Cell Organelles PPT (Ms. Gardner)
advertisement

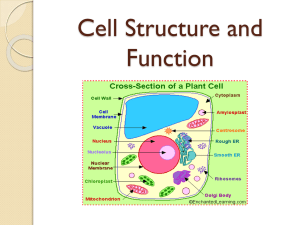
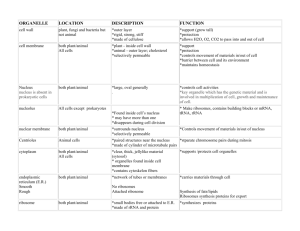
Organelles in Animal and Plant Cells Basics of Cell Structure Not all cells are alike! They vary in… A) size B) shape C) internal organization SIZE: range from .2m – 0.2um (most are 10-50um) -not all are microscopic (most are) ex: giraffe’s nerve cells extend 6.5 ft. down it’s leg!! Cells are limited in size by the ratio between their outer surface area and their volume Eukaryotic Cells Large Genetic material is ENCLOSED IN A NUCLEUS Contain a variety of organelles – membrane-enclosed structures that perform specific functions within the cell Cell Walls Stiff coatings on outer surfaces of bacteria, plants, fungi, and some protists are cell walls Support and protect fragile cells; usually porous Cell walls are composed of polysaccharides like cellulose or chitin Cell walls in plants may have multiple layers Primary cell walls in plants are outermost Secondary cell walls are innermost Cell walls of adjacent cells joined by middle lamellae Plasma Membrane Double layer of phospholipids Isolates cell contents from external environment Regulates flow of materials into and out of the cell Interaction with other cells and extracellular environment (outside of cell) Cytoplasm All material and structures that lie inside the plasma membrane, but outside nucleus Cytosol: fluid potion; water, salts and organic molecules; site of biochemical reactions Cytoskeleton Protein fibers, give shape an organization to the cell Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules 3 functions: 1. Shape (intermediate filaments) 2. Cell/Organelle Movement (microfilaments and microtubules) 3. Cell Division (microfilaments and microtubules) Cell Movement Cilia (“eyelash”) - move cell through fluid/fluid past cell Flagella (“whip”) - move cell through fluid Structure: • Ring of nine, one pair in the center • Outer pairs of arms interact to cause movement • Arise from basal body (just below plasma membrane) • Use ATP to move Centrioles and centrosome • Produce the microtubules of cilia and flagella, and those that form the spindle during animal cell division Nucleus Membrane bound hold chromosomes 3 components Nuclear membrane Chromatin Nucleolus The Nucleus The nuclear envelope separates chromosomes from cytoplasm Envelope is a double membrane with nuclear pores for transport Outer membrane is studded with ribosomes The Nucleus The nucleus contains DNA in various configurations Compacted chromosomes (during cell division) Diffuse chromatin (as DNA directs reactions through an RNA intermediate by coding for proteins) The Nucleus Darker area within the nucleus called the nucleolus Functions as the site of ribosome synthesis Ribosomes synthesize proteins Free Floating Ribosome: make proteins for the cell Ribosomes attached to ER: make proteins to be exported from the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum: (ER) acts as a highway for molecules to move around the cell. Smooth ER: does NOT contain ribosomes; Contains enzymes that detoxify drugs (in liver cells) or synthesizes lipids Rough ER: does contain ribosomes; Produces proteins and phospholipids destined for other membranes or for secretion (export) Golgi Apparatus (Body) A set of stacked flattened sacs product is assembled (moves from ER to golgi, where it is put together and adjusted) product is packaged (in new sacs) product is mailed out (sent out of cell) Lysosome Membrane enclosed vesicles Contain digestive enzymes Digest food particles by fuding with food vacuoles and digest food into basic nutrients Vacuole Fluid-filled sacs with a single membrane Functions of vacuoles Contractile vacuoles in freshwater organisms used to collect and pump water out Plant central vacuoles used in several ways Maintain water balance Store hazardous wastes, nutrients, or pigments Provide turgor pressure on cytoplasm to keep cells rigid Mitochondria Extract energy from food molecules and store in high energy bonds of ATP • Energy extraction process involves anaerobic and aerobic reactions Plastids a) chloroplasts : site for photosynthesis b) chromoplasts: stores red and yellow pigment c) leucoplasts: non pigmented Chloroplasts A type of plastid Functions of plastids Storage for photosynthetic products like starch Storage of pigment molecules giving color to ripe fruit Cell Wall Cell Wall: rigid covering made of cellulose, protects cell, goes OUTSIDE cell membrane, porous enough for certain substances Prokaryotes Small Surrounded by stiff cell wall Surface features – capsules and slime layers Single circular chromosome in central region called nucleoid; DO NOT CONTAIN A NUCLEUS Ribosomes