Microevolution
advertisement

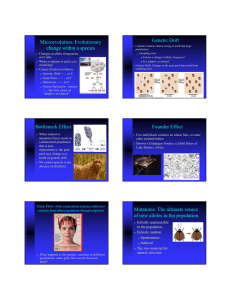
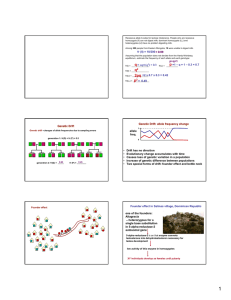
Microevolution • Microevolution is the Change in allele frequency due to one of the following processes: – – – – Natural Selection Mutations Genetic Drift Gene flow Types of Natural selection • Direction Selection – Selection favors one of the extreme types in the population. – Often the result in directional changes in the environment – Examples: Pesticide and antibiotic resistance Types of Natural Selection cont. • Stabilizing Selection – Selection favors the intermediate forms while selecting against the extremes. – Occurs in stable environments in which organisms are well adapted Types of Natural Selection cont. • Disruptive Selection – Selection favors both extremes while the intermediate forms are selected against. – Over long periods of time disruptive selection may lead to speciation. Sexual Selection • Individuals will select potential mates according to specific characteristics. • These traits may or may not be healthy for the species. • Example: Irish Elk Mutations • Mutations are the raw material for all new alleles. • New mutations will change gene frequency. • Natural selection will either amplify or diminish mutations in a population. Genetic Drift • Genetic drift is a random change in allele frequencies over the generations, brought about by chance events. • Genetic drift is most powerfully felt in small populations. • The founder effect and the bottleneck effect are two examples where genetic drift changes allele frequency in a population. Founder Effect • The founder effect occurs when a small group becomes isolated from its larger population. • The new group will likely have a different allele frequency than the parent group it originated from. • Example: Mutiny on the Bounty Bottleneck • A bottleneck is a severe reduction in a population brought about by intense selection pressure or some natural calamity. • The population is regenerated by means of the few individuals left. • The genetic diversity is greatly diminished compared to the original population. Gene Flow • The movement of alleles between different populations of the same species. • Alleles are lost from a population when individuals leave (emigrate). Alleles enter a population when new individuals move in (immigrate)