The Components of the System Unit
advertisement
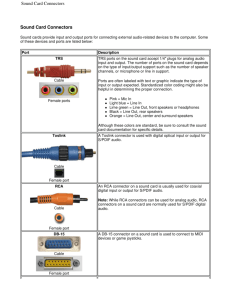
Created By: N.AlJaffan Modified By:S.Abudawood & Tr.Asma Aleisa System Unit is a case that contains electronic components of the computer used to process data. Made of metal or plastic to protects the internal components from damage. All computers have a system unit. It is available in variety of shapes & sizes. The Components of the system unit System unit System unit System unit System unit System unit Handheld controller The Components of the system unit 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Processor interprets & carries out the basic instructions that operate a computer. Memory holds data waiting to be processed & instruction waiting to be executed. Processor & Memory are connected to a circuit board called the motherboard. Adapter cards (expansion slots): are circuit boards that provide connections and functions not built into the motherboard. Devices outside the system unit often attach to the ports. A drive bay holds one or more disk drive. The Power supply provide the computer with the electricity. Motherboard called system board. It is a main circuit board of the system unit. Many electronic components attach to the motherboard, others are built into it. Ex: adapter cards, a processor chip and a memory module. http://www.howstuffworks.com/microprocessor.htm Processor called the central processing unit (CPU), Microprocessor. Its contain a control unit & an arithmetic logic unit (ALU). These 2 components work together to perform processing operations. CPU Control Unit Arithmetic/ Logic Unit (ALU) Processor Control Unit ALU Instructions Data Information INPUT DEVICES Data MEMORY Instructions Data Information Storage Devices information OUTPUT DEVICES The operations typically performed by a CPU are 1. CPUs control the reading of programs and input files. 2. CPUs process data according to instructions in a program. 3. CPUs control the creation of output. The Components of the system unit The Arithmetic Logic Unit performs arithmetic, comparison and other operations. The Control Unit Handles the transmission of data into and out of the CPU and supervises its overall operations. Registers The CPU contain special storage areas called registers. Their function is to hold instructions, data values, memory addresses of both the instructions and data. There are 4 basic types of it: 1. Instruction register hold instruction 2. Address register hold address of( data , next instruction ). 3. Storage register store data retrieved from main memory prior to processing. 4. Accumulator store the results of arithmetic & logic operations The System Clock Every CPU has a clock, It’s a small quartz crystal circuit , which generates regular clock pulses that control the timing of all computer operations. Processing actions occur at each “tick” of the electronic clock. The Speed of the clock determines the speed at which the CPU can process data. Speed is measured in megahertz (MHz) or (GHz). Comparison of Personal computer Processors The leading processor chip manufacturers for personal computers are Intel (used in PCs) AMD ( advanced Micro Devices) (used in PCs) Motorola ( used in Apple) Alpha (used in workstations and high-end servers) How the CPU represents data Binary system based on two digits 0 and 1. 0 : off 1 : on Bit is a the smallest unit of data the computer can process. Byte a group of 8 bits. A byte can be represent characters. Characters can be a letter, digit, or symbol. 8-bit byte for the number 3 Binary Digit (bit) Electronic Charge Electronic State How the CPU represents data The different combinations of 0s and 1s are defined by patterns called a coding schema. There are tow popular coding scheme: 1. ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. 2. EBCDIC stand for Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code. Data Representation 8-bit byte for the number 3 8-bit byte for the number 5 8-bit byte for the capital letter T Memory Memory consist of electronic components that store instructions waiting to be executed by the processor, data needed by those instructions, and the results of processed data ( information). Memory usually consist of one or more chips on the motherboard. Memory Stores 3 basic categories of items: 1. The operations 2. Application programs 3. The data being processed by the application programs and resulting information. Memory sizes It’s the number of bytes the chip or devices has available for storage. Term Abb. Approximate no. of byte Exact no. of byte Kilobyte KB or K 1000 1,024 Megabyte MB 1Million 1,048,576 Gigabyte GB 1Billion 1,073,741, 824 Terabyte TB 1 Trillion 1,099,511,627,776 Type of Memory The system unit contains tow types of memory: 1. Volatile memory - Loses its