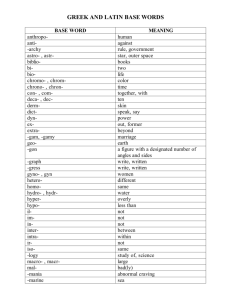
Chap5PathologyCV
advertisement
Cardiovascular System Pathology Medical Terminology Chapter 5 Atheroma ather/o = plaque -oma = tumor Plaque within the arterial wall Atherosclerosis athero = fatty plaque sclerosis = abnormal hardening Hardening & narrowing of arteries due to a buildup of cholesterol plaque Angina pectoris Severe episodes of spasmodic choking chest pain Ischemia Deficiency of blood supply due to constriction or obstruction of blood vessels Infarct Localized area of necrosis caused by an interruption of blood supply Myocardial infarction (MI) Heart attack Closing off of a coronary artery resulting in an infarct of the affected myocardium Coronary artery disease (CAD) Atherosclerosis of coronary arteries that may cause angina, myocardial infarction & sudden death End-stage CAD: final phase with severe angina & severely limited lifestyle Congestive heart failure (CHF) Heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs; leads to fluid accumulation in legs, lungs Forms of Carditis Endocarditis: inflammation of the inner layer of the heart Bacterial endocarditis: inflammation of the lining or valves of heart caused by bacteria Myocarditis: inflammation of the myocardium Pericarditis: inflammation of the pericardium Valvulitis valvul/o = valve -itis = inflammation Mitral valve prolapse Protrusion of the mitral valve thus incomplete closure of the valve Mitral stenosis Abnormal narrowing of the mitral valve also tricuspid stenosis Arrhythmia or dysrhythmia Irregular rhythm of the heart Bradycardia brady = slow card = heart -ia = abnormal condition Abnormally slow heartbeat Flutter Atrial contractions are rapid but regular Tachycardia tachy = fast card = heart -ia = abnormal condition Abnormally fast heart rate Paroxysmal tachycardia Sudden onset of fast heartbeat Fibrillation Rapid, random, & ineffective heart contractions Atrial fibrillation (A-fib): atria faster than ventricles Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib): fatal unless reversed by electric defibrillation Angi/o = vessel Angiitis or vasculitis Angionecrosis Angiospasm Angiostenosis Hemangioma hemangi/o = blood vessel -oma = tumor benign tumor of blood vessels Hypoperfusion Deficiency of blood passing through an organ or body part Aneurysm Localized balloon like enlargement of the wall of an artery Arter/o, arteri/o = artery Arteritis Polyarteritis Arteriosclerosis Raynaud’s phenomenon Intermittent attacks of pallor, cyanosis, & redness of fingers & toes secondary to arterial contraction & caused by cold or emotion Phlebitis phleb/o = vein -itis = inflammation Inflammation of a vein Varicose veins Abnormally swollen veins usually occurring in the legs Thrombus & Embolus Thrombus: blood clot attached to wall of a vein or artery Embolus: foreign object, such as blood clot or tissue, that is circulating in blood stream Thrombotic occlusion Blocking of an artery by a clot Coronary thrombosis Damage to the heart caused by a thrombus blocking a coronary artery Embolism Blockage of a vessel by an embolus Hemochromatosis (iron overload disease) Hem/o = blood Chromat/o = color -osis = abnormal condition Genetic disorder in which intestines absorb too much iron Septicemia (blood poisoning) Presence of pathogenic microorganisms or their toxins in the blood Cholesterol Lipids that travel in the blood stream as lipoproteins Low density lipoprotein (LDL): bad cholesterol; excess contribute to plaque buildup HDL: good cholesterol -penia = deficiency of Leukopenia Thrombocytopenia Erythrocytosis erythr/o = red cyt/o = cell -osis = abnormal condition Abnormal increase in number of RBCs Leukemia leuk/o = white -emia = blood condition Malignancy with progressive increase of abnormal leukocytes Anemia an- = without or less than -emia = blood condition Lower than normal numbers of RBCs Aplastic anemia Absence of all formed blood elements due to failure of blood cell production in bone marrow Hemolytic anemia hem/o = blood -lytic = to destroy Blood cells destroyed faster than bone marrow can replace them Megaloblastic anemia Bone marrow produces large abnormal RBCs with a reduced ability to transport oxygen; usually from a vitamin deficiency Pernicious anemia RBCs are abnormally formed due to an inability to absorb Vitamin B12 Sickle cell anemia Genetic disorder that causes abnormal hemoglobin & RBCs have a sickle shape Hypertension=high blood pressure Essential or primary hypertension: unknown cause Secondary hypertension: caused by a different medical problem such as kidney disease Malignant hypertension: sudden onset of severely elevated blood pressure