2. Stomata
advertisement

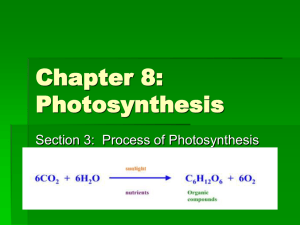
Photosynthesis How plants make energy 1. Mesophyll 1. Mesophyll A layer of cells that contain chloroplasts & are responsible for most of the plant’s photosynthesis Page 2 Page 2 O2 2. Stomata Openings in plant leaves that allow for gas exchange to occur Carbon Dioxide (CO2) passes in and Oxygen (O2) passes out. CO2 Mesophyll Cell Chloroplast The site of Photosynthesis Double-membrane bound organelle Outer membrane Inner membrane Page 2 8. Grana 7. Thylakoid Chlorophyll resides in these membranes 6. Stroma 8. Grana Page 2 Bond Energy and Energy Storing Compounds ATP, NADPH, FADH2, NADH How is energy stored in organic compounds? • When bonds are made by dehydration synthesis, energy is stored within the bonds of the compounds. How is energy released? • When bonds are broken by hydrolysis, energy is released from the bonds. What are some examples of common energy storing compounds? 1. ATP (Most important usable energy for the cell.) 2. NADPH 3. FADH2 4. NADH How is ATP made? • ATP is made from the precursor AMP (Adenosine Mono-phosphate) • If a phophate and energy is added to AMP, ADP is created. • Furthermore, if another phosphate is added to ADP, ATP is created. How ATP is Made • AMP A P • ADP A P P • ATP A P P P Equation for ATP synthesis • ADP + P + energy ATP How are NADPH, FADH2, and NADH made? • • • • NADP+ + H+ + electrons NADPH FAD+ + H+ + electrons FADH2 NAD+ + H+ + electrons NADH Notice that high energy electrons and hydrogen ions are needed to create NADPH, FADH2 and NADH. Draw and label the parts of the chloroplast Photosynthesis (definition) • The making of food in the form of _______________ (such as glucose) by autotrophic organisms by using sunlight, ____________ gas, and _________________. What are the two main steps of photosynthesis? 1. ________________ 2. ________________ Cycle The Nature of Light • In addition to the wave-like nature of light, light consists of discrete particles called photons . Page 5 What happens in the light reaction? • • Green ______________ pigment embedded in the ________________________ captures the light energy ____________ from the sun. ____________(e-) are taken from __________, and are excited to a higher energy state by the light captured by the chlorophyll pigment. What happens in the light reaction? • • • A complex series of enzymatic reactions occur, and ____ molecules of oxygen gas (O2) are created as a waste product. Meanwhile, the energy from the excited electrons is used to create the compounds, __ __ __ and __ __ __ __ __. Both ATP and NADPH are high energy compounds used to fuel the ____________ Cycle. Summary of the Light Reaction + + NADPH ++ + + 2e4e+ + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + + ATP What happens in the Calvin Cycle? • • • The energy from the ATP and NADPH is released when their ___________ are broken. The energy released from ATP and NADPH starts another series of enzymatic reactions in the ______________, where __CO2 gas is captured and converted into monosaccharides such as glucose (_____________). Glucose serves as “food” or _________ energy for the plant. PGAL What is the overall chemical equation for photosynthesis? • __H2O • (water) • LR • LR = • CC = + __CO2 + sunlight C6H12O6 + __O2 (carbon dioxide gas) CC (glucose) + (oxygen gas) CC LR Page 4 Pathway of Photosynthesis On your own, balance this equation: 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + (Light) 1 C6H12O6 + 6 O2 Reactants must equal Products Carbon 6 Carbon 6 Hydrogen 12 Hydrogen 12 Oxygen 18 Oxygen 18