RAD 354 Chapt 8 X
advertisement

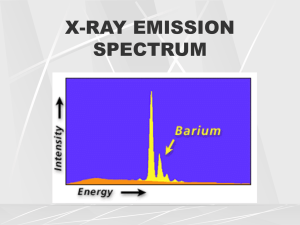
RAD 354 Chapt 8 X-ray Production • The primary purpose of an x-ray tube is to accelerate electrons across the tube and suddenly stop them in the target to produce electromagnetic x-ray photons – 99% of the electrical energy is dissipated as heat – mAs DIRECTLY affects the AMOUNT of photons produced – kVp makes the PRODUCTION of x-rays “slightly” more efficient X-rays are made via two ways • Brems Characteristic X-rays produced • X-rays are emitted “isotropically” (in all directions) • The x-ray beam is “Polychromatic” (many energies • MAX energy is produced by min wavelength – Duane-Hunt Law 12.4/kVp = min. wavelength kVp effects • kVp increase is equal to the “square of the factor by which kVp is raised” • kVp increases – Results in increased energies at ALL levels – The GREATER the increase, the GREATER the energies – Increases “skew” the x-ray emission spectrum to the RIGHT Filtration • Inherent - .5mm al equiv. (will increase over time as tungsten “boils off and coats” the window • Added – 2.0 al added for the 70-80 kVp level • Total filtration is the SUM of inherent and added – INCREASES the average “hardness” of the beam – Does NOT INCREASE any photon’s energy, only raises the AVERAGE hardness Target thoughts • Increasing the atomic # of the rarget (anode) will INCREASE the production of x-rays • INCREASE in mAs = INCREASE in numbers of PHOTONS • INCREASE in kVp = INCREASE in QUALITY and slight increase in production efficiency of xrays Wave forms • Half wave • Full wave • 3 phase – 6 pulse – 12 pulse High frequency generators