Name of Religion____native spirituality__________ Era Most
advertisement
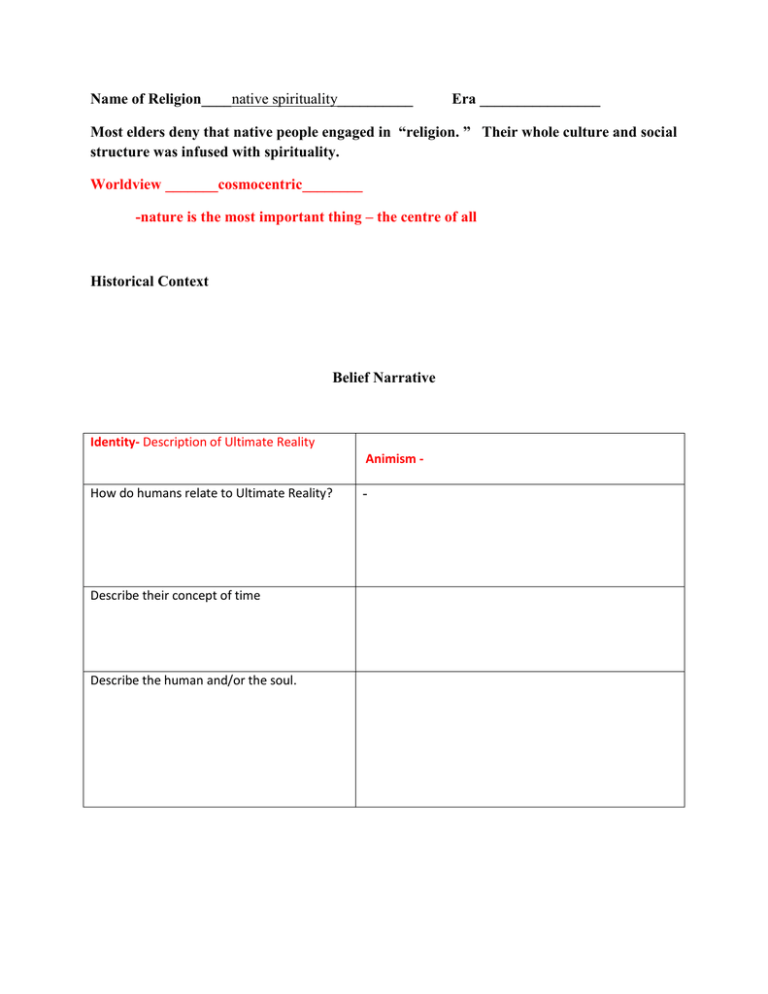
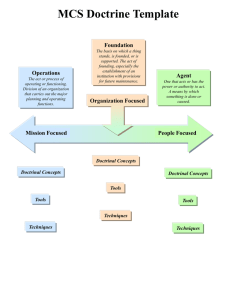
Name of Religion____native spirituality__________ Era ________________ Most elders deny that native people engaged in “religion. ” Their whole culture and social structure was infused with spirituality. Worldview _______cosmocentric________ -nature is the most important thing – the centre of all Historical Context Belief Narrative Identity- Description of Ultimate Reality Animism How do humans relate to Ultimate Reality? Describe their concept of time Describe the human and/or the soul. - Hope What do they hope for in this life? Hope What do they hope for in the afterlife? Conflict What makes it difficult to achieve that which they hope for? Resolution How should one live their life in order to achieve what they hope for? Much of this will be covered in the Seven Dimensions, but summarize the main idea. Seven Dimensions of Religion 1. Practical and p. 78 – sacredness of every action, types of prayer, Ritual p. 79 - smudging 2. Experiential and Emotional 3. Narrative pg. 80 sweat lodge, 81- vision quest No texts /Mythological Pg 79 – oral tradition 87 – trickster 4. Doctrinal and pg. 88 – oral teachings, shaman, medicine wheel Philosophical 5. Ethical 6. Institutional p. 89 none 7. Material Pg 71 – petroforms and petroglyphs p. 76 – eagle feather p. 89 – drums p. 89 - circle Seven Dimensions of Religion Ninian Smart proposed that all religions include the following elements. 1. Practical and Ritual Worship, Praying, Regular Gatherings, Rites of Passage 2. Experiential and Emotional People react when they have encountered something which they believe is very profound. Includes religious experiences such as visions, revelations, enlightenment, and general religious ecstasy. The acute and earth-shaking, as well as the gentler, more mundane religious feelings. 3. Narrative / Mythical Stories which explain and inspire. Includes written as well as oral tales, formal as well as informal teachings, alternative histories, predictions, etc 4. Doctrinal and Philosophical This is the official, formal teachings which underpin the narrative/mythic parts of a religion. Provides rational for many of the practices and ideas of the religion. Doctrine doesn't necessarily predate the narrative. In Christianity, for instance, it was the existence of a cult following the life of Jesus, and their stories and rituals, which led to the formation of the Christian doctrine. Note that very few doctrines are actually unchanging over time, though their authors usually like them to appear so. 5. Ethical The ideas and laws that shape behavior. Ex: Laws of Manu, 5 Precepts, Ten Commandments, Beatitudes 6. Institutional Social outgrowth of religious experience. Ex: Church, Synagogue, Sangha 7. Material - An outgrowth of religious experience/encounter. a) Music b) Art c) Symbol d) Architecture