Biology First Semester Final Exam Study Guide What is the
advertisement

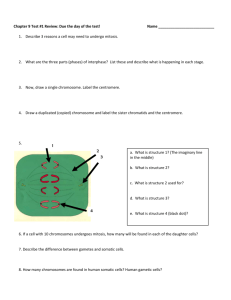
Biology First Semester Final Exam Study Guide Identify the building blocks for the following macromolecules: Define the following terms: Independent variable: ____________________ Proteins: __________________________ ______________________________________ Carbohydrates: _____________________ Dependent variable: _____________________ Lipids: ____________________________ ______________________________________ Nucleic Acids: ______________________ Experimental group: _____________________ ______________________________________ Identify the following parts of a phospholipid: hydrophobic and hydrophilic Control group: __________________________ ______________________________________ What is the importance of a control in an experiment? How many variables do you test at one time during an experiment? Answer the following question regarding scientific experiments. Harvester ants often strip a bush of all its leaves. Some people believe this helps the plant grow thicker, healthier stems. In an experiment, a student stripped off all the leaves from a set of plants. In a second set of identical plants, the student allowed ants to strip off the plants’ leaves. What needs to be added to the experimental design in order to improve the overall experiment? How would you accomplish this task? Read the following experiment and answer the accompanying questions. A student investigated the effect of radiation on the germination of bean seeds. He thought that exposure to radiation would limit the seeds ability to germinate (grow) much like ultraviolet light causing skin cancer. Three hundred seeds were soaked in distilled water for one hour. They were then divided into three groups. One group was placed in a microwave oven on high for three seconds. Another group was microwaved on high for six seconds. The last group was not microwaved. The seeds were then planted in three separate flats and given the same amount of water. The flats were placed in a location with constant temperature of approximately 27 degrees Celsius. Each day for two weeks the number of seeds that germinated each group was recorded. Three sec of radiation: 54 Six sec of radiation: 26 No radiation: 88 What is the dependent variable? What is the independent variable? What is the experimental and control group? Identify which characteristic of living things is being described in each of the statements below A. all living things contain cells B. all living things contain DNA C. all living things obtain and use energy D. all living things reproduce E. all living things respond to stimuli F. all living things maintain an internal balance (homeostasis) G. all living things grow and Develop H. all living things evolve as a Population ___ 1. An adult hydra is producing its offspring trough budding. ___ 2. An amoeba is a unicellular organism. ___ 3. A pill bug eats a carrot. ___ 4. Over three years, Tim’s height has increased from 5’4” to 5’11”. ___ 5. A caterpillar hibernates in a cocoon, and emerges as a butterfly. ___ 6. It is thought that humans are chimpanzees once shared a common ancestor. ____ 7. A tulip opens up in the morning at sunrise and closes up in the evening at sunset. Lab safety Questions: 1. What important eye equipment needs to be used during a lab? __________________ 2. Before you leave the lab for the day you should always _________________________ _________________________________ (2 answers) 3. This should happen before you begin work in a lab ______________________________ 4. Waste should always be deposited in one of these ___________________________ 5. These should not be worn on your feet in a Identify whether the substance is an acid or a base. 1. Baking soda (8.2) 2. Coca Cola (2.5) 3. Saliva (6.2) 4. Bleach (12) 5. Ammonia (11.6) 6. Stomach Acid (2) 7. Battery Acid (less than 2) _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ What is the activation energy? What is the purpose of a biological catalyst? Identify the following parts of the compound light microscope Fine adjustment knob Eyepiece Course adjustment knob Arm High powered objective Base Low powered (scanning) objective Light source lab______________________________. Match the vocabulary word to the correct definition. a. adhesion d. polarity b. cohesion e. covalent bond c. ionic bond _____ 1. A bond that results when electrons share electrons _____ 2. The attraction between molecules of different substances _____ 3. A bond that results when electrons are transferred between atoms _____ 4. The attraction between molecules of the same substances _____ 5. Oppositely charged poles are produced as a result of an unequal distribution of electrons What organelles are found in plants, but not in animal cells? What organelles are found in animals, but not in plant cells? Label the following cell parts on both the plant and animal cells: cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, chloroplast, golgi body, nucleus, nucleolus, central vacuole, centriole, smooth ER, rough ER, flagella, and cilla Fill out the Venn diagram for prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryote Eukaryote What is osmosis? Identify the images as either Isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic