The Future of….. - II Sem Notes
advertisement

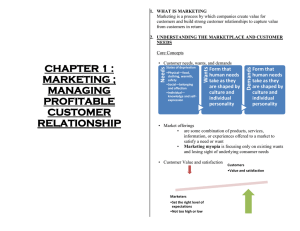
The Future of….. Individuals Groups Institutions Organisations Society Country World All depends on…. MARKETING & INVENTIONS/INNOVATIONS There is a mistaken belief that companies are customer oriented. But that’s not true; they are paying lip service. They are still product centric. - Marketing Guru Philip Kotler Are they really marketing oriented? In the car Park, the Prime Parking spots are reserved for Directors & Senior staff rather than customers When confronted with a problem from a customer, an employee will refer the customer on to another employee without trying to resolve the matter themselves. The company listens to customers comments & complaints, but has poorly defined procedures for acting on them. Advertising is based on what senior staff want to say , rather than a sound analysis of what prospective customers want to hear. Goods and services are distributed through channels that are easy for the company to set up, rather than on the basis on what customers prefer. MARKETING MANAGEMENT Market+ Marketing+ Marketing Management Markets The word ‘market’ is derived from the Latin word ‘Marcatus’ which means merchandise ,trade or a place where business is conducted. A market is a set of actual and potential buyers who might transact with a seller. Sellers constitute the industry and buyers constitute the market. Evolution of Market The Cave Man- Food Gatherers Nomadic Hunter Stage-Hunting for Food Agrarian Period- Family system Market Continued… Division of Labour-Barter System Melas-Local Market(No Permenant shop) Shops,Bazzars-Permanent (Small Shops) Places Market Continued…. Department Multiple Super Stores Shops Market/Bazzars Market Continued….. Mail to order Tele Marketing Internet Marketing Mobile Marketing Market Continued….. Thus the evolution of Market demanded a new concept/meaning to a Market. A market can be an environment in which both demand and supply or customer and supplier can come in to a contact and effect the trade. 09/02/2009 Elements of Market 1. Customers 2. Producers 3. Product/service 4. Intermediaries 5. Competitors 6. Service Providers (Insurers, Transporters,Warehouses,Financ iers etc.) Types of Market Markets have been classified, on the basis of different approaches, in various ways. o On The basis of Geographical Area: 1. Local Market: When buyers and sellers, belong to a local area or areas, say a town or village, participate in market, it is called local market. Here demand is limited in a small area. E.G : Un-branded Products, vegetables, fish etc. 2. State Market: When sellers and buyers belong to a state, it is called state market. E.G: KSEB (only excess is sold to other states) Supply is limited to a state. 3. National Market: A country is regarded as a market. E.g.: Consumer Durables, fashionable items 4. World Market: Involvement of buyers and sellers beyond the boundaries of a Nation. E.g.: Capital Goods, spices etc. On the Basis of Commodities /Goods A. Commodity Markets: Produced goods are bought and sold. 1. Produce Exchange Market: This type of markets is found only in developed industrial centres/cities. Sellers & buyers of a certain particular commodity is traded. E.G.: The Cotton Exchange Market of Mumbai 2. Manufactured Goods Market 3. Bullion Market: This type of market deals with the purchase & sale of gold, silver etc. E.g.: Bullion Markets of Mumbai, Calcutta, Kanpur etc. B. Capital Markets Financial needs are met by capital Markets. 1. Money Market: It consists of short-term and call money market. London is the world’s biggest money market. 2. Foreign Exchange Market: This type of market helps exporters and importers, in converting their currencies into foreign currencies and vice versa. 3. The Stock Exchange Market C. On the Basis of Economics: 1. Perfect Market: conditions; a. Large number of Buyers &Sellers b. Uniform price throughout the market c. Buyers & sellers have perfect knowledge about the goods and services Goods can be moved from one place to another without any restrictions. 2.Imperfect Market: conditions a. Products are similar but not identical b. Prices are not uniform c. There is lack of communication d. Restrictions on the movements of goods. D. On the basis of Transaction 1. Spot Market: Physical delivery of goods are takes place immediately. 2. Future Market: Contracts are made over the price for future delivery. E. On the basis of Regulation 1. Regulated Market: These are types of Markets which organised, controlled and regulated by statutory measures. E.g.: Sock Market by SEBI, Money Market by RBI, Insurance Market by IRDA etc. 2. Unregulated Market: Less control on price, quality, commission etc. Absolute free market is An utopia. F. On the basis of Time 1. Very short Period Market: deals in perishable goods like fruits, milk, fish etc. There is no change in the supply of goods. Price is determined on the basis of demand. 