Speed, Velocity, Acceleration
advertisement

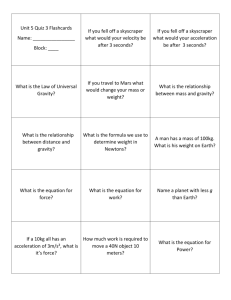
Free Fall Physics Date: Engagement Why is easy to step off a curb, but very scary (and dangerous) to step off the top of building? Objectives • Describe the motion of an object in free fall and how it is different from motion we have previously studied • Describe the motion of an object thrown straight up and allowed to fall until it hits the ground • Evaluate how speed and the distance play a part in a falling object at any time after an object is dropped from rest, when air resistance is negligible Intro to Free Fall Questions What is free fall? Facts What is an example of something in free fall? Dropping something (not throwing it down) Throwing something up and allowing it to fall back down When the only thing affecting an object is gravity (there is no air resistance) A little background on gravity A free-falling object is an object that is falling under the sole influence of gravity. Gravity can be measured as an acceleration which is the result of the central attractive force that matter exerts on other matter. This is because all accelerations are the result of force (we will learn more about this). All objects exert gravity on each other; however, the gravity we experience is the gravity of the Earth. Gravity is constant on Earth; therefore, the acceleration is constant (does not change) when an object is in free fall even though the velocity is changing! Gravity Questions What is gravity What might be the units for gravity? Why? What is the value for gravity? Facts • Force pulls to center of Earth which produces he acceleration that an object has when in free fall m/s2 Because gravity is measured as an acceleration Actual = 9.8m/s2 For class = 10 m/s2 More about gravity Questions Facts What type of motion - Linear, horizontal have we studied so motion far? (v=d/t) (a=v/t) What type of motion - Linear, vertical motion do we witness with free fall? How Does Gravity Work? What is happening to the velocity? Why? As the ball falls the velocity is increasing because gravity has more time to act. At each point, gravity remains 10 m/s2 t=0s v = 0 m/s t=1s v = -10 m/s t=2s v = -20 m/s t=3s v = -30 m/s t=4s v = -40 m/s t=5s v = -50 m/s How Does Gravity Work? Now you try to complete the figure! Explain the figure!!! t = _______ v = _______ t = _______ v = _______ t = _______ v = _______ t = _______ v = _______ t = _______ v = _______ t = _______ v = _______ How does gravity work? Consider what happens when an object is thrown straight up and falls back down. How Does Gravity Work? Facts Question Moving up- the velocity is Explain what decreasing because the happens when an object is moving object is thrown against gravity. straight up and Falling Down- the object allowed to fall gains speed at the back down. same rate it was slowed down because gravity is constant? How gravity works? Question What will happen if you drop 2 different objects at the same time from the same height? Why? Facts] They will hit the ground at the same time because… Gravity is constant and is not dependent on the mass or weight of an object. Check for Understanding • If you drop a feather and a coin at the same time in a vacuum tube with no air resistance, which will reach the bottom of the tube first? Neither, they will both hit the ground at the same time! What affects free fall? Question Facts The higher (more How does distance distance) an object play a part in a falls, the more time falling object at gravity has to act; any time after an therefore, the faster object is dropped the object will hit the from rest? ground. Let’s go back to the engagement Questions Why is easy to step off a curb, but very scary (and dangerous) to step off the top of a building? Facts A curb is only a small distance from the ground; therefore, gravity acts only for a small time and velocity is not greatly gained. From a building, the distance is greater, giving gravity more time to act, which results in a greater velocity when hitting the ground- Ouch! Check for understanding A freely falling object starts from rest. After falling for 1 second, it will have a speed of about a. 5 m/s. b. 10 m/s. c. 20 m/s. d. 40 m/s. Check for Understanding A ball is thrown upwards and caught when it comes back down. In the absence of air resistance, the speed of the ball when caught would be a. less than the speed it had when thrown upwards. b. more than the speed it had when thrown upwards. c. the same as the speed it had when thrown upwards. Check for Understanding When a basketball player jumps to make a shot, once the feet are off the floor, the jumper's acceleration a. varies with body orientation. b. is usually greater for taller players (but not always). c. depends on all the above. d. is g; no more, no less. Remember, Gravity is constant on Earth; therefore, the acceleration is constant (does not change) when an object is in free fall even though the velocity is changing! Check for Understanding A ball is thrown straight up. At the top of its path its instantaneous speed is a. 0 m/s. b. about 5 m/s. c. about 10 m/s. d. about 20 m/s. Homework Review Free Fall Notes and Reading! Memorize units!!!!