1 Server process
advertisement

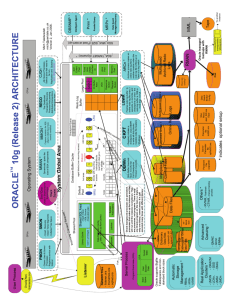
1 Oracle Architectural Components Objectives • Listing the structures involved in connecting a user to an Oracle server • Listing the stages in processing a query • Listing the stages in processing a DML statement • Listing the stages in processing COMMITS 1-2 The Oracle Server Oracle server Server 1-3 Application/ network server Users Connecting to a Database Client User process User 1-4 Server process Server Oracle server User Process • Runs on the client machine • Is spawned when a tool or an application is invoked • Runs the tool or application (SQL*Plus, Server Manager, Oracle Enterprise Manager, Developer/2000) • Includes the User Program Interface (UPI) • Generates calls to the Oracle server 1-5 Server Process • Runs on the server machine (host) • Services a single user process in the dedicated server configuration • Uses an exclusive PGA • Includes the Oracle Program Interface (OPI) • Processes calls generated by the client • Returns results to the client 1-6 Oracle Instance Instance SGA Background processes An Oracle instance: • Is a means to access an Oracle database • Always opens one and only one database 1-7 Oracle Database Control files Parameter file Password file Data files Database 1-8 Redo log files Archived log files Other Key Physical Structures Parameter file Password file 1-9 Database Archived log files Processing a Query • Parse: - Search for identical statement -Check syntax, object names, privileges - Lock objects used during parse -Create and store execution plan • Execute: identify rows selected • Fetch: return rows to user process 1-10 Processing a Query (cont.) SELECT * FROM emp ORDER BY ename; Statement Handle Handle User process Server process Results OK OK Parse 1-11 Execute Fetch The Shared Pool Shared pool Library cache Data dictionary cache • Size defined by SHARED_POOL_SIZE • Library cache contains statement text, parsed code, and an execution plan • Data dictionary cache contains table and column definitions and privileges 1-12 Database Buffer Cache • Number of buffers defined by DB_BLOCK_BUFFERS • Size of a buffer based on DB_BLOCK_SIZE • Stores the most recently used blocks 1-13 Program Global Area (PGA) Server process PGA • Not shared and not writable • Contains – Sort area – Session information – Cursor state – Stack space 1-14 Processing a DML Statement 1. If data blocks not in the buffer, server process reads them into the buffer 2. Server process places locks on rows to be modified 3. The redo log buffer is modified with the changed values 4. The data blocks are changed 5. Before image is recorded in the rollback block 1-15 Processing a DML Statement (cont.) UPDATE emp SET sal=sal*1.1 WHERE empno=7369 Server process 3 Instance SGA 4 5 Shared pool Library cache Database buffer cache Redo log buffer Data dictionary cache 2 1 1-16 Data files Control files Database Redo log files Rollback Segment Old image Table New image Rollback segment DML statement 1-17 Redo Log Buffer • Size defined by LOG_BUFFER • Records changes made through the instance • Used sequentially • Circular buffer 1-18 Other Instance Processes • Other required processes - Database Write (DBW0) - Log Writer (LGWR) - Process Monitor (PMON) - System Monitor (SMON) - Checkpoint (CKPT) • Archive process (ARC0) is optional; is used in production database 1-19 Database Writer (DBWR) Instance SGA Shared pool Database buffer cache DBW0 writes when: • There are many dirty buffers • There are few free buffers DBWR • Timeout occurs • Checkpoint occurs Data files 1-20 Control files Redo log files Log Writer (LGWR) Instance SGA Shared pool Redo log buffer LGWR writes when: • There is a commit LGWR • The redo log buffer is one-third full • There is more than 1MB of redo • Before DBW0 writes Data files 1-21 Control files Redo log files COMMIT Processing 1. Server process places a commit record and system change number (SCN) in redo log buffer. 2. LGWR writes redo log to redo log files. 3. User is informed COMMIT is complete 4. Server process records trans. Is complete and locks can be released. 1-22 COMMIT Processing (cont.) 1 Instance SGA Server process 4 Database buffer cache Shared pool Redo log buffer LGWR 3 2 User process Data files Control files Database 1-23 Redo log files SMON: System Monitor • Automatically recovers the instance -Rolls forward changes in redo logs -Opens the database for user access -Rolls back uncommitted transactions • Coalesces free spaces • Deallocates temporary segments 1-24 PMON: Process Monitor Cleans up after failed processes by: • Rolling back the transaction • Releasing locks • Releasing other resources 1-25 Archiving • Database archive mode - NOARCHIVELOG for databases that do not require recovery after disk failure - ARCHIVELOG mode for production •ARC0 process • Automatically archives online redo log files • Preserves the record of all changes made to the database 1-26 Summary Instance SGA Shared pool Server process PGA User process DBWR Control files Parameter file Password file LGWR Redo log files Data files Database 1-27 Archived log files Summary (cont.) You should have learned: • Explain the SGA, Instance, memory structures • Explain the database files • Explain the primary background processes (DBW0, LGWR, CKPT, PMON, SMON, ARC0) •Explain SQL processing steps •Explain the COMMIT process 1-28