Biomes of Planet Earth
advertisement

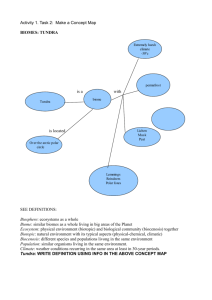
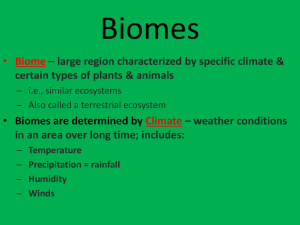
Biomes of Planet Earth • An ecosystem is all the living and nonliving factors that affect an organism. (abiotic and biotic) • A biome is a major region that is characterized by its climate,soil type(s), and the dominant plants, animals, and other organisms that live there. A biome is made up of many individual ecosystems. Ecotone • Boundary between two biomes Alike but Different The species that live In each biome are different, but may look and act similar to species in other biomes. Because of similar niches in each biome. Kaibab Squirrel (north rim) Abert’s Squirrel (south rim) Climate • Climate defines the boundaries of terrestrial biomes Types of Biomes • • • • • • • • • Tundra Desert Grassland Taiga Temperate forest Tropical rainforest Polar ice Freshwater Marine • • • • • • • • • • Is the temperature of each Biome: Hot, moderate, or cold? Mountains Tundra Desert Chaparral Temperate Grassland Tropical savanna Taiga Temperate forest Tropical rainforest Polar ice - Is the temperature of each Biome: Hot, moderate, or cold? • • • • • • • • • • Mountains - Moderate Tundra - Cold Desert - Hot Chaparral - Moderate Temperate Grassland - Moderate Tropical savanna - Hot Taiga - Cold Temperate forest - Moderate Tropical rainforest - Hot Polar ice - Cold Latitude and Altitude Affect the Climate • Gets colder the higher up you go (altitude) • Gets colder the farther north/south of the equator you go (latitude) • Most of food on Earth is grown between 3060 degrees north and south of the equator • -- Do we live in this latitude??-- Climatograms • A climatogram is a graph that shows average monthly values for two factors: temperature and precipitation. • Temperature is expressed in degrees Celsius and is plotted as a smooth curve. • Precipitation values are given in centimeters and are plotted as a histogram. Population • All members of a species living in the same place at the same time. • Populations are described in terms of size, density (# of individuals/unit area or vol), or dispersion (relative distribution of its individuals within a given amount of space). Growth Rate • Change in population size = births deaths Also calculated as: change in population time What Limits Population Growth? • Carrying Capacity • Resource Limits—consuming a natural resource at the same rate as which the ecosystem produces the resource • Competition within a population—social dominance, territory, mates, food, homes for their families Population Growth Carrying Capacity Steady State Exponential Phase Lag Phase Two Types--Population Regulation • Density Dependent—cause of death is rapidly increased due to limited resources, predation and disease resulting in densely populated groups. • Density Independent—a certain proportion of the population dies regardless of its density (weather, natural disasters) Niche (pattern of use of its habitat) • Includes: • a species’ physical home • the environment factors necessary for the species to survive • All of the species’ interactions with other organisms. Types of Interactions • Competition—organisms attempt to use the same limited resource. • Predation—organism that feeds on another • Parasitism—organism that lives in or on another • Mutualism—two species provides a benefit to the other • Commensalism—one species benefits but other is not harmed or helped by it Relationships • Symbiosis—two organisms live in close association If carried on long enough the two species can co-evolve—flowers matching the feeding habits of insects and birds. Desert Ecosystems Location: Depending on type of desert, you will find them in various locations. Desert Abiotic factors <10 in/yr of rain Little to no topsoil due to high winds. Minerals not deep in soil. Too dry for decay http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/msese/earthsysflr/ taiga.html While there are many types of deserts, they all share one characteristic: They are the driest places on Earth! Barrel Cactus Desert Plant Adaptations: Spines Succulents Thick, waxy cuticle Shallow, broad roots Joshua Tree http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/desert_plant_page.htm Ocotollio Bob Cat Desert Animal Adaptations: Armadillo Lizard Get water from food Thick outer coat Burrow during day Large ears Smaller animals = less surface area http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/desert_animal_page.htm Javelina http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/world_biomes.htm Threats to the Desert Residential development Off road recreational activities destroy habitat for plants and animals. Some plants are removed by collectors, endangering the population. Sonoran Desert Dry Desert Tundra Location: Found north of the Arctic Circle http://www.runet.edu/~swoodwar/CLASSES/GEOG235/biomes/tundra/tundra.html Tundra Abiotic Factors <25 in/year Temp rarely higher than 100C Permafrost layer Short growing season http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/msese/earthsysflr/taiga.html Reindeer lichen Tundra Plant Adaptations Growing close to the ground Having shallow roots to absorb the limited water resources. Trees grow less than 1 m high! cottongrass Perennials Woody shrubs Heaths Examples of Tundra Plants http://www.runet.edu/~swoodwar/CLASSES/GEOG235/biomes/tundra/tundra.html snowy owl Arctic fox Small ears Insulation, thick coat Tundra Animal Adaptations Many visitors, migration Few predators Grizzly Bear Little Competition Threats to the Tundra One of the most fragile biomes on the planet Tufted Saxifrage Oil drilling is proposed in Alaska and other areas! Polar Bear The tundra is slow to recover from damage.