2. Short Period Market: In this market supply can be adjusted to meet the demand to certain extend. E.G.: Meat Market 3. Long Period Market: Supply is adjusted to meet the demand. E.G.: Durable goods G. On the Basis of Volume of Business: 1. Retail Market: goods are sold in small quantity. Directly to Consumers 2. Whole Sale Market: Deals in large Quantity. To dealers and/or directly to customers also. H. On the Basis of importance: 1.Primary Market: producers sells to the intermediaries/customers directly invest in the organisations. 2. Secondary Market: Intermediaries sell goods to customers/customers invest in organisations through stock exchanges. A Definition of Marketing Marketing: the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of ideas, goods, services, organizations, and events to create and maintain relationships that will satisfy individual and organizational objectives. Another Definition Marketing: an organizational process for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders. Marketing is “The process of discovering and translating consumer needs and wants into product and service specifications, creating demand for these products and services and then in turn expanding this demand”.Prof.H.L.Hansen Core Marketing Concepts Needs, Wants, and Demands Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Adapted 8 level Hierarchy of Needs diagram, based on Maslow's theory Transcendence helping others to self-actualise Self Actualization Aesthetic needs beauty, balance, form, etc Cognitive needs knowledge, meaning, self-awareness Esteem Needs (self-esteem) Social Needs (sense of belonging, love) Safety Needs (security, protection) Physiological Needs (hunger, thirst) Needs A human need is a state of felt deprivation. An unsatisfied person will do one of two things: Look for an object that will satisfy the needs Try to reduce the need. 10/02/09 Needs People in industrial societies try to find or develop objectives that will satisfy customers’ desires (e.g., substitutes or alternatives.) Physiological Needs- for food, cloth and shelter Taj Hotles, K.R Bakes Reymond,Zero, Sowgandhika Haritha Apartments, Oceanus Homes etc. Social Needs for belonging, affection, fun, and relaxation. Greeting Cards Diamond Necklace, Titan Watches Black Thunder, Veega Land Movies, Parks etc. Esteem needs for prestige, recognition, and fame BMW car,Omega watches, member of International Clubs etc. Wants Wants are how people communicate their needs. Wants are described in terms of objectives that will satisfy needs. As people are exposed to more objectives that arouse their interest and desire, producers try to provide more want-satisfying goods and services. Restaurants were once able to satisfy the hunger Today’s restaurant customers are more sophisticated and want and expect hygiene, prestige & quick service along with food. Wants The sellers confusing wants and needs suffer from “marketing myopia.” They are so taken with their products that they focus only on existing wants and lose sight of underlying customer needs. They forget that a physical product is only a tool to solve a consumer problem The customer have the same need but want a new product Demands Customers choose products that produce the most satisfaction for their money (i.e., economic value) due to the fact that people have unlimited wants, but limited resources. When this decision process is backed by buying power, wants become demands. Motel 6 and Sleep Inns mean basic accommodations, a low price, and convenience. Four Seasons and Ritz Carlton mean luxury, comfort, and status. Needs, Wants, and Demands Understanding customer needs, wants, and demands in detail provides important input for designing marketing strategies. All Disney World managers spend one week per year on the front line – taking tickets, selling popcorn, or loading and unloading rides. Most successful writers personally reads letters and of guest comment cards submitted by customers. Managers can identify customer needs, wants, demands through market research & open door policy. Product A product is anything that can be offered to satisfy a need or a want. The concept of product is not limited to physical objects. Products include experience, persons, places, organizations, information, and ideas. What are some travel and tourism “products” that you can list? Disneyworld is an experience. Starbucks and Barnes & Noble have turned buying books into an experience (relaxation). Marriott vacation club and Marriott time-share resort create customer experience such as dolphin safari for its New Port Beach property or a water rafting trip for its Utah property. One of the most interesting areas of marketing is product planning and development. – Travel industry develops heritage tourism or eco-tourism in response to customer needs. Value, Satisfaction, and Quality Customer value is the difference between the customer benefits from owning and/or using a product and the costs of obtaining the product. The purpose of marketing