1. Marketing Introduction
advertisement

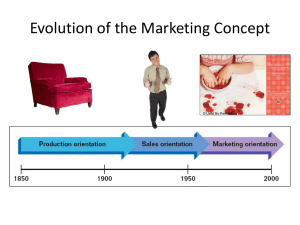
An Introduction to Marketing Previous Next To replay any audio, click on the sound icon 1 Course Contents • Nature and Scope of Marketing: • Understanding Marketing Concept & Marketing Management • Core Concepts of marketing • Evolution of Marketing • Marketing Mix • P’s of Marketing What is Marketing? Personal Selling? Advertising? Making products available in stores? Maintaining inventories? All of the above, plus much more! Marketing Defined A Philosophy An Attitude A Perspective A Management Orientation A Set of Activities, including: Products Pricing Promotion Distribution Understanding marketing • Marketing ,more than any other business function, deals with customers. • Simply put, Marketing is managing profitable customer relationships. • Most of the highly successful companies know that if they take care of the customers, market share and profits will follow like Wall Mart, Nokia, Dell, McDonald. Marketing defined • A social and managerial process whereby individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others Core Marketing concepts • Need: A state of felt deprivation of some generic satisfaction arising out of the human condition. E.g food, clothing and shelter. • Wants: Desires for specific satisfiers of these ultimate needs. The form human needs take as they are shaped by culture and individual personality. A person needs food but wants a pizza. • Demand: Human wants that are backed by purchasing power. • Product: Anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a want or need. • Service: Any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in ownership of anything. Customer Value The ratio of benefits to the sacrifice necessary to obtain those benefits Needs and Wants can be satisfied through • • • • Self-Production Coercion Supplication Exchange (Marketing Exists) The Concept of Exchange At Least Two Parties Necessary Conditions for Exchange Something of Value Ability to Communicate Offer Freedom to Accept or Reject Desire to Deal With Other Party Conditions for Exchange • There must be at least two parties and each party… • • • • Must have something the other party values Must communicate and deliver goods Must be free to accept or reject offer Must want to deal with other party Definition of Marketing • It is a human activity directed at satisfying needs and wants through exchange products. • It is a societal process by which individuals and groups obtain, what they need and want through creating, offering and freely exchanging products and services of value with others. • Simply put: Marketing is the delivery of customer satisfaction at a profit. American Marketing Association Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals. Marketing Management Can you name the four marketing management philosophies? Stages in the Evolution of Marketing Production Orientation Late 1800’s Sales Orientation Early 1930’s Marketing Orientation Mid 1950’s Societal Orientation 1990’s Industrial Revolution Mass production Available & affordable Great Depression Problem not to produce but to sell High promotional activity End of World War II Huge pent up demand More demanding customers Concern towards society and consumer Marketing Management Philosophies Production Sales Competing Philosophies Market Societal Marketing Marketing Management Philosophies Philosophy Production Sales Market Societal Key Ideas Focus on efficiency of internal operations Focus on aggressive techniques for overcoming customer resistance Focus on satisfying customer needs and wants Focus on satisfying customer needs and wants while enhancing individual and societal well-being Production Orientation • • • • • The firm is focused on what it does best Less concerned on customers’ needs Customers favour available & affordable products. Businesses concentrate on achieving high production efficiency, low cotsts & mass distribution Examples: Sales Orientation • Based on assumption that consumers , if left alone will either not buy or not buy enough. • Organisation must therefore undertake aggressive sales techniques • Focus on product • Practiced with unsought goods like insurance Market Orientation The marketing concept states that the social and economic justification for an organization’s existence is the satisfaction of customer wants and needs while meeting organizational objectives. The Marketing Concept Focuses on customer wants and needs to distinguish products from competition Integrates all organization’s activities to satisfy customer wants and needs Achieves organization’s long-term goals by satisfying customer wants and needs Sales vs. Market Orientations Organization’s Focus Sales Orientation Market Orientation Firm’s Business For Whom? Primary Profit Goal? Tools to Achieve Inward Selling goods Everybody Maximum Primarily promotion and services sales volume Outward Satisfying wants and needs Specific Customer Coordinated groups of satisfaction use of all marketing people activities Societal Marketing • Organisation’s task is to determine the needs and wants of target markets & to deliver more effectively and efficiently than competitiors in a way that preserves or enhances the consumer’s and the societal well being. • Firms make marketing decisions in an ethical and socially responsible manner. • Practise Green Marketing Societal Marketing Orientation Marketing that preserves or enhances an individual’s and society’s long-term best interests Less toxic products More durable products Products with reusable or recyclable materials Marketing Mix The set of controllable marketing toolsproduct, price, place and promotion-that the firm blends to produce the response it wants in the target market. Marketing Objectives • Characteristics – Consistent with company objectives – Measurable – Time specific • Benefits – Energize employees – Set standards of performance Marketing Mix • • • • Product Place (Distribution) Promotion Price Marketing Mix Variables Product Place(Distrib ution) Goods, services, or ideas that satisfy customer needs The ready, convenient, and timely availability of products Promotion Activities that inform customers about the organization and its products Pricing Decisions and actions that establish pricing objectives and policies and set product prices Product Shape, size, taste, flavour, colour, quality, brand, style, design, packaging Place(Distrib ution) Wholesalers. Retailers, Exclusive distribution Promotion Advertising, PR, Personal Selling, Direct marketing, Sales promotion Pricing List Price, Allowances, Discounts Scope of Marketing • • • • • • • • • • Products Services Places Organisation Properties Information Experience Events Ideas Persons Components of Strategic Marketing FIGURE 1.1 Marketing Strategy • Select one or more target markets • Set market objectives • Develop & maintain a marketing mix