Air Pressure Forces and Wind
advertisement

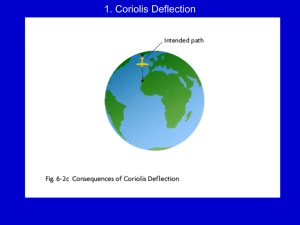
AIR PRESSURE FORCES AND WIND Definition: The difference in atmospheric pressure per unit distance PGF acts at right angles to isobars of equal pressure H L 102.2 99.8 101.4 100.6 600 km Pressure Gradient Force = 2.4 kPa / 600 km = 0.4 kPa / 100 km Where are winds strongest ? Oct 18, 2004 Solution: HUDSON BAY Check the spacing of the isobars of equal surface pressure Source: NASA Surface roughness decreases wind speed Reduces impact of Inertial Coriolis Force Winds cross isobars, spiralling out of ANTICYCLONES (H), and into CYCLONES (L) H L weather.unisys.com H L Air tends to be unstable in low pressure (tendency to rise) Air tends to be stable in high pressure (tendency to fall) 1. Equatorial Low Pressure Trough 2. Subtropical High Pressure Cells 3. Subpolar Low Pressure Cells 4. Weak Polar High Pressure Cells ICE CAP TUNDRA BOREAL MIXED TEMPERATE BROADLEAF DESERT SAVANNA RAIN FOREST SAVANNA DESERT MIXED TEMPERATE TUNDRA ICE CAP How does this relate to the “jet stream”? Geostrophic wind (above strong influence of friction) CHAPTER 10 ULTRASONIC SOUND WAVES DETERMINE WIND SPEED, DIRECTION & TEMPERATURE Sonic http://www.wrds.uwyo.edu/wrds/rmfres/fendrift.htm Also SW Ontario Cooling At MALR 6°C/km Cooling At MALR 6°C/km Warming At DALR 10 °C/km Warming At DALR 10 °C/km Cooling At DALR 10 °C/km X VANCOUVER 8°C X LETHBRIDGE 12°C More sensible heat Santa Ana Winds Entrained Particle Exposed section Buried Portion Which circulation cell extends from the equator to the subtropics? A. Polar cell B. Hadley cell C. ITCZ D. Ferrel cell Which circulation cell extends from the equator to the subtropics? A. Polar cell B. Hadley cell C. ITCZ D. Ferrel cell Which circulation cell extends from the subpolar lows to the poles? A. Polar cell B. Hadley cell C. ITCZ D. Ferrel cell Which circulation cell extends from the subpolar lows to the poles? A. Polar cell B. Hadley cell C. ITCZ D. Ferrel cell Which circulation cell extends from the subtropics to the subpolar lows? A. Polar cell B. Hadley cell C. ITCZ D. Ferrel cell Which circulation cell extends from the subtropics to the subpolar lows? A. Polar cell B. Hadley cell C. ITCZ D. Ferrel cell Which global wind belt is between the subtropical highs and the subpolar lows? A. trade winds B. westerlies C. ITCZ D. easterlies Which global wind belt is between the subtropical highs and the subpolar lows? A. trade winds B. westerlies C. ITCZ D. easterlies Which global wind belt is between the ITCZ and the subtropical highs? A. trade winds B. westerlies C. ITCZ D. easterlies Which global wind belt is between the ITCZ and the subtropical highs? A. trade winds B. westerlies C. ITCZ D. easterlies What occupies the region labeled “A”? A A. cyclone B. jet stream C. tornado D. semi permanent cell What occupies the region labeled “A”? A A. cyclone B. jet stream C. tornado D. semi permanent cell What are the dashed lines? A A. isotherms B. isobars C. pressure heights D. isohyets What are the dashed lines? A A. isotherms B. isobars C. pressure heights D. isohyets What do the lines on this map show? A. many isobars B. a cold front C. a middle latitude cyclone D. Rossby waves What do the lines on this map show? A. many isobars B. a cold front C. a middle latitude cyclone D. Rossby waves Which season is depicted in the photo? A. summer B. winter C. fall D. spring Which season is depicted in the photo? A. summer B. winter C. fall D. spring Where will the Santa Ana winds likely occur? A. New York B. Florida C. Texas D. California Where will the Santa Ana winds likely occur? A. New York B. Florida C. Texas D. California Which type wind is depicted? A. katabatic wind B. land breeze C. sea breeze D. Santa Ana wind Which type wind is depicted? A. katabatic wind B. land breeze C. sea breeze D. Santa Ana wind