is to generate customer value. Free delivery (Domino’s and Pizza Hut) Free continental breakfast (by most mid-scale hotels) Customer satisfaction is perceived value delivered relative to a buyer’s expectations. – Customer delight creates an emotional tie to a goods or service, not just a rational preference, and this creates high customer loyalty. – Satisfying the guest is not enough, only when guests leave very satisfied are they likely to come back. Quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy customer needs. – It is closely linked to customer value and satisfaction. Exchange, Transactions, and Relationship Marketing Exchange is the act of obtaining a desired object from someone by offering something in return. A transaction is marketing’s unit of measurement and consists of a trade of values between two parties. – Monetary transaction • IBM gives $500 to Hilton and obtains the use of a meeting room. – Barter transaction • A restaurant might provide free meals to a radio station in return for free advertising on that station. – A transaction involves at least two things of value, a time of agreement, and a place of agreement. Relationship marketing is building strong economic relationships with social ties by following through on promises. Both transaction parties involved frequently seek long-term benefits. 11/02/09 Evolution of Marketing 1.Barter Era 2.Production Era: It originated with the industrial revolution in the 18th Century. Mass production oriented No preference for customer Profit was the ultimate purpose at any cost 3. Sales Era:(1920s) Production capacity increased supply of goods exceeded demand compelled to sell all the produced goods selling activity became dominant No consideration for customer satisfaction 4. Marketing Era:(1950s) Emphasis on customer Needs Customer satisfaction Long term Profitability Marketing Research 5. Management Era: Marketing function has to do Planning,Organising,Directing & Controlling of: 1. Product 2.Price 3. Market 4. Marketing Research 5. Promotion 6.Distribution etc. Traditional vs. Nontraditional Marketing Traditional Marketing – Goods – Services Non-Traditional – Places – Events – Causes – Persons Marketing Marketing As Utility Type Description Examples Organizational Function Responsible Form Conversion of raw materials and components into finished goods and services Boeing 767 aircraft, Pen, Paper etc Production Time Availability of goods and services when consumers want them One-hour dry cleaning; Federal Express’ guarantee of package delivery by 10:30 a.m. the next day etc. Marketing Place Availability of goods and services at convenient locations coffee and snacks in bookstores; day cares in office complexes; ATM machines in gas stations; mail boxes outside convenience stores etc. Marketing Ownership (possession ) Ability to transfer title to goods or services from marketer to buyer Retail sales (in exchange for currency or credit-card payment) etc. Marketing MOTTS The copy reads: “Same ingredients. Ours just fits through a straw.” and “MOTTS MEANS FRUIT” Nature of Marketing A. It is an Economic Function B. It is a Legal Process C. It is a System D. It is an Interrelated Activity E. It is a Managerial Function F. It is a Philosophy G. It may not be a Profit Making Activity H. It is a Social Process o Scope of Marketing 1. Understanding Customers’ Needs and Wants 2. Study of Buyer Behaviour 3.Product Planning & Development 4. Pricing 5.Distribution 6.Promotion 7. Mktg. Information & Demand Forecasting 8. Consumer satisfaction 9. Marketing Audit MARKETING PROCESS Concentration Small Lot Output Assembly of Parts To Facilitate Regular Supply Dispersion Equalisation Function of Exchange Mktg. Functions Function of Physical Supply Facilitating Functions Function of Exchange 1. Buying & Assembling 2. Selling Function of Physical Supply 1. Transportation 2. Storage Facilitating Functions 1. Financing 2. Risk-bearing 3. Standardisation & Grading 4. Pricing 5. Advertising & Sales Promotion Marketing as Demand Satisfaction Demand is a measure of the desire that potential customers have for a product or service . . . plus their willingness and ability to pay for it Marketing Concept – Serve existing demand – Reactive Market Orientation Demand Creation – Create products to satisfy unstated needs – Proactive Market Orientation How to Create Customers Through Marketing Concept – Identifying customer needs – Designing goods and services that meet those needs – Communicating information about those goods and services to prospective buyers – Making the goods or services available at times and places that meet customers’ needs – Pricing goods and services to reflect costs, competition, and customers’ ability to buy – Providing for the necessary service and follow-up to ensure customer satisfaction after the purchase Target Market Group Distribution Product Target Market Promotion © PhotoDisc Price of people toward whom the firm decides to direct its marketing efforts Marketing