The metaphysical poets

Chapter Three
English Literature of the 17th century
Overview of the period
Features of literature
The influential writers of the period
John Donne, John Bunyan, John
Milton, John Dryden
The Overview of the Literature
(
1640-1688
)
1. The revolution period
( 1 ) The metaphysical 玄学派 poets;
( 2 ) The Cavalier 骑士派 poets;
(3) The Revolutionary poets 革命派 .
2. The restoration period.
( 1 ) The restoration of Charles II ushered in a literature characterized by reason, moderation 适度 , good taste, deft 灵巧的 management, and simplicity. ( school of Ben
Johnson )
( 2 ) The ideals of impartial 公平的 investigation and scientific experimentation promoted by the newly founded Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge
( 1662 ) were influential in the development of clear and simple prose as an instrument of rational communication.
( 3 ) The great philosophical and political treatises of the time emphasize rationalism 理性
主义 .
( 4 ) The restoration drama.
( 5 ) The Age of Dryden.
Features of literature
1. the Elizabethan poets and Metaphysical poets.
A metaphysical poet beyond physical, e.g.
Shakespeare says how beautiful you are, but Donne says how he loves you. He talks about what love is in a seemingly philosophical way.
The words Elizabethan poets used are elegant, graceful and musical, while metaphysical poets are the words and cadences of common speech.
With the use of conceit 奇喻 , 怪喻 , a dramatic metaphor, Donne’s images are strange and fresh. The fore is frequently that of an argument, but not the regular lyric of iambic metrical forms.
2. Cavalier poets and Metaphysical poets.
Although both poets are interested in mysticism, the cavalier poets attempt to gain a knowledge of real truth and a union with God by prayer or meditation.
They wrote in short songs about the flitting joys of the day. The tone of their poems seems happy and light, but reading their poems, readers can sense their awareness of mortality
(death), for they emphasize the transitoriness of human glory and joy.
The metaphysical poets are also aware of mortality, but they express it in a serious and sad tone.
3. Beside the metaphysical and Cavalier poets, the revolutionary spirit of the time also found its strong reflection in literature.
During the revolution of 1640, the pamphlets of John Milton and others played in an active part in pushing on the revolutionary cause.
Even after the Restoration in 1660, Milton and
John Bunyan, both Puritans, continue to defend in their works the ideas of the Revolution.
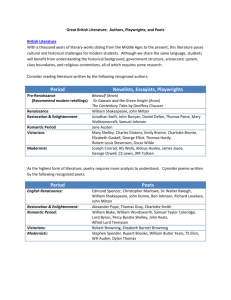
Some influential writers
John Donne, John Bunyan,
John Milton, John Dryden
John Donne
Features of Donne ’ s poems
With various experiences and attitudes and a free range of feelings and moods, his poems give a theatrical impression.
The mode is dynamic rather than static, with ingenuity of speech, vividness of imagery and vitality of rhythm.
Realistic – real life not a poetical world.
He wrote poems in elegies 挽歌 , satires 讽刺 , lyrics 抒情 in early period, religious poems and prose 散文 in later period.
He often applied conceits. – easy and difficult ones.
He wrote in the tone of argument.
John Milton
Literary creation:
Three groups: the early poetic works, the middle prose pamphlets and the last great poems. After the restoration, when he was blind and suffering, poor and lonely, Milton wrote his three poetical works: Paradise
Lost 失乐园 , Paradise Regained 复乐园 , and
Samson Agonistes 力士参孙 , among the three, the first is the greatest.
Features of Milton ’ s Poety
1. works with revolutionary spirit. Milton was political in both his art and his life; he was an outstanding pamphleteer of the period of the English Revolution, and a greatest English revolutionary poet of the 17th century.
2. Milton was a great stylist, he is famous for his grand style, which is the result of his long classical and biblical study.
3. Milton is a master of Blank Verse 无韵诗 .
4. he makes language new through unexpected use of words. Uses Latinism-words used in sense of the Latin word from which they are derived. Also used Latin grammar and long sentences.
5. his sublimity 庄严 of thought and majesty of expression.
气宇非凡词语
John Bunyan
The main works: The Pilgrim ’ s Progress 天路历程
Features of his works:
1. Bunyan ’ s style was modeled after that of the
English Bible.
2. his works are in the form of religious allegory
宗教预 ( 喻 ) 言
3. his language is simple, colloquial and easy for the reader of the least education to understand.
4. He had rich imagination and a narrative gift.
John Dryden
1. Life:
( 1 ) the representative of classicism in the Restoration.
( 2 ) poet, dramatist, critic, prose writer, satirist.
( 3 ) changeable in attitude.
( 4 ) Literary career — four decades.
( 5 ) Poet Laureate 桂冠诗人
2. His influences.
( 1 ) He established the heroic couplet as the fashion for satiric, didactic, and descriptive poetry.
( 2 ) He developed a direct and concise prose style.
( 3 ) He developed the art of literary criticism in his essays and in the numerous prefaces to his poems.