What is the difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution? Match the organelle to the correct function. a. Mitochondria e. Centriole b. Chloroplast f. Golgi body c. Nucleolus g. Lysosome d. Ribosome ____ 1. Helps in separating chromosomes during cell division ____ 2. Manufactures ribosomes ____ 3. Distribution, packaging, and shipping of proteins ____ 4. Brakes down food to produce ATP through a series of chemical reactions ____ 5. Manufactures proteins ____ 6. Digests and recycles cell material ____ 7. Uses the energy of the cell to produce glucose through a series of chemical reactions What is the difference between active and passive transport? What is the difference between active transport and facilitated diffusion? What are the three principles of the cell theory? What do all cells have in common? Identify the images as either heterotrophs or autotrophs. 6 CO2 + 6 H2O 6 C6H12O6 + 6 O2 1. What formula does this chemical reaction represent? 2. Where does this chemical reaction take place? 3. What is produced at the end of this process? 6 O2 + 6 C6H12O6 6 CO2 + 6H2O + Energy 1. What formula does this chemical reaction represent? 2. Where does this chemical reaction take place? 3. What is produced at the end of this process? Identify the stages of mitosis and meiosis shown in the images below. Match the term to the appropriate definition. a. Light Reaction b. Dark Reaction c. Chlorophyll d. Lactic Acid Fermentation e. Cellular Respiration f. Photosynthesis g. Alcoholic Fermentation ____ 1. Pigment that absorbs light energy ____ 2. A series of chemical reaction that produces ATP and NADPH to fuel the dark reaction ____ 3. The process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen ____ 4. Breaks down food molecules in the absence of oxygen by producing CO2, ethyl alcohol, and carrier molecules ____ 5. Uses ATP, NADPH, and carbon to produce glucose ____ 6. Uses light energy to synthesize glucose from carbon dioxide and water ____ 7. Breaks down food molecules when there is not enough oxygen in the muscle cells of animals Label the steps of the cell cycle. Cytokinesis, S phase, G2 phase, M phase, and G1 phase, Interphase What takes places during interphase? What is the difference between haploid and diploid? What are the advantages of sexual reproduction? During which phase of the cell cycle do cells spend most of their time? What is the diploid and haploid number for humans? What are the advantages of asexual reproduction? Fill out the Venn diagram for Mitosis and Meiosis What takes place during crossing over? Mitosis Meiosis What is genetic recombination? Why is genetic recombination important for the survival organisms? How is cytokinesis different between plants and animals? Match the stage of mitosis to the correct description. a. prophase d. telophase b. metaphase e. cytokinesis c. anaphase What is cancer? ___ 1. Sister chromatids align along the center of the cell ___ 2. Two new nuclei are formed, chromosomes start to uncoil, and the nucleolus re-forms ___ 3. The nuclear envelope disappears, chromosomes coil, centrioles appear ___ 4. Cell is pinched midway between the cell, equally dividing the cytoplasm between the two cells ___ 5. The sister chromatids are pulled apart, and each chromatid is pulled to the opposite poles What are homologous chromosomes? How many cells are produced at the end of mitosis? of meiosis? What causes cancer? How does the genetic make-up of the cells produced in mitosis compare to the cells produced during meiosis? What is the difference between malignant and benign cancer? Match the correct stages of meiosis. Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Cytokinesis II Label the following parts of a nucleotide: nitrogen base, phosphate group, and sugar Describe the structure of DNA. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA? What are the complementary base pairing rules for DNA and for RNA? What happens during transcription? What is produced at the end of transcription? What are the steps of replication? Mrs. Smith has a baby named Tyra. She believes one of two men can be the father of her child. A paternity that is done and the results are shown below. Which of the 2 men are baby Tyra’s father? __________ Why is one strand replicated continuously and the other discontinuously? Where does transcription take place? Mr. and Mrs. Jones just gave birth to fraternal twins- Bob and Jane. Unfortunately, the nurse has confused the Jones twins with 4 other babies. The doctors took samples of DNA from each of the babies and Mr. and Mrs. Jones. Which of the 6 children are Mr. and Mrs. Jones twins? When does translation begin? Where does translation take place? What is produced at the end of translation? What are codons and anti-codons? Use the codon wheel below to complete the protein synthesis problem DNA mRNA amino acid CGT TCA ATA GCG GGT CCT AAG DNA mRNA amino acid TGG CTC TCT AGG GTA CGT GTA Describe what during each of the chromosomal mutations pictured below. What occurs during a framshift mutation? What is the difference between a spontaneous mutation and an induced mutation? In the case of a point mutation, what happens during a deletion? a substitution? an insertion? What is the central dogma? How are genes regulated?