Mix Distribution Product Target Market Promotion Price Blending the four strategy elements of marketing decision-making – Product – Price – Distribution – Promotion to satisfy chosen target markets Product Strategy Deciding Distribution Product Target Market Promotion © PhotoDisc Price – What goods or services to offer – Customer service – Package design – Brand names – Trademarks – Warranties – Product Life Cycle – Positioning – New – product development Pricing Strategy Distribution Product Target Market Promotion © PhotoDisc Price Deals with the methods of setting profitable and justifiable prices PRICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Credit Terms Payment Period Discount Commission Differentials etc. Distribution Strategy Decisions about Distribution Product Target Market Promotion © PhotoDisc Price – Modes of transportation – Warehousing – Inventory control – Order processing – Marketing channels Promotional Strategy Blending Distribution Product Target Market Promotion © PhotoDisc Price together the various elements of promotion to communicate most effectively with the target market. Promotional elements include advertising, sales promotion, public relations, and personal selling. Distribution Strategy Decisions about Distribution Product Target Market Promotion © PhotoDisc Price – Modes of transportation – Warehousing – Inventory control – Order processing – Marketing channels Companies should view the 4 Ps in terms of the Customer’s 4 Cs • • • • Product Price Place Promotion • • • • Customer Needs Cost to the Customer Convenience Communication A rapidly evolving global market is shifting the focus from 4Ps to 4Cs, and now 4 Ts. Are Indian Companies ready for the Change? 4 Ps to 4 Ts • • • • Product Price Place Promotion • Trade • Tariff • Transportation • Transformation (Source: USP AGE; March- 2007) Trade Globalisation Urguary Round GAAT India’s share of world Trade – 0.67% Expected Share-1% Export Processing and Special Economic Zones TARIFF Proliferation of Trade Barriers America had the Tariff around the 40% America, Japan, Italy, Australia, Finland &France were high tariff Countries WTO prefer Tariff To Non Tariff Barriers (NTB) TRANSPORTATION Air Freight and Air Services JIT Intelligent Transport System (ITS)-reduced cost Shopper’s stop, Viveks and Subhiksha are in the path of ITS Air service has a vital role –direct flight to relevant locations/good inter connections) 12/02/09 Research shows that: Businesses in computing, software, R&D, Biotechnology, food, finance and Insurance heavily depends on Air Freight and Air Services. TRANSFORMATION More aware and intelligent customer than before Television no more a favourite of advertisers Advertising cost more than its worth Getting more importance to P.R More interest in Web sites, blogs etc. F.M a new media habit Prosumers- New interest of Marketers account for 20% or more for any category of products 12/02/09 Importance of Marketing Mix It act as the link between the business firm and its customers Since marketing mix are based on customer needs it helps increase sales, customer satisfaction and profit It signifies that these four elements are closely inter-related It helps to adapt different environment and customers by changing the elements Expanded Marketing Mix 4 P’s added another 4 P’s 5. Packaging 6. People – attitude, style, sense of responsibility of people who come into contact with customers 7. Physical Evidence-to make customer induced & confident 8. Process-The process involved in transferring product from manufacturer to customer. 6,7&8 are more important in service sectors. Why is marketing planning necessary? Systematic futuristic thinking by management better co-ordination of company efforts development of better performance standards for control sharpening of objectives and policies better prepare for sudden new developments managers have a vivid sense of participation Objectives of the marketing plan Acts as a roadmap assist in management control and monitoring the implementation of strategy informs new participants in the plan of their role and function to obtain resources for implementation to stimulate thinking and make better use of resources Standard Planning Framework Analysis - where are we now? Objectives - where do we want to be? Strategies - which way is best? Tactics - how do we ensure arrival? Control - are we on the right track? The contents and structure of the marketing plan The executive summary table of contents situational analysis and target market marketing objectives marketing strategies marketing tactics schedules and budgets financial data and control Behavioural planning problems Planning recalcitrance: resistance and nonco-operation by managers in planning fear of uncertainty in planning: a lack of comfort in planning activities political interests in planning activities:resource bargaining, padding of requirements, and avoidance of consensus planning avoidance: compliance rather than commitment