Motion
advertisement

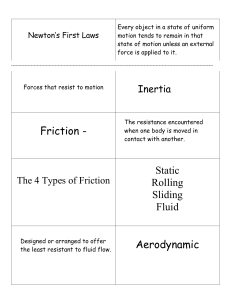
Motion Motion Vocabulary 1. motion 16. momentum 2. speed 17. work 3. velocity 18. joule 4. acceleration 19. power 5. force 20. watt 6. newton 21. work input 7. net force 22. work output 8. friction 23. wave 9. gravity 24. transverse wave 10. weight 25. longitudinal wave 11. mass 26. amplitude 12. terminal velocity 27. wavelength 13. free fall 28. reflection 14. projectile motion 29. refraction 15. inertia Speed vs. Velocity Speed - SI unit m/s distance traveled divided by the time interval during which the motion occurred Velocity – SI unit m/s plus direction speed of an object in a particular direction Acceleration – pg. 514 rate at which velocity changes over time; an object accelerates if its speed, direction, or both change. a = v2 – v1/ t Force – SI unit N – pg. 517 a push or a pull exerted on an object in order to change the motion of the object; force has size and direction net force – combination of all the forces acting on an object balanced force – when the forces on an object produce a net force of 0 N copy question & answer in notebook 1. How is velocity different from speed? 2. How does the direction of the net force on a object compare to the direction of its motion? 3. How does a net force of 0 N impact an object’s motion? Friction – pg. 521 a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact kinetic friction – pg. 522 static friction – pg. 523 Gravity – pg. 527 a force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses mass affects gravitational force – pg. 528 distance affects gravitational force – pg. 529 weight vs. mass weight mass measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object a measure of the amount of matter in an object Newton’s 1st law of motion An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Newton’s 2nd law The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. F=mxa a = F/m Newton’s 3rd law When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. Momentum a quantity defined as the product of the mass and velocity of an object p=mxv Science math equations to know speed average speed = total distance / total time s=d/t Newton’s 2nd law Force = mass x acceleration F=mxa acceleration average acceleration = final velocity – initial velocity / time a = v2 – v1 / t momentum momentum = mass x velocity p=mxv