2 - Florida International University
advertisement
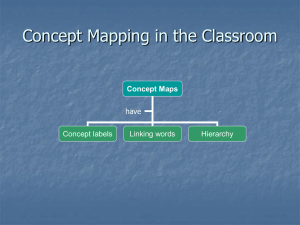
Developmental Theory Chapter 2 Novak & Pelaez The Importance of Theories • Organize & bring Coherence to views • Worldviews – overarching viewpoints that bias our observations – Pepper’s Worldviews • Mechanistic • Organismic • Contextualistic (Behavioral Systems Theory) Novak & Pelaez Dimensions on Which Theories Differ • • • • Structure vs. function Description vs. explanation Nature vs. nurture Continuity vs. discontinuity Novak & Pelaez Dimensions on Which Theories Differ • Description versus Explanation – Explanation • • • • Prediction Control Circular Explanations Reification Putting the cause inside the child Behaviors become explanations e.g., dyslexia; autism • Real Explanations – “Under what conditions?” not Why? Novak & Pelaez Nature versus Nurture • • • • False Dichotomy “How” do nature and nurture interact Not “How Much?” Nature & nurture are both a function of selection by consequences (Skinner) • Nature & nurture are not causes but processes and products (Oyama). Novak & Pelaez • • • • • • • • • Judging Developmental Theories - Nine Criteria 1) Accuracy 2) Clarity 3) Predictability 4) Practicality 5) Internal Consistency 6) Parsimony 7) Testable 8) Productivity 9) Self-SatisfyingNovak & Pelaez Group Research Designs in Studying Behavioral Development • Cross-sectional – Problems- Cohort Effects • Longitudinal – Problems• Practice Effects • Selective Attrition • Sequential – Combination of CrossSectional & Longitudinal Novak & Pelaez The problem with using age as a variable • Age is an empty variable • Focus should be on the process variables that produce behavior and are correlated with age. Novak & Pelaez Behavioral research methods – Single Subject Designs • Functional Analysis- manipulate variables to see cause-effect relations. Novak & Pelaez Behavioral Research Designs • ABAB reversal design • Multiple-treatments (alternating treatments) design • Multiple treatments designs • Changing Criterion designs • Combined within & between subjects designs Novak & Pelaez ABehavioral Systems Approach Novak & Pelaez Transaction of 5 Factors • • • • • Genetic-Constitutional Make-up History of Interactions Current Physiological Conditions Current Environmental Conditions Behavioral Dynamics Novak & Pelaez Principles of Dynamical Systems • • • • • • • • • Multiple Determination Multiple Determination means Equifinality Models of Development Nonlinearity Phase Shifts = Developmental Stages Coalescent Organization Selectionism Behavioral Attractor States Developmental Trajectories Novak & Pelaez Multiple Determinism • Transaction of 5 Factors • Sensitivity to Initial Conditions Butterfly Effect • Leading Parts - Disproportionate Influence • “Impossible” to predict outcomes • Equifinality is the norm Novak & Pelaez Equifinality Point of Equifi nality for Three Individuals ` With Di fferent Trajectories 20 Moe Larry 15 Curly Smiles/ hr. 10 5 0 Time A Time B Time C Novak & Pelaez Models of Development Novak & Pelaez Linear Model B A Novak & Pelaez Transactional Model A B Novak & Pelaez Nonlinear Model X A B A B A Novak & Pelaez Emergent Properties & Phase Shifts • Sudden, nonlinear changes (e.g., A to X) • Qualitative Difference • Result of Coalescent Organization • Result is “Organized” • When Universal, called “Stage” Novak & Pelaez Coalescent Organization • Multiple Determinants • Coming together of all conditions leads to reorganization of organism/behavior Novak & Pelaez Selectionism: Organization by Consequences • Phylogenic Selection – Changes in species • Ontogenic Selection – Changes in individuals (learning) • Cultural Selection – Changes in cultures • Any selection requires variability Novak & Pelaez Selectionism - 3 Requirements • Variability (Response Classes) • Selection – Ontogenic - Natural Selection – Phylogenic - contingencies of learning • Retention (Physiology) Novak & Pelaez Behavioral Attractors • • • • Organized patterns of behavior “Soft” (loose) assemblies Assembled by Consequences Form (Structure) follows Function Novak & Pelaez Developmental Trajectories • Behavioral Momentum • Stability vs. Phase Shifts Novak & Pelaez “Behavioral Cusps” not “Stages” • Cusps are important new behaviors that emerge that enable the development of many other behaviors. (e.g., walking; reading). Novak & Pelaez An Organism-Environment Model (Horowitz, 1987) • Organismic Dimension – Impaired to unimpaired – Vulnerable to nonvulnerable • Environment Dimension – Non-facilitative to facilitative Novak & Pelaez The transaction of organismic & environmental variables produces • Developmental Outcome – Minimal to Optimal Novak & Pelaez