to planning Cautionary notes for effective planning Don’t blindly rely on mathematical and statistical calculations. Use your judgement as well Don’t ever assume that past trends can be exploited into the future forever if drawing conclusions from statistical data, make sure the sample size is sufficiently large Objectives of the marketing plan Acts as a roadmap assist in management control and monitoring the implementation of strategy informs new participants in the plan of their role and function to obtain resources for implementation to stimulate thinking and make better use of resources Importance of Marketing To the Firm It helps to understand the Consumer Behaviour It helps to decide about the product, price, promotion and distribution It generate revenues to the firm It gives vital information to take decisions in other areas like production, finance and human resources Marketing & innovation/inventions became two basic functions to stay and grow in this cut throat competition To the Customers Customer is considered as the kingBeginning & End is the customer Customers’ preferences are taken in to consideration Customers get wide choice Better customer service Healthy competition To the Society Improves the quality of life Ensures optimum production and optimum consumption It creates place, time and possession utilities It provides employment opportunities It converted yesterday’s luxuries into today’s necessities It is also helpful in making aware of social causes, social events etc To the Nation (Particularly developing countries) Development of Various Manufacturing and service industries Improved standard of living Increase in the National Income Maximum utilisation of Available Resources Dvelopment of Basic Infrastructure (transportation,communication etc.) Balanced National Growth Increased Exports Increased Foreign Exchange Increased National Image Criticisms of marketing planning Formal plans can be quickly overtaken by events Elements of the plan my be kept secret for no reason gulf between senior managers and implementing managers the plan needs a sub-scheme of actions Marketing & Relationship with other business functions 1. Financial Management 2. Production and Operations Management 3. Human Resource Management Marketing & Other Disciplines 1. Psychology 2.Sociology 3.Statistics 4.Law 5.Economics Marketing and Social Responsibility 1. Customers prefer goods from ‘good citizen’ organisations 2.Improving Standard of Living 3. Balanced Growth 4.Marketing Social Causes & Events 5. Societal Marketing Marketing- Is a science or an art? Science- it is a systematised body of knowledge. Art- it is the exercise of systematic knowledge to reap a good result. Marketing is an art, because; 1. Each marketer applies marketing concepts in his/her own way 2. The aim is to get satisfaction from the consumers. The marketer adjusts or tackles the situation, aiming to success in his field 3. The success of a marketer depends on his/her ability and skill 4. As an art, it creates interest, feelings, satisfaction etc. 5. It deals with human behaviour 6.No scientific approach to deal with a problem/situation 7. Re-testing of marketing situation is little bit of difficult Marketing cannot be called as exact science like physics, chemistry etc. 1.Of course, it developed as a body of theory 2.Systematic approach can be developed to handle the situations 3. In marketing research, scientific method of study is adopted-setting hypothesis, testing hypothesis, generalising in to the theories etc. We can conclude that Marketing is an art as well as science Approaches to the study of Marketing Product or Commodity Approach- analyses the problem relating the commodity/product 1.Source and Conditions of Supply 2.Nature and extend of Demand 3.Mode of Transporting 4. Storage 5. Standardisation 6. Packing 7. After Sales Services Institutional Approach: Focus on the study of Institutions i.e. The number of, functions of, problems of 1.Intermediaries 2. Importers & Exporters 3. Agencies (Advertising, Parcel services etc.) 4.Warehouses 5.Financial Institutions etc. Functional Approach: It gives importance to different functions of Marketing 1. Buying & Selling 2.Pricing 3. Standardisation 4. Storage 5. Transportation 6. Promotion 7. Packing 8. After sales Service Management Approach: Under this management functions of Planning, organising, staffing, directing and controlling is applied on: 1. Controllable Factors 2. Uncontrollable Factors Controllable Factors: a. Product b. Place c. Price d. Promotion Uncontrollable Factors: a. Consumer’s Buying Behaviour b. Trader’s Behaviour c. Competitor’s behaviour d. Government Behaviour e. Public Behaviour (Media Public also) Systems Approach: It focus on interrelationships and interconnections among the functions of Marketing and interrelationship with other areas of business. Legal Approach: Emphasise only aspect i.e. legal aspect with respect to 1. Transfer of Ownership 2.Relationship with third parties