Acids and Bases
advertisement

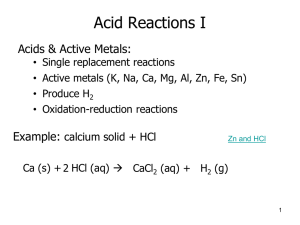
Acids and Bases Arrhenius Acid & Base Which beaker contains a base? Bronsted Lowry Acid and Base • Acid is a proton donor • HF + H2O H3O+ + F• Base is a proton acceptor NH3 + H30+ NH4++H20 Conjugate acid base pairs Fill in the following table with the appropriate conjugate acid or base Acid H2SO4 Base PO43- NH4+ F- H20 H20 Polyprotic acid • • • • Monoprotic HCl, ClDiprotic H2S, HS-, S2Diprotic H2SO4, HSO4-, SO42Triprotic H3PO4, H2PO4-, HPO42-, PO43- Naming acids • Binary acids • Hydro ____________ ic acid • Ternary acids • ______________ ic acid • ______________ous acid Name the following acids • • • • • • H2S (aq) H2SO3 HClO2 HNO3 HF(aq) HC2H3O2 Strong acids completely ionize in water Strong acids (memorize) Strong acids: Completely ionize in water Weak acids in water are in equilibrium They don’t completely Ionize in water Bases donate OHor accept H+ • • • • • NaOH Mg(OH)2 Al(OH)3 NH3 PO43- Neutralization reactions Acid + base react to form salt + water HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O H2SO4 + 2NaOH Na2SO4 + 2 H2O How many moles of phosphoric acid are needed to react with 5.0 moles of sodium hydroxide? Identify each of the following as an acid, base or salt Acid HC2H3O2 MgCl2 H2SO4 Ca3(PO4)2 Sr(OH)2 Al(NO3)3 Base Salt Complete the following neutralization reactions and balance • HBr + NaOH CaCl2 + H2O Sr3(PO4)2 + H2O pH=-log H3 + O Equations to determine pH • • • • Kw = [H30+][OH-] Kw = 1x10-14 pH = -log [H3O+] [H30+] = 10 –pH Fill in the following graph pH [H3O+] [OH-] 6.60 1.8 x 10-3 2.91 3.89 x10-2 5.9 x 10-6 13.12 Acid/base? pH [H3O+] [OH-] Acid/base? 6.60 2.51 x 10-7 4.0x10-8 acid 11.1 5.6x10-12 1.8 x 10-3 base 2.91 1.23 x 10-3 8.13 x 10-12 acid 1.41 3.89 x10-2 2.57 x 10-13 acid 8.8 1.7 x 10-9 5.9 x 10-6 base 13.12 7.59 x 10-14 0.13 base compound H3O+ 0.00000510 M HNO3 6.69x10-2 M KOH _____M HCl OH - pH 2.3 Stomach produces HCl, how does it protect itself? The acid in the stomach is hydrochloric acid, HCl, and has a pH of about 2. Acid of pH 2 can be quite corrosive - observe the effect of placing an iron nail in hydrochloric acid solution with pH =2 Buffer • Buffer resists change in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added • A buffer is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt, • Weak acid + its salt is the acid and its conjugate base Buffer system Weak acid Salt of the acid (conjugate base) A Buffer consists of HSO4- and NaOH is added to the solution. Who is the shark? SO42- Did you pick HSO4-? • Write the reaction A Buffer consists of H2CO3 and HCl is added to the solution. Who is the shark? HCO3- Predict whether each pair would form a buffer. Explain your answer. Pairs of compounds KOH, KCl HI, NaI NH4I, NH3 NaH2PO4, H3PO4 Explanation Write an equation showing the buffering action of each of the following aqueous solutions • NH4I / NH3 adding OH• NaH2PO4/H3PO4 adding H3O+ Buffers in the body The body has many systems to control pH of the blood