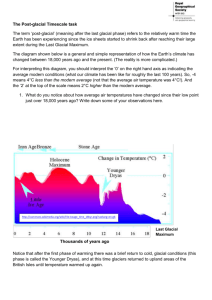
climate_change_5
advertisement
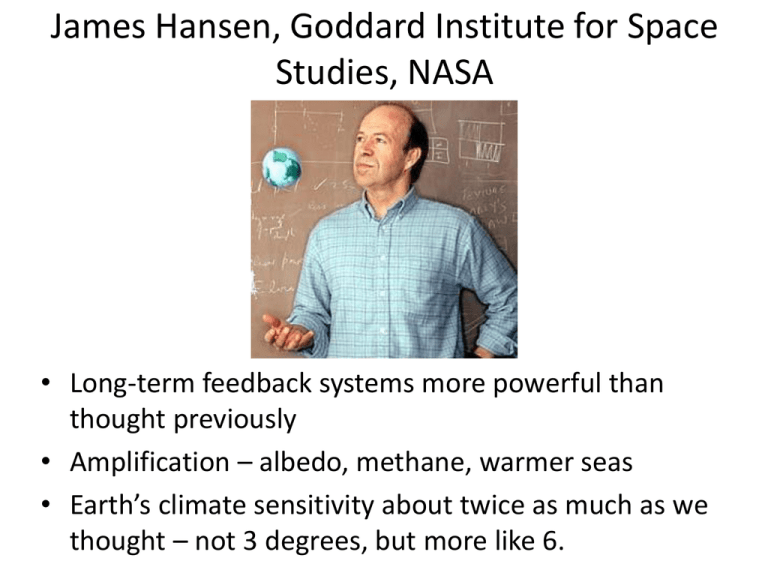
James Hansen, Goddard Institute for Space Studies, NASA • Long-term feedback systems more powerful than thought previously • Amplification – albedo, methane, warmer seas • Earth’s climate sensitivity about twice as much as we thought – not 3 degrees, but more like 6. Back to the ice….and its cousin, the permafrost…. “The thaw and decay of permafrost carbon is irreversible.” Methane is 25 times as potent a heat-trapping gas as CO2 over a 100 year time horizon, but 72 times as potent over 20 years . Yet, no climate model currently incorporates the amplifying feedback from methane released by a defrosting tundra. The carbon comes from plant material frozen in soil during the ice age of the Pleistocene: the icy soil trapped and preserved the biomass for thousands of years. Schaefer equates the mechanism to storing broccoli in the home freezer: “As long as it stays frozen, it stays stable for many years,” he said. “But you take it out of the freezer and it will thaw out and decay.” They found that between 29-59 percent of the permafrost will disappear by 2200. That permafrost took tens of thousands of years to form, but will melt in less than 200 . Photo: melting permafrost, Alaska Also like fossil fuels, the PCF is irreversible: once the permafrost carbon thaws and decays, no process on human time scales can put the carbon back into the permafrost. Thawing permafrost feedback will turn Arctic from carbon sink to source in the 2020s, releasing 100 billion tons of carbon by 2100 (National Snow and Ice Data Centre (NSIDC) 2011), “Release of even a fraction of the methane stored in the shelf could trigger abrupt climate warming.”Methane and carbon release from the Arctic is the most dangerous amplifying feedback in the entire carbon cycle. This research finds a key “lid” on “the large sub-sea permafrost carbon reservoir” near Eastern Siberia “is clearly perforated, and sedimentary CH4 [methane] is escaping to the atmosphere.” Planetary temperature over the last 65 million years… Lessons for today… and tomorrow. Eocene peak This is a graphical interpretation by David Spratt, Melbourne Climate Action Centre, of aspects of recent paleoclimate research by Hansen et al, available in draft form at: http://arxiv.org/abs/1105.1140 http://www.columbia.edu/~jeh1/mailings/2011/20110118_MilankovicPaper.pdf http://www.columbia.edu/~jeh1/mailings/2011/20110514_PaleoAndImbalance.pdf Version 1.2 of 3 June 2011 Antarctic glaciation ~ 34 million years ago… Eocene peak Around 34 million years ago, glaciation of Antarctica as temperature drops from Eocene peak. Asteroid impact cluster (~35mya): opening of Drake Passage leads to the circum Antarctic cold current Northern hemisphere glaciation ~ 4.5 million years ago… Eocene peak Around ~4.5 million years ago, northern hemisphere glaciation. Associated with the rise of the Panama Cordillera which isolates the Pacific from the Atlantic oceans and leads to intra-oceanic circulation (Gyres) which introduces warm currents and moisture to the North Atlantic – resulting in increased snow fall and formation of ice in Greenland, Laurentia and Fennoscandia. The last million years… Carbon dioxide and methane over last 500,000 years Climate swings between ice ages and warm inter-glacial periods over last million years. CO2 between 180 and 300 parts per million. The last 10,000 years – the Holocene Peak Holocene temp. Peak Holocene: over last 10,000 years up 1900AD Holocene: after the last ice age, relatively stable temperatures (+/–0.5C) and sealevels over last 10,000 years – the period of human civilisation Today temperature rises above the Holocene maximum CO2 level today is 393ppm but “thermal inertia” (delay as ocean mass warm) means temperature will increase further. Temperatures have risen ~0.83C since 1900 and are now ~0.6C over peak Holocene. 2010 Peak Holocene: over last 10,000 years up 1900AD Global average temperature now ~0.6C above peak Holocene 2 degrees – goodbye to Greenland ice sheet… When climate system reaches equilibrium, present level of CO2 will produce >2C of warming with feedbacks… +2C Peak Holocene: over last 10,000 years up 1900AD Global average temperature now ~0.6C above peak Holocene 2C of warming: consequence of current level of greenhouse gases … which is sufficient for large parts of Greenland and West Antarctic ice sheets to be lost, leading to at least a 6-7 metre sea-level rise over time “Goals to limit human-made warming to 2°C.. are not sufficient – they are prescriptions for disaster” — Dr James Hansen +2C Peak Holocene: over last 10,000 years up 1900AD Global average temperature now ~0.6C above peak Holocene 2C of warming: consequence of current level of greenhouse gases 4 degrees – goodbye, goodbye … Best present emission reduction commitments by all governments (if implemented) will still lead to 4 degrees of warming by 2100… +4C Peak Holocene: over last 10,000 years up 1900AD Global average temperature now ~0.6C above peak Holocene 2C of warming: consequence of current level of greenhouse gases 4C of warming …and likely loss overtime of all ice sheets. No ice sheets on planet = 70 metre sea-level rise over time… … amongst many devastating impacts. Read more about 4 degrees hotter at http://www.climateactioncentre.org/resources +4C Peak Holocene: over last 10,000 years up 1900AD Global average temperature now ~0.6C above peak Holocene 2C of warming: consequence of current level of greenhouse gases 4C of warming It’s up to you….