Bacteria Reproduction
advertisement

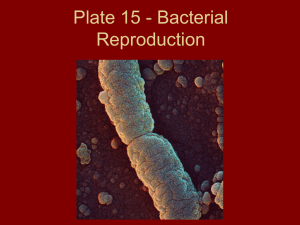
Bacteria Reproduction Asexual Reproduction - Offspring are identical to parent (CLONE) - Carried out by Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes - Simple & Efficient - Binary Fission and Mitosis Sexual Reproduction - Offspring is created from 2 diploid parents combining haploid gametes - Carried out by only Eukaryote - Offspring has genetic traits from both parents (23+23=46) - Meiosis Complexity and Steps Asexual Sexual Simple Complex Not many Many steps Steps where things can go wrong Time Asexual Sexual Happens fast Can take more And efficient time, many checkpoints Parent and Offspring Asexual Sexual One Parent two parents One Offspring Usually one offspring Not much Requires a lot Energy needed of energy, time Requires mating and competition Genetic Diversity Asexual Sexual Little to none Can quickly (caused by adjust genetic Mutations) diversity by (Meiosis Xover) Cell Cycle and Timeline Lag Phase - cells may be growing in volume or mass, synthesizing enzymes, proteins, RNA, etc., and increasing in metabolic activity. Log (Exponential) Phase - phase of growth is a pattern of balanced growth wherein all the cells are dividing regularly by binary fission, depending on environment Stationary Phase - Population growth is limited by one of three factors: 1. exhaustion of available nutrients; 2. accumulation of inhibitory metabolites or end products; 3. exhaustion of space Death phase - the number of viable cells decreases Cell Cycle and Timeline Binary Fission During binary fission, the single DNA molecule replicates and both copies attach to the cell membrane. Next, the cell membrane extends between the two DNA molecules. Once the bacterium just about doubles its original size, the cell membrane begins to pinch inward. A cell wall then forms between the two DNA molecules dividing the original cell into two identical cells. Binary Fission Transformation Transformation is the uptake and expression of foreign DNA. • Can be good and bad! Why? Conjugation During conjugation, a hollow bridge forms between two bacterial cells, and genes move from one cell to the other. This transfer of genetic information increases genetic diversity in populations of bacteria. Conjugation Transduction Transduction is the process by which DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus. • The virus is known as a Bacteriophage