Punnett Squares WS monohybrid
advertisement
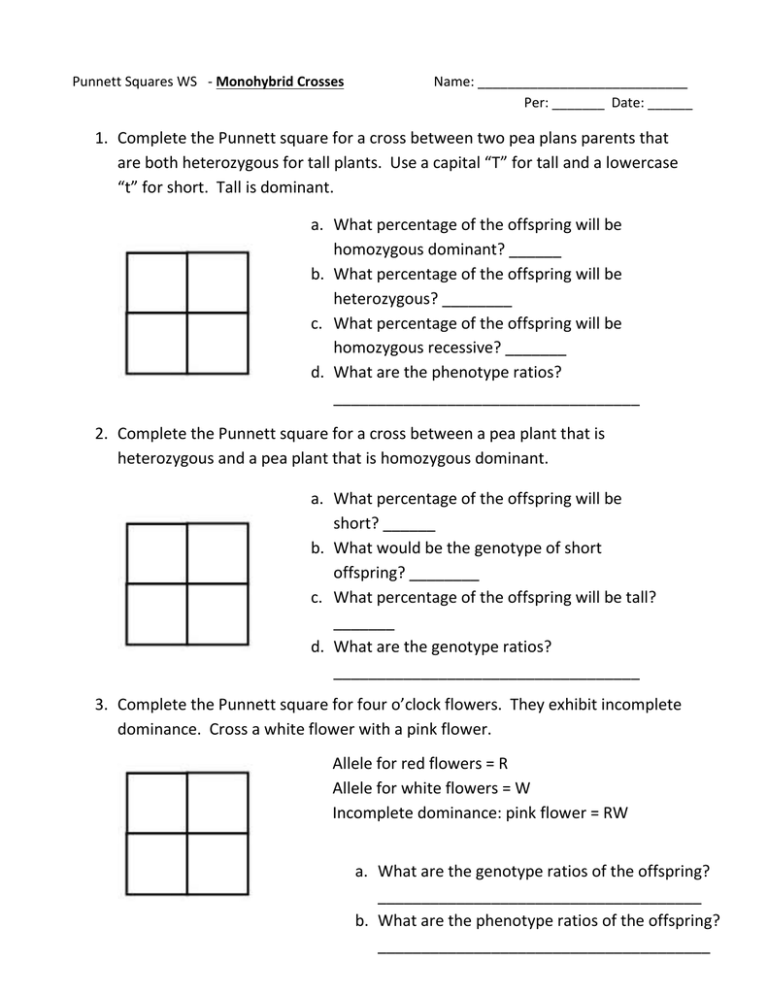
Punnett Squares WS - Monohybrid Crosses Name: ____________________________ Per: _______ Date: ______ 1. Complete the Punnett square for a cross between two pea plans parents that are both heterozygous for tall plants. Use a capital “T” for tall and a lowercase “t” for short. Tall is dominant. a. What percentage of the offspring will be homozygous dominant? ______ b. What percentage of the offspring will be heterozygous? ________ c. What percentage of the offspring will be homozygous recessive? _______ d. What are the phenotype ratios? ___________________________________ 2. Complete the Punnett square for a cross between a pea plant that is heterozygous and a pea plant that is homozygous dominant. a. What percentage of the offspring will be short? ______ b. What would be the genotype of short offspring? ________ c. What percentage of the offspring will be tall? _______ d. What are the genotype ratios? ___________________________________ 3. Complete the Punnett square for four o’clock flowers. They exhibit incomplete dominance. Cross a white flower with a pink flower. Allele for red flowers = R Allele for white flowers = W Incomplete dominance: pink flower = RW a. What are the genotype ratios of the offspring? _____________________________________ b. What are the phenotype ratios of the offspring? ______________________________________ 4. Complete the Punnett square for a white chicken crossed with a heterozygous chicken. Allele for black feathers = FB Allele for white feathers = FW a. Write the P generation cross: ____ ____ X ____ ____ b. What type of trait is this? _____________________________________ c. Complete the Punnett square. If there are 20 offspring, how many would you expect to be black? _________ 5. Complete the Punnett square for blood type. Cross a person with blood type AB with a person with blood type O. P generation cross: ____ ____ X ____ ____ a. What are the genotype ratios? ___________________________________ b. What are the phenotype ratios? ___________________________________ c. Is it possible that the offspring will have the same blood type as their parents?________ 6. Hemophilia is a recessive sex-linked disease found on the X chromosome. Complete the following Punnett square for a cross between a male with hemophilia and a woman who is a carrier of hemophilia. P generation cross: ____ ____ X ____ ____ a. What percentage of their male children will be normal? ______ b. What percentage of their male children will have the disease? ________ c. What percentage of their male children will be carriers? _______ d. What percentage of their female children will be normal? ______ e. What percentage of their female children will have the disease? ________ f. What percentage of their female children will be carriers? _______ Dihybrid Crosses: for all problems, complete the Punnett square. Remember, in dihybrid crosses you do not need to figure out the percentages (unless it is obvious) but rather give your answers in ratios or lowest common terms. 7. In guinea pigs, rough coat (R) is dominant over smooth coat (r) and black fur (B) is dominant over white fur (b). R & B are genes that are on different chromosomes so they are not linked. Cross a homozygous rough, homozygous black guinea pig with a smooth, white ginea pig. What will be the phenotypes of the F1 generation? P generation = ____ ____ X ____ ____ F1 phenotypes = 8. Now cross two of the F1 guinea pigs. What are the resulting phenotype ratios of this cross? P generation = ____ ____ X ____ ____ F1 phenotypes =