Writing Short Reports
advertisement

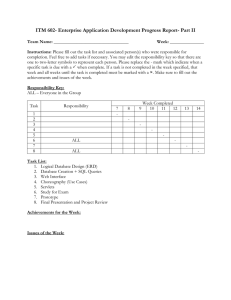
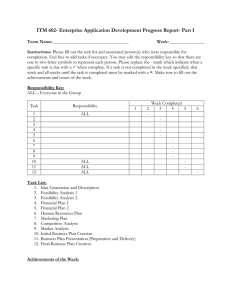
LECTURE 23 Short Reports • A report presents comprehensive information on a specific subject. Its main function is to inform, offer expert opinion, advice to managers, keep a check on progress, plan for the future and make decisions. Planning Steps • • • • • Indicate your purpose clearly Give accurate and objective information Apply suitable headings Organize the points Lead logically to a conclusion • 1: Take time to identify your task • 2: Consider your reader’s needs • 3: Identify and list your and sourcing requirements • 4: Avoid being side-tracked • 5: Discard anything irrelevant Order of Information • 1: Indirect order • 2: Direct order • 3: Routine order Four types of Short Reports 1: Justification Report • 1 Purpose statement (subject line) • 2: Structure of information • Describe the current situation • Describe the change • Justify the change • Describe the cost factor • Discuss the advantages and disadvantages • 3: Conclusion • Make a conclusion • Close with a recommendation 2: Progress Report • 1: Purpose statement • 2: Structure of information • Open with the current status • Work or goals completed so far • Follow with details of the operation’s achievements • Present any problems/delays and suggest their solutions • Change of plans (give details) • 3: Conclusion • Give advantages of the change introduced • Indicate the future • • • • • • • • • 3: Periodic Report 1: Purpose statement 2: Structure Open with facts and figures Present objective information on achievements and problems Cost factors involved 3: Conclusion Summarize the findings Close with recommendations • 4:Incident Report: • Written on forms generated by the organization • • • • Involving clients Unusual delays Accidents Special events