Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence
advertisement

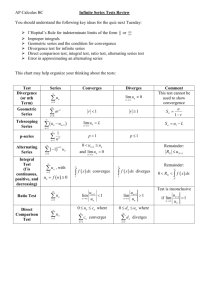
ALTERNATING SERIES 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 series with positive terms series with some positive and some negative terms 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 ( 1) n 1 1 n odd 1 n even n 1 ( 1) n 1 alternating series n n-th term of the series an (1)n 1un un are positive ALTERNATING SERIES alternating series (1) n 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 n 2 3 4 5 6 n 1 alternating harmonic series 1 n 1 1 1 1 ( ) 2 2 4 8 6 n 1 (1) n1 1 1 1 1 1 p p p p p n 2 3 4 5 n 1 alternating geomtric series alternating p-series ALTERNATING SERIES THEOREM: (THE ALTERNATING SERIES TEST) 1) un 0 2 ) un1 un un 0 3) lim n (1) n 1 alternating n 1 un (1) decreasing n 1 lim = 0 Remark: The convergence tests that we have looked at so far apply only to series with positive terms. In this section and the next we learn how to deal with series whose terms are not necessarily positive. Of particular importance are alternating series, whose terms alternate in sign. n 1 un convg Example: Determine whether the series converges or diverges. (1) n1 n n 1 ALTERNATING SERIES THEOREM: (THE ALTERNATING SERIES TEST) 1) un 0 alternating 2 ) un1 un decreasing un 0 3) lim n (1) n 1 Example: Determine whether the series converges or diverges. 2 n n 1 ( 1 ) 3 n 1 n 1 un (1) n 1 lim = 0 n 1 n 1 un convg ALTERNATING SERIES THEOREM: (THE ALTERNATING SERIES TEST) 1) un 0 alternating 2 ) un1 un decreasing un 0 3) lim n (1) n 1 un (1) n 1 lim = 0 n 1 n 1 un convg Example: Determine whether the series converges or diverges. 3n ( 1) 4n 1 n 1 n ALTERNATING SERIES L ( 1) ui i 1 i 1 n S n (1) i 1 ui i 1 THEOREM: (THE ALTERNATING SERIES ESTIMATION THEOREM) satisfies the three (1) n 1 u n conditions n 1 Sn approximates the sum L of the series with an error whose absolute value is less than the absolute value of the first unused term u n 1 the sum L lies between any two successive partial sums S n and S n 1 the remainder, Rn L S n has the same sign as the first unused term. THEOREM: (THE ALTERNATING Example: SERIES ESTIMATION THEOREM) (1) n 1 n 1 un satisfies the three conditions (1) n 1 n 1 1 0.66 6 2 n 1 1 S5 1 12 14 18 16 0.6875 1 S6 S5 32 0.65625 L Sn un1 L S5 1 32 S n L S n1 OR 0.65625 S6 L S5 0.6875 S n1 L S n sign ( L S n ) sign (1st unused) sign ( L S5 ) negative ALTERNATING SERIES n S n (1) i 1 ui L ( 1) ui i 1 i 1 i 1 THEOREM: (THE ALTERNATING SERIES ESTIMATION THEOREM) (1) n 1 n 1 un satisfies the three conditions L Sn un1 S n L S n1 OR S n1 L Sn sign ( L S n ) sign (1st unused) Example: Find the sum of the series correct to three decimal places. (1) n1 n! n 0 ALTERNATING SERIES Example: Find the sum of the series correct to three decimal places. (1) n1 n! n 0 ALTERNATING SERIES n S n (1) i 1 ui L ( 1) ui i 1 i 1 i 1 THEOREM: (THE ALTERNATING SERIES ESTIMATION THEOREM) (1) n 1 n 1 satisfies the three u n conditions L Sn un1 S n L S n1 OR S n1 L Sn sign ( L S n ) sign (1st unused) REMARK: The rule that the error is smaller than the first unused term is, in general, valid only for alternating series that satisfy the conditions of the Alternating Series Estimation Theorem. The rule does not apply to other types of series. ALTERNATING SERIES TERM-102 ALTERNATING SERIES TERM-101 ALTERNATING SERIES TERM-092 Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence an 1 n 1 a n 1 n 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 a n 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 