Galactose • • Very important at the cellular level Found with glucose (lactose) in dairy products GLUCOSE AND GALACTOSE Slightly different structure= entirely different function Glucose Glucose Combining monosaccharides to make… DISACCHARIDES! Maltose Glucose Fructose Sucrose Glucose Galactose Lactose How are the two monosaccharides joined? Glycosidic Bond However, to form this, another molecule has to be released. Can you figure out what it is? H2O 6C 12H 6O 6C 12H 6O 12C 22H 11O How are the two monosaccharides joined? Glycosidic Bond +H2O Partner Practice Draw the monosaccharides below on a whiteboard. Then, choose a disaccharide to make by doing the reaction. • Monosaccharides: • Fructose • Glucose • Galactose • Disaccharide: • Sucrose • Lactose First Five 1. What is the chemical formula for glucose? 1. Describe the differences between the 3 forms of glucose. Today’s Announcements • • Cell Structure Unit Exam • Corrections due no later than, Thursday, February 27 Quiz: Carbohydrates & Lipids • Friday, February 28 [Gold 1] Individual Practice - Disaccharides Can you… Draw on the diagram where a glycosidic bond will form and complete the diagram to show the disaccharide that will be produced. Individual Practice - Disaccharides Can you… Draw on the diagram where a glycosidic bond will form and complete the diagram to show the disaccharide that will be produced. Polysaccharides Polysaccharides are carbohydrate polymers made from many linked monosaccharide monomers to form long chain-like molecules. glycogen starch polysaccharides - made from glucose monomers cellulose Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose There are three main types of naturally occurring polysaccharides. They are cellulose, glycogen, and starch that are of major importance. Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose Cellulose: used to construct cell walls in plants Glycogen: energy storage in animals (e.g. in liver and muscle tissues) Starch: energy storage in plants Polysaccharides • • • Functions: storage, structure, recognition Starch and glycogen are storage molecules Chitin and cellulose are structural molecules Cell surface polysaccharides (polysaccharides embedded in the cell surface membrane) are recognition molecules Starch • • • Starch is a plant storage polysaccharide There are two forms of chains in starch • amylose • amylopectin Most starch is 10-30% amylose and 7090% amylopectin Starch • • Amylose: compact, energetic spirals of α-glucose molecules Amylopectin: compact, branched, energetic shapes of α-glucose molecules First Five Describe the similarities and differences between the two types of chains in starch: amylose and amylopectin. Starch Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose Amylose has an unbranched structure. 28 Starch Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose Amylopectin has a branched structure. 29 Starch Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose An important reaction during digestion is the hydrolysis of starchy foods as shown below. starch disaccharides glucose 30 Glycogen Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose Glycogen is a carbohydrate polymer that is stored in the liver and muscle tissues in animals. It is the energystorage carbohydrate in animals. 31 Glycogen Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose Glycogen has a structure similar to amylopectin (starch) except that it is more highly branched 32 Cellulose Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose • • Cellulose is a plant structure molecule. It is the most abundant organic molecule • • found in all cell walls breaks down very slowly in nature Cellulose Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose • Cellulose is formed from the β-glucose molecules • • β-glucose forms more hydrogen bonds because of the orientation of the –OH group on each glucose ring. Both starch and glycogen are formed from α-glucose molecules Polysaccharides Derived from Glucose Practice with Vocab: Frayer Models In your notebook, Create a frayer model for the following topics: Monosaccharide, Disaccharide, Polysaccharide Definition: Drawing of structure: Characteristics: (Write topic here) Example: Polysaccharides Practice Problems Begin in class. Finish as homework. • DUE WEDNESDAY