Unit 2 Mathematical Vector Addition
advertisement

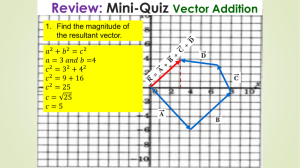
Mathematical Vector Addition Mathematical Addition of Vectors The process of adding vectors can be accurately done using basic trigonometry. If you follow each step carefully, you will break down each vector into it's x and y componets and determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector. We have provided you with a "Vector Worksheet" to help you organize your work. Let's say that we are adding three vectors A, B, and C. STEP #1 - Deconstruct each vector into it's X & Y components. A) To do this, you must first find the Theta angle to the x axis for each vector. 00 30 Km/hr @ 450 60 Km/hr @ 3150 900 2700 60 Km/hr @ 1350 1800 B. Now calculate the X & Y components of each vector treating the magnitude of each vector as the hypotenuse of a right triangle 00 X component = Magnitude x cos -x = (60)(cos45) = -42.4 +y 2700 900 -x y component = Magnitude x sin y = (60)(sin45) = +42.4 1800 60 Km/hr @ 3150 60 Km/hr @ 1350 30 Km/hr @ 450 = 45o = 45o = 450 -42.4 00 +y 2700 90 -x 0 +42.4 1800 B. Now calculate the X & Y components of each vector treating the magnitude of each vector as the hypotenuse of a right triangle 00 X component = Magnitude x cos -x = (60)(cos45) = -42.4 +x = (30)(cos45) = +21.2 +y +y 2700 +x -x 900 y component = Magnitude x sin y = (60)(sin45) = +42.4 +y = (30)(sin45) = +21.2 1800 60 Km/hr @ 3150 60 Km/hr @ 1350 30 Km/hr @ 450 = 45o = 45o = 450 00 + 21.2 +x = (30)(cos45) +y = +21.2 +y 2700 +x -x 900 +42.4 +21.2 1800 -42.4 B. Now calculate the X & Y components of each vector treating the magnitude of each vector as the hypotenuse of a right triangle 00 X component = Magnitude x cos -x = (60)(cos45) = -42.4 +x = (30)(cos45) = +21.2 +x = (60)(cos45) = +42.4 +y +y 270 +x 0 900 +x -x y component = Magnitude x sin -Y y = (60)(sin45) = +42.4 +y = (30)(sin45) = +21.2 -Y = (60)(sin45) = -42.4 1800 60 Km/hr @ 3150 60 Km/hr @ 1350 30 Km/hr @ 450 = 45o = 45o = 450 STEP #2 - List and add all x components and y components. Including all signs. These sums are the components of the resultant vector. 00 + 21.2 +42.4 +63.6 -42.4 -42.4 +x = (30)(cos45)+y= +21.2 +y 2700 +x +21.2 900 +x -x -Y +42.4 +21.2 -42.4 0 180 +63.6 -42.4 +21.2 STEP #3 - Convert the resultant components into navigational vector notation. To do this, first use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine the hypotenuse 00 + 21.2 +42.4 +63.6 -42.4 -42.4 +21.2 +x = (30)(cos45) = +21.2 +y +y 2700 +x -x +21.2 900 +x +21.2 -Y +42.4 +21.2 -42.4 0 180 +63.6 -42.4 +21.2 Resultant = √21.2 +21.2 2 2 The magnitude of the resultant is 29.9 Km/hr. Now, find the Theta θ of the resultant using the inverse tangent formula. tan-1= l y/x l = θR 00 + 21.2 +42.4 +63.6 -42.4 -42.4 +x = (30)(cos45) = +21.2 +y +y 2700 +x +21.2 900 +x -x -Y +42.4 +21.2 -42.4 0 180 +63.6 -42.4 +21.2 Since the θR = 45 , the navigational direction o of the resultant vector is NAV = 90 - θR = 45 . o 00 + 21.2 +42.4 +63.6 NAVR = 45o -42.4 -42.4 θR=45o +y = (30)(cos45) = +21.2 +x +y +x 270 +x -x +21.2 900 0 -Y +42.4 +21.2 180 -42.4 0 +63.6 -42.4 29.9 Km/hr +21.2 45o Use this guide to get the navigational angle in other quadrants. Quadrant #1: NAV = 90 - θR Quadrant #2: NAV = 270 + θR Quadrant #3: NAV = 270 - θR Quadrant #4: NAV = 90 + θR Congratulations! You have successfully calculated a vector addition! The resultant vector = 29.9 Km/hr @ 45 o