32 4 2 5 2 6 2 n 1 (1) n 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 n 2 3 4 5 6 n 1 DEF: a n 1 Is called Absolutely convergent converges absolutely IF 1 an 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 32 4 2 5 2 6 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 n 2 3 4 5 6 n 1 Example: n n a n 1 n convergent Test the series for absolute convergence. (1) n1 2 n n 1 Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence DEF: a n 1 Example: n Is called Absolutely convergent a IF n 1 n convergent converges absolutely DEF: n 1 sin( n) 2 n n 1 Example: a Test the series for absolute convergence. n Is called conditionally convergent Test the series for absolute convergence. if it is convergent but not absolutely convergent. REM: a n 1 convg n a n 1 (1) n1 n n 1 n divg Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence DEF: a n 1 Example: n Is called Absolutely convergent a IF n 1 n convergent converges absolutely DEF: a n 1 n Is called conditionally convergent if it is convergent but not absolutely convergent. REM: a n 1 convg n a n 1 n divg Test the series for absolute convergence. Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence THM: a n 1 n Absolutely convergent THM: a n 1 a n 1 n convergent n convg convg n a n 1 Example: Determine whether the series converges or diverges. cosn 2 n n 1 Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence a n 1 an n 1 a n 1 n conditionally convergent Absolutely convergent a n 1 n convergent n divergent a n 1 n a n 1 n Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence DEF: a n 1 Example: n Is called Absolutely convergent a IF n 1 n convergent converges absolutely DEF: a n 1 n Is called conditionally convergent if it is convergent but not absolutely convergent. REM: a n 1 convg n a n 1 n divg Choose one: absolutely convergent or conditionally convergent Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence REARRANGEMENTS n ( 1 ) Divergent n 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (1 1) (1 1) (1 1) (1 1) 1 (1 1) (1 1) (1 1) (1 1) 0 If we rearrange the order of the terms in a finite sum, then of course the value of the sum remains unchanged. But this is not always the case for an infinite series. By a rearrangement of an infinite series we mean a series obtained by simply changing the order of the terms. Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence REARRANGEMENTS n ( 1 ) Divergent n 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (1 1) (1 1) (1 1) (1 1) 1 (1 1) (1 1) (1 1) (1 1) 0 (1) n1 n n 1 convergent See page 719 1 12 13 14 15 16 17 1 12 13 14 15 16 17 ln 2 1 12 13 14 15 16 17 12 ln 2 Alternating Series, Absolute and Conditional Convergence REARRANGEMENTS REMARK: an n 1 Absolutely convergent any rearrangement has the same sum s with sum s Riemann proved that an n 1 Conditionally convergent r is any real number there is a rearrangement that has a sum equal to r. SUMMARY OF TESTS SUMMARY OF TESTS Special Series: Series Tests lim an 0 1) Test for Divergence 2) Integral Test 1 n 2) Harmonic Series f ( x)dx bn an n an 7) Alternating Series Test 4) p-series alt , dec, lim 0 1 n (b b 1 p n 1 n 5) Alternating p-series an 1 n a n L lim n 3) Telescoping Series bn L lim n 1 n 1 4) Limit Comparison Test c lim an n 6) Root Test 1) Geometric Series n 1 3) Comparison Test 5) Ratio Test ar n n 1 n 1 ) (1) n np n 1 SUMMARY OF TESTS 1) Determine whether convg or divg 2) Find the sum s 5-types 3) Estimate the sum s 5) Partial sums 4) How many terms are needed within error ALTERNATING SERIES TERM-101