4_More Genetics_Dihybrid_Laws
advertisement

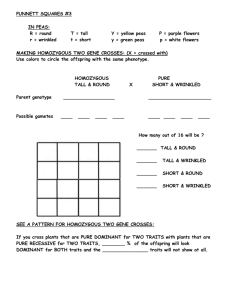
Welcome Back!!! Today you will need: - Your journal - The handout as you come in (QUIZ) Genetics…continued… Law of Segregation Law of Independent Assortment Dihybrid Crosses Karyotyping DNA Fingerprinting The Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment Law of Segregation • During the formation of gametes (eggs or sperm), the two alleles responsible for a trait separate from each other. • Alleles for a trait are then "recombined" at fertilization, producing the genotype for the traits of the offspring. 8 Applying the Law of Segregation 9 Law of Independent Assortment • Alleles for different traits are distributed to sex cells (& offspring) independently of one another. • This law can be illustrated using dihybrid crosses. 10 Dihybrid Cross • Traits: Seed shape & Seed color • Alleles: R round r wrinkled G green g yellow • RrGg RG Rg rG rg x F O I L RrGg RG Rg rG rg All possible gamete combinations 12 Dihybrid Cross RG Rg rG rg RG Rg rG rg 13 Dihybrid Cross RG Rg rG rg RG Rg rG rg RRGG RRGg RrGG RrGg RRGg RrGG RrGg RRgg RrGg Rrgg RrGg rrGG rrGg Rrgg rrGg rrgg Round/Green: 9 Round/yellow: 3 wrinkled/Green: 3 wrinkled/yellow: 1 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio 14 Let’s do it another way… • Rule of Multiplication: – Independent events in sequence (law of Independent Assortment) • “and”…(x) • What are the odds of flipping a coin 3 times and getting tails all 3 times? – They are ALL independent of one another…just as traits. • What are the odds that an offspring will be Heterozygous for two traits if the parents are both heterozygous for the same two traits? • Parents: AaBb x AaBb • What are the odds that an offspring will be Heterozygous for both traits if the parents genotypes are: AABb x AaBB • What are the odds that an offspring will be Heterozygous for 3 traits if the parents genotypes are: AabbCC x AABbcc Test Cross • A mating between an individual of unknown genotype and a homozygous recessive individual. • Example: bbC__ x bbcc • • • • • • BB = brown eyes Bb = brown eyes bb = blue eyes CC = curly hair Cc = curly hair cc = straight hair bC b___ bc 21 Test Cross • Possible results: bc bC b___ C bbCc bbCc or bc bC b___ c bbCc bbcc 22 Summary of Mendel’s laws LAW DOMINANCE SEGREGATION INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT PARENT CROSS OFFSPRING TT x tt tall x short 100% Tt tall Tt x Tt tall x tall 75% tall 25% short RrGg x RrGg round & green x round & green 9/16 pods 3/16 pods 3/16 pods 1/16 pods round seeds & green round seeds & yellow wrinkled seeds & green wrinkled seeds & yellow 23 Genetic fingerprinting 13 DNA analysis can be used for catching criminals, establishing parentage, finding how closely organisms are related and many other applications. The pattern of bands in a gel electrophoresis is known as a genetic fingerprint or a ‘genetic profile’ The genetic fingerprint found in a sample of blood or other tissue (containing DNA) is then compared to other known samples to determine it’s origin…based on how similar the banding patterns are to each other. A DNA sample can be obtained from the suspect using blood, cheek epithelial cells taken from the mouth lining or even the cells clinging to the root of a hair…as long as the tissue contains DNA Genetic fingerprinting DNA profiles V S S1 S2 S3 V Victim S Sample from crime scene S1 Suspect 1 S2 Suspect 2 S3 Suspect 3 More than 20 fragments from Suspect 1 match those taken from the crime scene 16 20 Genetic fingerprint of … 1 mother 2 child 3 possible father A 4 possible father B There is a match between one of the child’s restriction fragments and one of the mother’s. There is also a match between the child’s other fragment and one from possible father A. 1 2 3 4 Starting position of sample Neither of the child’s restriction fragments match those of possible father B Paternity test Karyotype Picture of chromosomes arranged in pairs 1.sex chromosomes – pair #23 that determine the sex of an individual (XX or XY) 2.autosomes (autosomal chromosomes) – the remaining 22 pairs of chromosomes