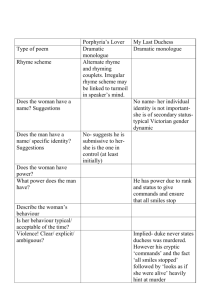
lit term (modified notes)
advertisement
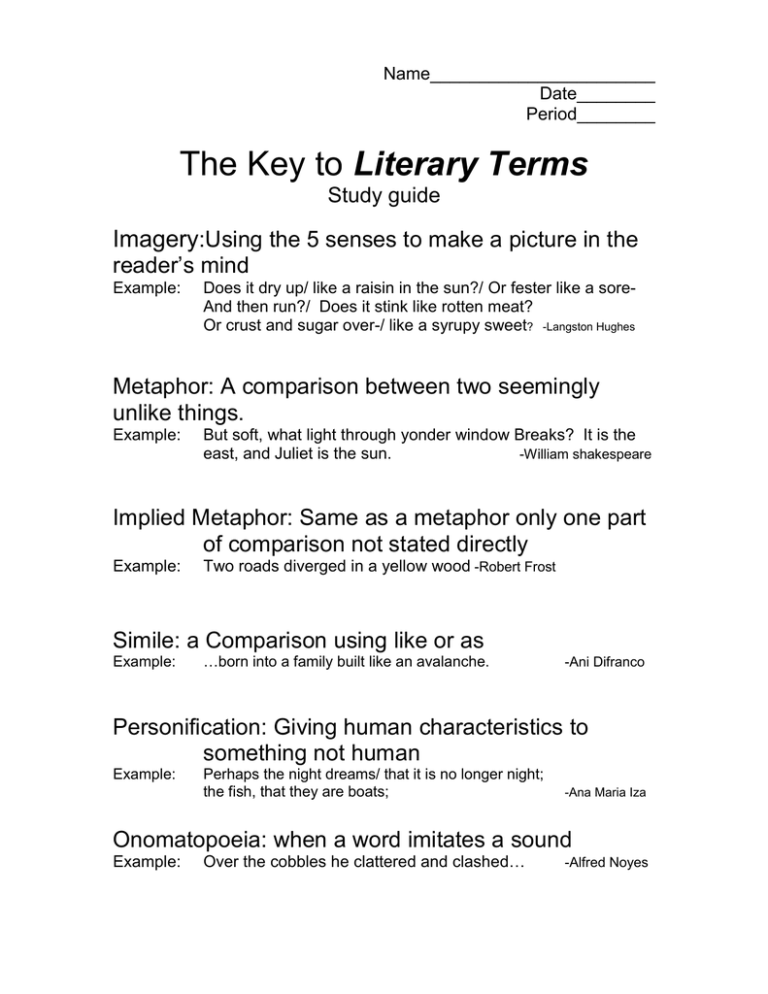
Name_______________________ Date________ Period________ The Key to Literary Terms Study guide Imagery:Using the 5 senses to make a picture in the reader’s mind Example: Does it dry up/ like a raisin in the sun?/ Or fester like a soreAnd then run?/ Does it stink like rotten meat? Or crust and sugar over-/ like a syrupy sweet? -Langston Hughes Metaphor: A comparison between two seemingly unlike things. Example: But soft, what light through yonder window Breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun. -William shakespeare Implied Metaphor: Same as a metaphor only one part of comparison not stated directly Example: Two roads diverged in a yellow wood -Robert Frost Simile: a Comparison using like or as Example: …born into a family built like an avalanche. -Ani Difranco Personification: Giving human characteristics to something not human Example: Perhaps the night dreams/ that it is no longer night; the fish, that they are boats; -Ana Maria Iza Onomatopoeia: when a word imitates a sound Example: Over the cobbles he clattered and clashed… -Alfred Noyes Alliteration: The repetition of consonant sounds Example: while/ All the world wondered. -Alfred, Lord Tennyson Stanza: A group of lines End Rhyme: rhyme that happens at the end of lines Example: Theirs not to make reply, Theirs not to reason why, Theirs but to do and die; -Alfred. Lord Tennyson Internal Rhyme: rhyme that happens inside of lines ___________________________________________ Example: I want to sail on a swallow’s tail and peep through the sky’s blue glass. I want to see if the dreams in me shall perish or come to pass. -Georgia Douglas Johnson Narrative Poem: a poem that tells a story Speaker: The voice of the poem; not the author Oxymoron: Putting 2 opposite word together Ex. Jumbo shrimp Hyperbole: An exaggeration Ex: These books weigh a ton.