contents . Temporary memory. Example, RAM. 2. Nonvolatile memory- doesn't lose its content when power is removed form the computer. Permanent memory. Example, ROM, Flash memory, and CMOS. RAM ( Random Access Memory ), Also Called main memory. consists of memory chips that can be read from and written to by the processor and other devices. The content my changed. Saving is a process of copying items from RAM to a storage device such as a hard disk. Memory RAM ( Random Access Memory ) RAM chips usually reside on a memory module, which is a small circuit board. Memory slots on the motherboard hold memory modules. ROM ( Read Only Memory) The data on most ROM chips cannot be modified. Manufacture of ROM chips often record data, instructions, or information on the chip when they manufacture the chip. Computers almost always contain a small amount of read-only memory that holds instructions for starting up the computer. Types of ROM PROM (programmable read-only memory): A PROM is a memory chip on which you can store a program. But once the PROM has been used, you cannot wipe it clean and use it to store something else. Like ROMs, PROMs are non-volatile. EPROM (erasable programmable read-only memory): An EPROM is a special type of PROM that can be erased by exposing it to ultraviolet light. EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory): An EEPROM is a special type of PROM that can be erased by exposing it to an electrical charge. Memory Access Time It is the amount of time takes the processor to read data, instructions, information from memory. It’s affects how fast the computer process data. Access time on memory can be more than 200,000 times faster than accessing data on a hard disk because the mechanical motion of it. Memory Memory Access Time Term Abb. Speed Millisecond ms One-thousandth of a second Microsecond μs One-millionth of a second Nanosecond ns One-billion of a second Picosecond ps One-trillionth of a second Expansion Slot and Adapter Cards Expansion slot is a socket on the motherboard that can hold an adapter card Adapter card sometimes called an expansion card is a circuit board that enhances functions of a component of the system unit and/or provides connections to peripherals. Peripheral is a device that connects to a system unit and is controlled by the processor. Ex: keyboard, printer. Expansion Slot and Adapter Cards Types of adapter cards Adapter Card Purpose Graphics accelerator Increases the speed at which graphics are displayed Modem Connect other computers through telephone or cable TV line Network Connects other computers and peripherals Sound Connects speakers or microphone Video Connects a monitor Ports and Connectors Port is the point at which a peripheral attaches to or communicates with a system unit so the peripheral can send data to or receive information from the computer. the term jack sometimes is used to identify audio and video ports. Port have a different types of connectors, A connectors joins a cable to a peripheral. Ports and Connectors Serial Ports is a type of interface that connects a device to the system unit by transmitting data one bit at a time. Ports and Connectors Parallel Ports is an interface that connects a device by transferring more than one bit at a time. The printers using a parallel port. Ports and Connectors USB Ports, Short for universal serial bus port. Can connect up to 127 different peripherals together with a single connector. USB hub is a device that plugs in a USB port on the system & contains multiple USB ports. Ports and Connectors FireWire Ports Previously called an IEEE 1394 port. It is similar to a USB port in that it can connect multiple type of device that require faster data transmission speeds to a single connector, such as digital video camera, color printers, scanners, .. etc. Allow you to connect up to 63 devices together. You can use a FireWire hub to attach multiple devices to a single FireWire port. USB and FireWire are replacing all other types of port. Ports and Connectors Special-Purpose Ports These ports are not included in typical computers. MIDI Port SCSI Port IrDA Port Bluetooth Port Ports and Connectors MIDI Port, short for musical instrument digital interface. Serial port Connect the system unit to keyboard. SCSI Port A special high-speed parallel port. Allow you to attach SCSI peripherals such as disk driver and printers. Ports and Connectors Ports and Connectors BUSES a set of electronic signal pathways that allows information and signals to travel between components inside or outside of a computer. Buses transfer bits from input devices to memory. from the processor to memory, and from memory to the processor. from memory to output devices. Power Supply Power Supply Is a component of the system unit that supply computer with power.