Conic sections
advertisement

Conic sections
Claudio Alvarado
Rylon Guidry
Erica Lux
Look! A square!
Complete the Square
• Parabolas as well as other conic sections
are not always in the general form. The
general equation is Y=a(x-h)2 + k.
• In order to get a conic into the general
equation you must Complete the square
to change the equation of y = ax2 +bx +c
into the general equation.
Completing the Square
• Example:
y=3x2- 18x –10
• Step 1:Isolate the x
terms
y=3x2- 18x –10
+10
+10
y+10=3x2-18x
• Step 2: Divide by the
x2 coefficient.
y+10=3x2-18x
3
3
y+10=x2-6x
3
• Step 3:
(a) divide the x
coefficient by 2
then square it add the
product to both sides
of the equation
y+ 10= x2 +6x
3
-6/2=(-3)2=9
y+10+9= x2-6x+9
3
Completing the square
• Step 4: Factor the right • Step 5: Solve for y do
2 +k
that
y=a(x-h)
hand side of the
equation.
y+10+9=(x-3)2
y+10+9= x2-6x+9
3
3
This is
2
y+10+9=(x-3)(x-3) getting 3{y+10}=3(x-3)
3
3
tough!!!
2
y+10+27=3(x-3)
y+10+9=(x-3)2
y+37= 3(x-3)2
3
-37
-37
y=3(x-3)2 -37
Parabolas
Parabola-a set of all points in a plane that are
the same distances from a given point called
the focus and a given line called the
directrix
Latus Rectum- the line segment through focus
and perpendicular to the axis of symmetry
Parabola Graph
Directrix
Focus
Parabola
Form of Equation
y=a(x-h)2 +k
x=a(y-k)2+h
Axis of symmetry
x=h
y=k
Vertex
(h,k)
(h,k)
Focus
(h,k+1/4a)
(h+1/4a,k)
Directrix
y=k-1/4a
x=h-1/4a
Direction of
opening
Upward if a>0
Down if a<0
Right if a>0
Left if a<0
Length of Latus
Rectum
Abs (1/a) units
Abs (1/a) units
Circles
Circle- the set of all points in a plane that
are equal distances from a given point in
the plane called the center.
Radius-any segments whose endpoints are
the center and a point on the circle
Equation of a circle:
Pretty circle!
(x-h)2 + (y-k)2= r2
Center of a circle-(h,k)
Radius- r
Circles
Find the center and the radius
of a circle with and
equation of
x2+ y2+ 2x+ 4y-11=0
Step 2: Complete the
Square
x2 + 2x + y2+ 4y =11
x2+2x+1+y2+4y+4=11+1+4
Step 1: Put all like terms
together on the left hand
side of the equation; place
on constants on the right
x2+ y2+ 2x+ 4y-11=0
x2 + 2x + y2+ 4y =11
Step 3: factor
x2+2x+1+y2+4y+4=16
(x+1)2+(y+2)2=16
Center = (-1,-2)
Radius= 4
Finding Circle Equations
Write an equation of a circle
whose endpoints of its
diameter are at (-7,11) and
(5,-10)
Step 1: Find the center by
recalling the midpoint
formula
(x1+x2, y1+y2)= (h,k)
2
2
(-7+5, 11-10)
2
2
Find the radius using the
distance formula
D=((x2-x1)2+(y2-y1)2)1/2
D=((5-(-7))2+(-10-1)2)1/2
D=((12)2+(-21)2)1/2
D=(144+441)1/2
D=(585)1/2=24.187
Divide by 2 to find
radius=12.093
Write the equationCenter=(-1,.5) r2=146.41
(x+1)2+(y-k)2=146.41
Definition of an Ellipse
An ellipse is the set of all points in a plane such that the
sum of the distances form the foci is constant.
4x2 + 9y2 + 16x -18y
-11 = 0
Ellipses
Standard Equation for a
center (0,0)
A)
x2 + y2
a2 + b2 =1
Major Axis is“x”
because “a” under “x”
Foci (c,o) (-c,o)
a2 >b2
b2 = a2 –c2
Take me to
your Ellipses
B) x2 + y2
b2 + a2 =1
Major Axis is “y”
because “a” under
“y” foci (o,c) (o,-c)
True for both equations
Ellipses
Find the coordinates of
the foci and the length
of the major and minor
axis. Whose equations
is
16x2 + 4y2 = 144
x2 + y2 or x2 + y2
a2 + b2 = 1 b2 + a2
16x2 + 4y2 = 144
144 144 144
b2 = a2 – c2 -27 = -c2
9 = 36 – c2
c2 = 27
Since we know a2>b2
major axis is “y”
c=(27)1\2
c=(9)1\2
c=3(3)1\2
Length of your major
axis= 2a =12
Length of your minor
axis =2b =6
Foci (0,3(3)^1\2)
(0,-3(3)^1\2)
Ellipses
Ahh!!! Big
Big ellipse!!
When the center is Not at
the origin (0,0)
center(h,k)
Standard equation
A) (x-h)2
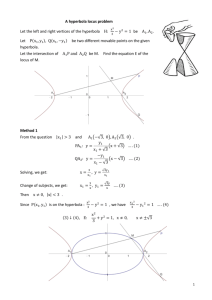
Hyperbola
Definition
• A hyperbola is the set
of all points in a plane
such that the absolute
value of the difference
of the distances from
any point on the
hyperbola to two
given points, called
the foci, is constant
Hyperbola
Standard Equations of
Hyperbolas with Center at
the Origin
• If a hyperbola has foci at
(-c,o) and (c,o0 and if the
absolute value of the
difference of the distances
from any point on the
hyperbola to the tow foci
is 2a units, then the
standard equation of the
hyperbola is x2 - y2
a2 - b2 =1, where c2 =
a2+b2.
Ahhh!
• If a hyperbola has foci at
(o,-c) and (o,c) and if the
absolute value of the
difference of the distances
from any point on the
hyperbola to the two foci
is 2a unit, and then the
standard equation of the
hyperbola is
y2 - x2
a2 – b2 = 1, where c2= a2
+ b2.
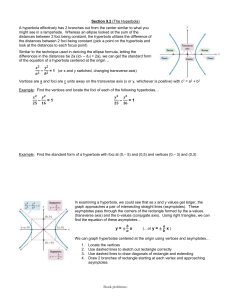
Hyperbola
Equation of
Hyperbola
Equation of
Asympote
Transverse
Axis
x2 – y2
a2 b2=1
y2 – x2
a2 b2 =1
b
Y=+/- ax
a
y = +/- bx
horizontal
vertical
Hyperbola
Standard Equations of
Hyperbolas with
Center at (h,k)
• The equation of a
hyperbola with center
at (h,k) and with a
horizontal transverse
axis x-h)2 - (y-k)2
a2
- b2 =1
• The equation of a
hyperbola with center
at (h,k) and with a
vertical transverse axis
is (y-k)2 - (x-h)2
a2 - b2 =1
References
And I
did all
this!
• Glencoe Algebra 2 textbook
Where’s • Internet : www.glencoe.com
www.wwfhhh.com
Rylon’s
• Erica’s notes
name
• Erica’s house
• Claudio’s house
Roles
• Erica – Poster manager keeper dudette
• Rylon – real life picture getter dude
• Claudio – with the help of Erica, did this wonderful
presentation for you to behold
This marvelous project
deserves a 100!!!!!