Societal Marketing Concept The pure marketing concept ignores possible conflicts between short-run consumer wants and long-run societal needs. Organization should determine the needs, wants, and interests of target markets and deliver the desired satisfaction more effectively and efficiently than competitors in a way that maintains or improves the consumer’s and society’s well-being. Societal marketing concept starts with the question about whether the marketing concept is adequate in an age of environmental problems, – Laws that increase restaurant liability for serving excessive alcoholic beverages to guests. – Disapproval of nutritional value of product sold in fast-food restaurants – Eco-tourism – Laws against resort development Marketing Ethics Ethics is essentially about the definition of what is right and wrong But what is write and what is wrong?-difficult to define Ethics is more or less affected by the culture of a particular region/country Whether marketers should give importance to ethics? Marketing Management “Marketing management is the analysis, planning, implementation, and control of programs designed to create, build, and maintain beneficial exchanges with target buyers for the purpose of achieving organizational objectives” - Philip Kotler Marketing Management Process 1.Analysis: 1. Where we are now? 2. How does the company’s market share compare with that of its competitors? 3. What are the strength & weaknesses of the company and its products? 4. What opportunities and threats does it face in its marketing environment? 2. Planning: A. Where we want to be? B. What is the mission of the business? C. What objectives should be set for the next year D. What strategy should be adopted to achieve the objective 3. Implementation: How we are going to put into effect the Strategy i.e tactics 4. Controlling. Marketing Management Philosophies Manufacturing (Production) Product Selling Marketing Societal Marketing Manufacturing Concept Consumers favor available and highly affordable products. Management should improve production and distribution systems. However, don’t forget the customer! Manufacturing oriented restaurant after dining hours. Customers are forced to cluster in one section of the restaurant, thus creating unnecessary density and customer dissatisfaction. this is usually done to facilitate cleaning or to enable to wait staff to provide service with a minimum of walking. Product Concept Consumers prefer existing products and product forms. Management’s job is to develop good versions of these products. Inward focused like the Manufacturing Concept, so don’t forget your customers! – Recent trend of seeking healthy food. – Victoria Station was a restaurant chain that specialized in excellent prime rib. They had an excellent product by maintaining the juices and avoiding shrinkage of the beef. Unfortunately, many customers no longer wanted red meat. They want chicken, seafood, and pasta. Selling Concept Consumers will not buy enough products unless the company undertakes large selling and promotion efforts. Aim is to maximize sales without worrying about customer satisfaction. Fails to establish a long-term relationship with customers because the sellers do not concern creating a product to meet the needs of the market – Restaurants often advertise when sales start to drop, without first analyzing why sales are dropping. They do not try to change their product to fit the changing market. They push their products on the customer through increased advertising and couponing. Eventually, they go out of business because their product no longer satisfies the needs of the marketplace. Market Concept Achieving organizational goals depends on determining the needs and wants of target markets and delivering desired satisfaction better than competitors Creates long term customer relationships Frequently confused with “Selling Concept”. – The selling concept takes an inside-out perspective. It starts with the company’s existing products and calls for heavy selling and promoting to achieve profitable sales. – The market concept starts with a well-defined market, focuses on customer needs, and integrates all the marketing activities that effect customers. It meets the organizational goals by creating long-term customer relationships based on customer value and satisfaction. Marketing and Sales Concepts Contrasted “We don’t have a Marketing department: we have a customer department.” – Herb Kelleher, CEO of Southwest Airline Marketing Management Vs. Sales Management • It is a modern concept • It is an old concept • Its objective is • Its objective is to customer satisfaction maximise sales &delight • It deals with the • It deals with the problems of customers problems of sellers Marketing Management Vs. Sales Management • Its Scope is wider - Discovering Needs - Obtaining Need - Customer Satisfaction & Delight - Repetition of Orders • It includes Sales Management • Its Scope is Narrow - Selling - Sales Promotion • It is