Some terms
Conceit
Essay
Metaphysical poets
Conceit
From the Italian Concetto, “ concept ” or “ idea ” ; used in Renaissance poetry to mean a precise and detailed comparison of something more remote or abstract with something more present or concrete, and often detailed through a chain of metaphors or similes.
Essay :
The term refers to literary composition devoted to the presentation of the writer ’ s own ideas on a topic and generally addressing a particular aspect of the subject. Often brief in scope and informal in style, the essay differs from such formal expository forms as the thesis, dissertation or treatise.
Metaphysical poetry :
The term “metaphysical poetry” is commonly used to designate the works of the 17th century writers under the influence of John Donne. Pressured by the harsh, uncomfortable, and curious age, the metaphysical poets sought to shat termths and replace them with new philosophies, new sciences, new worlds and new poetry.
Some exercises
Ten blanks
Try to read the following poem, think about its meaning, the writer and its features.
.
THE FLEA.
by John Donne
MARK but this flea, and mark in this,
How little that which thou deniest me is ;
It suck'd me first, and now sucks thee,
And in this flea our two bloods mingled be.
Thou know'st that this cannot be said
A sin, nor shame, nor loss of maidenhead ;
Yet this enjoys before it woo,
And pamper'd swells with one blood made of two ;
And this, alas ! is more than we would do.
O stay, three lives in one flea spare,
Where we almost, yea, more than married are.
This flea is you and I, and this
Our marriage bed, and marriage temple is.
Though parents grudge, and you, we're met,
And cloister'd in these living walls of jet.
Though use make you apt to kill me,
Let not to that self-murder added be,
And sacrilege, three sins in killing three.
Cruel and sudden, hast thou since
Purpled thy nail in blood of innocence?
Wherein could this flea guilty be,
Except in that drop which it suck'd from thee?
Yet thou triumph'st, and say'st that thou
Find'st not thyself nor me the weaker now.
'Tis true ; then learn how false fears be ;
Just so much honour, when thou yield'st to me,
Will waste, as this flea's death took life from thee
Blanks
1. Donne entered the Anglican Church (the
Church of England ) in 1615, where he rose rapidly to be Dean of __________, and the famous preacher of his time. (St. Paul
Cathedral)
2. The term ---- is commonly used to name the world of the 17th writers who wrote under the influence of John Donne. (Metaphysics)
3. With the use of _______, a dramatic metaphor, Donne ’ s images are strange and fresh. (conceit)
4. in Milton’s works, _________ is the greatest, indeed the only generally acknowledged epic in English literature since Beowulf. (Paradise Lost)
5. in 1637 Milton wrote the finest pastoral elegy in English, “_______” , to memorize the tragic death of a Cambridge friend.
(Lycidas)
6. ________ poets, often knights and squires, who sided with the king against
Parliament and Puritans. (Cavalier)
7. Cavalier poets wrote in short songs about the _____ joys of the day. (flitting)
8. Milton and Bunyan represented the extreme of English life in the 17th century. One left us a great epic since _________. The other a greatest religious _____. (
Beowulf, allegory)
9. Bunyan ’ s most important work is _________, written in the form of allegory and dream.
(
The Pilgrim ’ s progress)
10. In the Pilgrim ’ s Progress, the story begins with a man called ______setting out with a book in his hand and a great load on his back from the city of ________.
( Christian
Destruction)
1 . which event did not happen in the 17th century?(D )
A. the Great Plague B. the Great London
Fire
C. The Glorious Revolution D. the
Renaissance
2. (B ) was not among those great writers as the great Enlighteners in England.
A. John Dryden B. John Milton
C. Alexander Pope D. Joseph Addison
3. The neoclassical period witnessed the flourish of English poetry in the classical style from Restoration to about the second half of the century, climaxing with the following poets except (B ).
A. John Dryden B. Henry Fielding C.
Elexander Pope D. Samuel Johnson
4. (A ) was the Scottish peasant poet in the pre-romantic period.
A. Robert Burns B. William Collins C.
William Blake D. William Cowper
5. “(
C
)” was not John Bunyan’s works.
The Holy War B. The Pilgrim’s Progress
C. A Modest Proposal D. The life and Death of
Mr. Badman.
6. Choose the works not written by Daniel Defoe
(
D
).
A. Robinson Crusoe B. Captain Singleton C.
Moll Flanders D. Tom Jones
7. (
A
) ‘s novels are the first literary works devoted to the study of problems of the lower-class people.
A. Daniel Defoe B. Henry Fielding C. Jonathan
Swift D. Goldsmith
8. “(C )” brings its author Henry Fielding the name of the “Prose Homer”.
A. The history of Amelia B. The History of the Adventures of Joseph Andrews
C. Tom Jones D. The History of Jonathan
Wild the Great
9. Samuel Johnson was an energetic and versatile writer. He had a hand in all the different branches of literary activities, except
(A )
A. Novelist B. dramatist C. biographer D lexicographer