Biology 20 Virual Labs Renal Module Hillaby 2012
advertisement

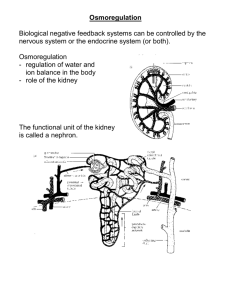
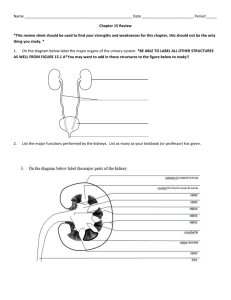
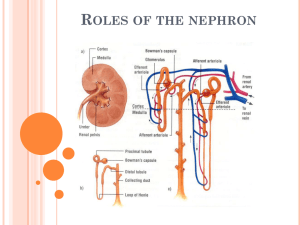
Name:_______________________ Biology 20 – My Virtual Body – Renal System Directions: Learn about the Urinary System by completing the activities from the following website: http://www.learnalberta.ca/content/sebr/index.html Login credentials are: Username: LA13 Password: 9418 Module Questions: 1. What are 4 things the renal system is responsible for? 2. Which of the following substances will be able to travel across the cell membrane by simple diffusion? 3. How will the concentration in the right-hand compartment change if the membrane in the box on the right is permeable to water only? 4. Complete the following definitions from the Electron Microscope View: 4.1. Glomerulus: 4.2. Nephron: 4.3. Cortex 4.4. Medulla 4.5. Afferent arteriole 4.6. Efferent arteriole 4.7. Bowman’s capsule 5. From the TEM, Glomerulus animation, which of the molecules are filtered? 6. What are the four basic mechanisms of transport that occurs in the nephron and kidney? 7. What is the tubular fluid volume (L/day) and concentration (mOsM) at the end of the collecting duct? Where along the nephron is the greatest tubular fluid volume? 8. How many times is the blood in a human adult filtered in a day? 9. Create a chart that identifies the substances that are filtered at the glomerulus and the substances that remains in blood. 10. Why is urine yellow? 11. Which molecules normally are filtered, reabsorbed, secreted, and/or excreted by the kidney? (place a checkmark in the appropriated boxes) Molecule Filtered reabsorbed secreted excreted none Glucose urea inulin albumin Na+ H+ Bicarbonate 12. Complete the Functional Anatomy Quiz and record the answers in the space below: 12.1. Where in the nephron would you expect to find the highest concentration of glucose? 12.2. Glomerular Filtrate – 12.3. The kidneys of desert animals have modified nephrons, which help them survive long periods without drinking any water. One would expect such a nephron to – 13. What is ADH? When and where is ADH secreted from? 14. List the steps of ADH secretion (5 steps). 15. When water is drawn from the filtrate and returned to the bloodstream, what happens to the urine? 16. Describe water reabsorption with and without ADH at the collecting duct. 17. Complete the Urine Formation Quiz: 17.1. Which region of the nephron contains the most dilute filtrate? 17.2. Glucose appears in the urine of a patient with diabetes mellitus because: 17.3. Put the following structures in the order through which urine passes through them: 17.4. Glomeruli 17.5. Put the nephron segments in the order through which filtrate flows: 17.6. Which of the following would not be filtered? 17.7. Which of the following distinguish reabsorption from secretion? 17.8. Which of the following findings would be expected in a patient with type I diabetes mellitus? 17.9. You are stranded on a hot, dry desert island. There seems to be no freshwater around. Why would drinking seawater NOT be useful for you? 18. In the regions labelled A and B in the diagram below, how do the diameters of the afferent and efferent arterioles need to change, respectively, in order to return the arterial blood pressure back to normal (120 mmHg)? 19. If the blood pressure in the glomerulus increases, how much the diameter of the afferent and efferent arterioles change in order to bring the filtration rate back to normal? 20. Define Diabetes Mellitus. What is the difference between type I and II? 21. What is Diabetes Insipidus? What are symptoms? 22. Describe on Dialysis (hemodialysis) works.