a part of Marketing Management Marketing Manager’s Responsibilities and Functions To have constant touch with the market-business research To find out Marketing Opportunities To interpret the Market situations To develop and improve marketing plans, proceedures etc. To develop sales force To avail of resources to be utilised effectively To forecast effectively To keep adequate inventory to meet demand To give suggestions to develop product/services based on the customers’ needs To adopt sound pricing policy for competing market To adopt most suitable and profitable channels of distribution To adopt effective promotion methods To maintain good inter-relation with both within and outside the firm To develop the existing market To exploit the new market To facilitate growth and diversification To control the marketing costs To evaluate the performance of persons coming under him. MARKETING ENVIRONMENT Objectives Identify the major trends& changes in the firm’s internal & External environments. Identify Strength, weakness, opportunites, and threats Understand how companies can react to the marketing environment. Key Environments Marketing Environment – The actors and forces that affect a firm’s ability to build and maintain successful relationships with customers. – Aspects of the marketing environment: • Micro environment • Macro environment Micro-Environment 1. Customers some of the situations where customer’s long term interest have been neglected by companies In 2002 Consumers, association launched a campaign against financial services companies which it claimed had sold mis-sold endowment policies to individuals Car Manufacturers often add expensive music system to cars as standard, but safety equipment to the status of ‘optional extra’ 2. Competitors: Identifying the competitors A. Direct Competitor B. Indirect Competitor C. Good Competitor D. Bad Competitor 3. Intermediaries: The number of intermediaries vitality of intermediaries for e.g. food manufacturers who do no get shelf space in the major supermarkets may find it difficult to achieve large-volume of sales The type of intermediaries Their selection, motivation, reward and control. 4. Suppliers: The number of Suppliers as partners scope for backward integration Bargaining Power of Suppliers Availability in crisis time Quality, Delivery Time, cost etc. 5. Government: 1. Tax Laws 2. Social Responsibility like sick benefits, maternity benefits etc. 3. Various Laws for regulating the marketing Activities 4. Government Organisations 6. The facilitators: A. The Bargaining Power B. The Number of Facilitators in Each categorie C. The Terms and Conditions D. The influencing group of facilitators Local Communities: A. Creating image through Charitable Contributions, Sponsorship of Local Events, giving support for the local environment B. The impact of Negative Image 7. Pressure Groups: 1. Consumer Associations 2.Nature Clubs/Associations 3. Trade Unions 4. Employers Associations 5. Feminists etc. 8. Value Chain: It may be through adding further components, changing the form of a product, or adding ancillary services to product offer etc. Value Chain Analysis S U P P O R T Figure 3 A C T I V I T I E S Procurement Human Resource Management Technology Development Procurement Primary Activities A value chain for coffee • Value chain member • Grower • Merchant • Functions performed • Produces coffee beans • Adds value by checking,grading,et c. • Coffee Manufacturer • Whole Saler • Retailers • Processing the coffee beans, adding other ingredients, packaging etc . • Stores without any defectives • Convenient purchasing and providing adquate information to the customers Coffee shop-adds value by providing a ready made cup off coffee in pleasant surroundings. The Macro Environment Economic Environment a. Nature of Economic Systems-monopoly, mixed etc. b. Structural Anatomy c. Role of Govt. c. Factor Endowment d. Markets d. Market Competitiveness 2. Political & Legal Environment a. The stability of the political system b. The philosophy of the political parties c. The Legislation d. The Govt. Support 1. 3.Social & Cultural Environment 1. The leisure is becoming a bigger part of many people’s life 2. Attitude towards the work 3. The role of women in decision making 4. The role of children in decision making 5. Greater life expectancy 6. growing concern for environment 7. The cultural difference between areas 8. The beliefs and attitudes. 4.The Demographic Environment 5.The Natural/physical Environment Air Pollution 2. Noise Pollution 3. Water Pollution 4.Green-house effect 5. Shortage of Input: power, water,oiletc. 6. Cost of Input 6. Technological Environment The Marketing Environment Analysis 1. Marketing & Environment Interface- Nature Exchange of Information Exchange of Resources Exchange of Influence and Power Strategies to deal with Marketing Environment 1. Anticipating and Adapting 2. Smoothing or Levelling 3. Rationing 4. Contracting 5. Coalescing 6. Procurement of Key Personnel