Biomes-1
advertisement

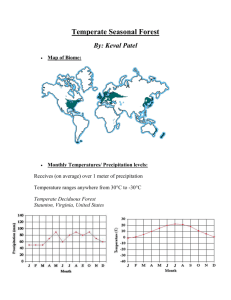
Biomes Introduction • A group of land ecosystems with similar climates and organisms is called a biome. • It is mostly climate conditions in an area that determine its biome. • We are going to talk about 7 land biomes and 3 aquatic biomes. Climatogram • graph 36 34 32 30 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 36 32 28 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -20 -24 -28 -32 -36 J F M A M J J A S O N D Months Pr e cipitation (C*) Te m pe r atur e (cm ) Tropical Deciduous • shows a biome’s monthly temperature and precipitation data in a single year Abiotic Factors Physical or NONLIVING component of an ecosystem Rocks, Sand, Cliffs Wind Snow, Rain, Hail Sun, Heat, Cold Biotic Factors • Living Parts of an ecosystem – Plants – Animals – Bacteria Rain Forest Biomes • Known for their abundance of – Rain – Plant life – Animal life • The climate (warm with plenty of rain) provides a great environment for plants. • The more plants there are the more animals that can be supported. Tropical Rain Forest • Typically found near the equator • The temperature range is between 20 and 25 degrees Celsius. ( 68- 77 degrees Fahrenheit) • Receive an average of 200 - 1,000 cm of precipitation each year Tropical Rain Forest • The abundant plant life provides habitats for many species of animals. – Millions of species of animals live here – Insects are a major food source – Probably contain more species of plants and animals than all the other biomes combined. Tropical Rain Forest • The tall tress in a tropical rainforest form a leafy roof called the canopy. • Under the canopy is a second layer of shorter trees and vines that form an understory. • The forest floor is nearly dark so only a few plants live there. Campa Pita, Belize Precipitation Campa Pita, Belize Temperature Temperate Rain Forest • Found along the northwestern coast of the United States and New Zealand. • Twilight was set in a Temperate Rain Forest. • Has more moderate temperatures that change throughout the year. • Between 200-350 cm of precipitation. • Further from the equator than tropical rain forests. Desert • Typically found between 25o and 40o latitude • Deserts are characterized by very dry climates. • They have a wide yearly temperature range. From -4 – 38 degrees Celsius. (24-100 F) • Receive less than 25 cm of rain each year. – The amount of evaporation is greater than the amount of precipitation Desert • Organisms must adapt to the lack of rain and extreme temperatures. – Stem of the saguaro cactus stores water – Gila monsters can spend weeks at a time in their cool underground burrows – Many other animals are most active at night El-Oasr el-Akhdar, Egypt Precip El-Oasr el-Akhdar, Egypt Temp Grassland Grasslands also known as prairie, pampas, steppes, and veldt, are areas that receive more rain than the desert but not enough to support trees. – Found on the interiors of continents between 30 and 50 degrees north and south latitude – Average temperatures are between -20 and 30 degrees Celsius (-4 and 86 F) – Receive 50-90 cm of rain each year – They have very rich soil – Home to many of the largest animals on Earth. Grasslands Grasslands Savannah • Grasslands that are closer to the equator • Warm temperatures with wet and dry seasons • Temperatures range between -16 and 34 degrees Celsius (3-94 degrees F) • Average precipitation is between 50-130 cm • Since there is more precipitation some trees can be found here Savannah Savannah Ingeniera White, Argentina Temp Ingeniera White, Argentina Precip Temperate Deciduous Forest • Where We Live! • Named for Deciduous trees that are found there – Trees that shed their leaves and grow new ones each year • Located between 30 and 50 degrees N and S Lat • Temperatures range from -30 – 30 degrees Celsius (-22 – 86 degrees F) • Average precipitation is between 75-150 cm Staunton, Virginia Temperature Staunton, Virginia Precipitation Temperate Deciduous Forest Boreal/Taiga or Coniferous Forest • Known for its Coniferous trees – Fir, Spruce, and Hemlock • Further north than Deciduous Biome • Between 50 and 60 degrees latitude • Very cold winters—average temp between -40 and 20 degrees Celsius (-40 and 68 F) • Average precipitation between 30-90 cm Boreal Forest / Taiga Beaverlodge, Alberta, Canada Beaverlodge, Alberta, Canada Tundra • Extremely cold and dry biome • Located between 55-70 degrees lat • Average temperature range between -40 and 18 