Cell Theory Notes
advertisement

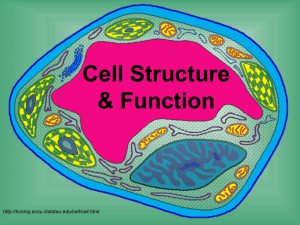
Cell Theory Key Concepts WHO is Responsible for coming up with the Cell Theory? WHAT IS THE CELL THEORY and how does it apply to living things? WHAT are the similarities and differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells? Vocabulary Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Organelle Robert Hooke (1635-1703) English Scientist Developed the First Compound Microscope Robert Hooke Looked at thin slices of cork Saw that there were small, hollow compartments that resembled the rooms that monks lived in. Developed the term “cell” Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) Dutch tradesman Ground lenses as a hobby and improved microscope Was the first to see living cells Microorganisms found in pond water Blood cells and his own teeth Matthias Schleiden (1804-1881) German botanist Observed and proposed that all plants are made of cells Theodor Schwann (1810-1882) German zoologist Saw structural similarities between animal and plant cells Determined animals are made of cells Stated all living things are made of cells. Rudolf Virchow (1821-1902) German Doctor Observed that cells reproduce from other cells Observed that animal cells are only found in animals and plant cells are only found in plants Cell Theory These three scientists discoveries led to the development of the cell theory. The 3 Parts of the Modern Cell Theory are: The cell is the basic unit of life All organisms are made of cells All existing cells come from other living cells Cell Theory Timeline 1665 HookeIdentified cells 1674 LeeuwenhoekObserved Living cells 1838 1839 SchleidenSchwannPlants are All living made of cells things come from cells 1855 VirchowAll cells come from other cells Organization of Life Organism Organ Systems Organs Tissues Cells Organization of Life Organisms can be unicellular or multicellular Multicellular organisms are organized into complex structures Multicellular organisms have specialized cells to perform a single function. What are some human cells specialized to do? Types of Cells Prokaryotic cells – primitive cells that have little internal structure. Eukaryotic cells – evolved from prokaryotic cells and contain numerous internal structures. Organelles – structures in the cell responsible for carrying out specific functions. “cell organs” What are some organelles found in cells and what are their functions? Prokaryotic Cells Do NOT have nucleus or other membrane bound organelles DNA found in the cytoplasm Always unicellular Very simple in structureCell wall or membrane surrounding cytoplasm Earth’s most abundant organism Eukaryotic Cells Arose from Prokaryotic cells Do HAVE a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles. Nucleus contains DNA. Can be uni- or multicellular Eukaryotic Cells Structure divided into 3 areas: NUCLEUS, CYTOPLASM, AND CELL MEMBRANE. Eukaryotic cells have numerous organelles Unicellular vs Multicellular Unicellular- Organisms composed of one cells, ex. Bacteria, and protozoa Multicellular- Organisms composed of many cells, including cells with different functions, ex. Humans, plants, fungi