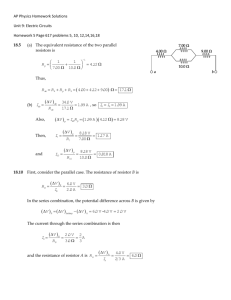
Calculating Equivalent Resistance in Parallel
advertisement

Notes: More Power and Equivalent Resistance Resistors Series Resistors in Parallel How to Identify Them: Connected at one end Not connect at the other No other paths intercepting What They Look Like How to Identify Them: Both ends are connected No other paths intercept What is the Same in the resistors: Current What the Resistors Share Voltage Vbattery= V1 + V2 + V3+…. Equivalent Resistance ∑R= R1 + R2 + R3 +… What is the Same in the resistors: Voltage What the Resistors Share Current Icircuit= I1 + I2 + I3 +... Equivalent Resistance 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + … 𝑹𝒆𝒒 𝑹𝟏 𝑹𝟐 𝑹𝟑 Series or Parallel? What They Look Like Equivalent Resistance Imagine that you put a black box around several resistors. You could measure the resistance inside the box, but you would have no way of telling what the resistors inside the box were. This is the idea behind equivalent resistance. Two resistors of 1Ω and 2Ω resistance in series would be equivalent of a 3Ω resistors. Calculating Equivalent Resistance in Series ∑R= R1 + R2 + R3 +… Practice Problem: Current, Voltage Drops, Power In the circuit, find the current and voltage drop through each resistor. Then find the power dissipated through Resistor 2. Calculating Equivalent Resistance in Parallel 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + … 𝑹𝒆𝒒 𝑹𝟏 𝑹𝟐 𝑹𝟑 Remember to flip your answer! Practice Question: Parallel Circuit Problem In the circuit to the right, find the voltage drop and current in each resistor. Find the power dissipated by R2. Combination Circuits Combination circuits occur when we combine series and parallel circuits. In that case, we need to combine the circuits together to find their equivalent resistance. Practice: Combining Series and Parallel Find the current through the circuit on the right. Then, find the voltage drop through the 5 Ω resistor. AP Practice: Power and a Combination Circuit If all of the resistors in the above simple circuit have the same resistance, which would dissipate the greatest power? (A) resistor A (B) resistor B (C) resistor C (D) resistor D (E) they would all dissipate the same power AP Practice: Finding the Power Supply In the accompanying circuit diagram, the current through the 6.0–Ω resistor is 1.0 A. What is the power supply voltage V? (A) 10 V (B) 18 V (C) 24 V (D) 30 V (E) 42 V AP Practice: Unusually Shaped Circuits A 9–volt battery is connected to four resistors to form a simple circuit as shown above. How would the current through the 2 ohm resistor compare to the current through the 4 ohm resistor? (A) one–forth as large (D) twice as large (B) one–half as large (E) equally as large (C) four times as large