degrees Celsius (-40 and 64 F) • Average precipitation less than 25 cm • Very few plants – Mosses – Dwarf trees • Layer of permanently frozen soil—Permafrost Tundra Yakutsk, Russia Precipitation Yakutsk, Russia Temperature Mountain and Ice • Not a true biome • As you move from the bottom to the top, you would pass through a series of biomes. • Animals with adaptations to ice – Penguins, polar bears, and seals Mountain Biome Freshwater Ecosystem • Types of freshwater ecosystems – Streams – Rivers – Ponds – Lakes • Bodies of water with high oxygen levels and less than 1% salt • Streams and Rivers have running water • Ponds and Lakes have standing water Freshwater Ecosystem • Plants include – Algae – Cattails – Swamp frond – Lilly pads – Grasses Freshwater Ecosystem • Animal Life – – – – Flagellates Diatoms Leeches River rats, Muskrats, Otters and Minks – – – – Sunfish and Bass Salmon and Perch Catfish species Turtle speices Marine Ecosystem • Ecosystems that exist in salt water. • This includes the oceans, seas, and estuaries • Oceans are divided into 4 different zones Marine Ecosystems • Intertidal zone—between the highest and lowest tide • Neritic zone—below the low-tide line and out over the continental shelf • Surface zone—on the surface of the open ocean • Deep zone—below the surface of the open ocean Intertidal Zone • Difficult to live here – pounding waves – sudden changes in temperature – covered with water and then exposed to air Neritic Zone • Rich with life • Many large schools of fish feed there • Coral reefs may form here • Where did Nemo live? Deep Zone • Throughout much of the deep zone it is completely dark • Some animals in the deep zone glow in the dark – Some use for camouflage or identification and attraction – Anglerfish: uses its glow as a lure Food Webs in the Ocean • Algae form the basis of almost all openocean food webs • Phytoplankton are also producers Estuary • A type of Marine ecosystem • Where fresh river water and salty ocean water meet • Algae and plants such as marsh grasses provide food and shelter for numerous animals. – Crabs, worms, clams, and fish • Many animals use the calm waters of estuaries for breeding grounds Temp Precipita Plant Life tion Animal Life Tropica near the l equator Rainfor Between the est 20-25° C 68-77° F 200 1,000 cm Bamboo Coconut trees Strangler fig Tualang tree Kapok tree Tiger, Bats Chimps, Sloth, Eagles, Monkeys, Toucan, many insects Rainfor Northwestern est US moderate temps Change throughout the year 200350cm Moss Ferns Redwoods Cedar Trees Wolves Bear, Raccoon Insects Birds, Deer Less than 25 cm a year Cactus Brittle Bush Creosote Bush Joshua Tree Soaptree Yucca Gila Monster Cactus Wren Coyote Kangaroo Rat Desert Tortoise Location Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn New Zealand Desert Between 25 -4 – 38°C and 40° N and S latitude 24-100° F Rain shadow of mountains Grassland Savannah Precipitat Plant Life ion Location Temp interiors of continents 30 and 45° north and south latitude -20 - 30° 50-90 C cm Closer to equator -16 – 34 C -30 – 30°C Temperate Where we Deciduous live! Forest Between 30 and 45° north and south latitude Grasses Milkweed Purple Coneflower Stinging Nettle Bald Eagle Badger Bobcat Bumble Bee Coyote Prairie Dog Swift Fox 50-130 cm Grasses and trees Lions, elephant, baboon, antelope zebra 75-150 cm Deciduous trees—oak, beech, birch, maple, walnut, ferns, moss Raccoons, Deer, squirrels, opossum, black bear -4 - 86°F -22-86° F Animal Life Taiga / Boreal Forest Precipitat Plant Life ion Location Temp Between 45 and 60° North -40 - 20° 30-90 C cm latitude -40 68°F Tundra 55° to 70° North latitude -40 – 18°C Permafrost -40 – 64° F Less than 25 cm Coniferous trees •Fir •Spruce •Hemlock •Pine •Spruce Animal Life Bobcat Canadian Lynx Gray Wolf Grizzly Bear Owl Red Fox River Otter Snowshoe Rabbit Wolverine No trees, Arctic Fox small bushes, Caribou moss Grizzly Bear Musk Ox Polar Bear Snowy Owl Fresh water Types/Location Characteristics Plant Life Animal Life Lakes Ponds have standing water Bodies of water with high oxygen levels and less than 1% salt Algae Cattails Swamp frond Lilly pads Grasses Leeches River rats, Muskrats, Otters and Mink Fish turtles Ecosystems that exist in salt water Sea grasses algae Phytoplankto n Plankton Fish sharks Rivers Streams have running water Marine oceans, seas, and estuaries Estuary Deltas Along coastlines Where fresh Algae river water and Marsh salty ocean grass water meet Crabs, worms, clams, and fish