Group Communication Notes revised

Group Communication
• What is the difference between a group & a crowd?
• Group- Consists of people who communicate with each other over time and share an interest in the same things or share a common purpose
• Groups may be formal or informal
• Purpose of group may be social, task, or a combination of social & task
Group Communication
Typically, members of a group…
Communicate regularly
Participate in planning, decision making or action
Feel connected to other members
Group Norms
Group norms- Standards for behavior within a group; how you are expected to interact
Whether it’s okay to arrive early or late, how hard to work, how to act or dress, whether taking a break is acceptable or not, when and how to disagree, what topics are acceptable to discuss, how much to divulge about personal life, etc.
Ideal Groups
Group size: Researchers have found ideal group size is 5-7 members
Cohesion- When members have respect for one another, share same values, and look to one another for support; when they all want to achieve the same goal
Group discussion-
Cooperative exchange of information, opinions, and ideas
Types of Group Discussion:
Panel- informal discussion that takes place before an audience; designed to help audience become more familiar with issues
Symposium- more formal; present opposing points of view; invited experts deliver short speeches on particular issues
Town Hall Meeting- members of the community discuss issues and usually vote for solutions
Leadership
Leadership functions: any kind of behavior that helps the group toward its goal (could be one or more members of a group who fulfill these roles; group can have effective leadership even without an official leader)
Characteristics of a good leader:
Good grasp of problem (well-informed)
Familiar with group process- can organize
(provide direction & structure)
Open-minded (consultant rather than boss)
Self-disciplined, respectful, empathetic
Good speaker (skillful communicator)
Can formulate goals & ideas for both group and self
Share rewards and give group credit
(believe in teamwork)
Good planner
Able to adapt to meet needs of group
Ways of becoming leader:
Appointed
Elected
Emerging
Shared
Duties of a leader:
Procedural matters
State topic
Call on individuals
Request specific info.
Open and close meeting
Interpersonal or climate matters
Promote group cohesiveness
Encourage members to respect one another
Help members get to know one another
Styles of Leadership
Laissez-faire: advises if called upon; observes, records; does not direct
Authoritarian: strongly directs; very goal-oriented
& opinionated
Democratic : guides; receptive to members’ suggestions; leaves decisions up to group
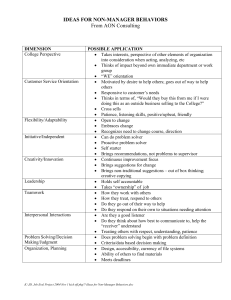
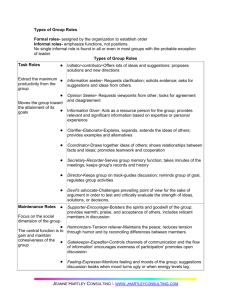
Group Roles
Initiator- Proposes new ideas, goals, procedures, methods, solutions
Information seeker- Asks for facts, clarification, or information from other members
Information giver- Offers facts and information, personal experiences, and evidence
Group Roles
Opinion seeker- Draws out opinions of others
Opinion giver- States own belief or opinion; expresses a judgment
Clarifier- Elaborates on ideas expressed by another, often by giving an example, explanation, or illustration
Group Roles
Coordinator- Clarifies relationships among facts, ideas, and suggestions; suggests an integration of ideas and activities of two or more group members
Orienter- Makes sure the group is focused on purpose or goal, defines position of the group, summarizes or suggests the direction of the discussion
Energizer- Prods the group to greater activity or to a decision; stimulates activity; warns the group to act while there is still time
Group Roles
Procedure developer- Offers suggestions for accomplishing ideas of others, or handles such tasks as seating arrangements, setting up the computer, handing out papers, running copies, etc.
Recorder- Keeps written record; serves as group’s “memory”
Supporter- Praises, agrees, indicates warmth and solidarity with others or goes along with them
Group Roles
Harmonizer- Mediates differences between others
Tension reliever- Jokes or brings out humor in a situation, reduces formality and status differences, relaxes others
Gatekeeper- Opens channels of communication, brings in members who otherwise might not speak; sees that everyone has a fair chance to be heard
Group Roles
Blocker- Constantly raises objections, insists nothing can be done, repeatedly brings up the same topic after the rest of the group has disposed of it
Aggressor- Deflates status of others, expresses disapproval, jokes at the expense of others, expresses ill will or envy
Recognition seeker- Boasts, calls attention to self, relates irrelevant personal experiences, seeks sympathy or pity
Dominator- Tries to run the group by giving directions, ordering, and interrupting; insists on his or her own way
Observer- Part of the group but only watches; not an active participant
Isolate- Does not participate; may not want to be part of the group