ELA instructional sh..
advertisement

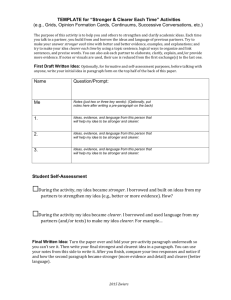
Getting on the Right Track: Investigating Instructional Shifts ELA/ELD Listening and Speaking with the Common Core Instructional Leadership Corp Presenters • Karin Barone, M.A. Ed, NBCT kbarone@orangeusd.org - 4th-6th grade GATE; STEM Specialist; Agenda 1. Zooming in on speaking and academic language in ELA Shifts 2 and 3 2. ELA Claims 3. Speaking Activity Type 1: “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activities (Output) 4. Speaking Activity Type 2: “Constructive Conversation” Activities (Interaction) 5. Four Domains 6. Applying Shifts: What are you taking back? 7. Next Steps Cognitive Learning Common Core requires High-Level Cognitive Demand Students Demonstrate Deeper Conceptual Understanding Application of Content Knowledge & Skills to New Situations and Tasks Applies Webb’s Depth of Knowledge (DOK) to Bloom’s Cognitive Process Dimensions – Bloom: What type of thinking is needed to complete a task? – Webb: How deeply do you have to understand the content to successfully interact with it? How complex or abstract is the content? 4 Webb, 5 4 Domains * Students Content Instruction & Pedagogy Claims & Assessment Knowing your students and attending to all strengths and needs Strong content knowledge Use of effective instructional strategies and Depths of Knowledge (DOKs) Incorporating the 4 SBAC Claims and multiple types of formative and summative assessments 6 Math Claims * Claim #1 Concepts & Procedures Claim #2 Problem Solving “Students can solve a range of complex well-posed problems “Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and interpret and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency.” in pure and applied mathematics, making productive use of knowledge and problem solving strategies.” Claim #3 Communicating Reasoning “Students can clearly and precisely construct viable arguments to support their own reasoning and to critique the reasoning of others.” Claim #4 Modeling and Data Analysis “Students can analyze complex, real-world scenarios and can construct and use mathematical models to interpret and solve problems.” 7 Claim Reading “Students can read closely and analytically to #1 ELA Claims comprehend a range of increasingly complex literary and informational texts.” Claim Writing “Students can produce effective and well-grounded #2 writing for a range of purposes and audiences.” Claim Speaking and Listening “Students can employ effective speaking and #3 listening skills for a range of purposes and audiences.” Claim Research/Inquiry #4 “Students can engage in research and inquiry to investigate topics, and to analyze, integrate, and present information.” 8 Differences Between the 1997 Standards and Common Core Standards 1997 Standards Common Core Standards Focused on CONTENT... The WHAT Focused on SKILLS… The HOW • Students will know… • Career and College Readiness Skills • Students will remember… • Critical thinking skills - Analyze • Students will - Compare and Contrast understand… - Show evidence - Synthesize - Create 9 ELA Shifts 1. Informational Text Building knowledge through content-rich non-fiction. 2. Evidence from Text Reading, writing, and speaking grounded in evidence from text, both literary and informational. 3. Text Complexity Regular practice with complex text and its academic language. Math Shifts 1. Focus Narrow the scope of content and deepen how time and energy is spent. 2. Coherence Integration across grades & subject areas. 3. Rigor Conceptual understanding, procedural fluency, and application of skills in problem solving situations. 10 Zooming in on ELA Shifts 2 and 3 2. Reading, writing, and speaking grounded in evidence from text, both literary and informational. 3. Regular practice with complex text and its We academic are here language. Speaking and Listening Anchor Standard 1: Prepare for and participate effectively in a range of conversations and collaborations with diverse partners, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly and persuasively. Standard 3: Evaluate a speaker’s point of view, reasoning, and use of evidence and rhetoric. Warming Up Speaking Skills with “Pro-Con” Topics: Camping, Shopping, Traveling, TV, Computers, Video Games, School, Cars, Conferences, Testing, Internet Transitions: However, On the other hand, Then again, Frames: but One advantage is … For example, … Another positive of … is… because… A negative aspect of ___ is … In spite of the positives of _____, Variations: Compare-contrast, Cause-Effect, For-Against; Whole class Pro-Con; Pro-Con Directions 1. Director directs three changes with a clap and prompt (e.g., “Pro!” “Con!” “Pro!” “Con”…). 2. Actor says as much as possible in the time, but using sentences and linking them, if possible. 3. Director listens for appropriate time to interrupt. 4. Director listens to decide and tell actor which side he or she leaned toward. Warming Up Speaking Skills with “Pro-Con” Topics: Cell phones used in school Transitions: However, On the other hand, Then again, Frames: but One advantage is … For example, … Another positive of … is… because… A negative aspect of ___ is … In spite of the positives of _____, Variations: Compare-contrast, Cause-Effect, For-Against; Whole class Pro-Con; Oral Output vs. Interaction 1. Output is one-way, one-time communication. Output activities tend to include think-pairshares, answering teacher questions, jigsaws, pro-cons, and oral presentations. 2. Interactions are back-n-forth conversations in which participants build on one another’s Idea ideas to build up and clarify knowledge that wasn’t in their minds before talking. “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activities (to fortify oral output) 1. Talk to a different partner each turn. 2. Opinions, ideas, and answers should become stronger (often longer) and clearer each turn. (This often includes supporting the idea with evidence and examples.) 3. Students borrow and use the language, ideas, and evidence of others for future turns. Clearer & Stronger Each Turn Activity: Opinion Formation Cards 1. Choose text quotations that support different sides of the issue and put them on small cards or strips. 2. Tell students the topic and have them start forming their own opinion. 3. Have students read their own card and think about how it supports, contradicts, or even changes their opinion. 4. Students then meet with students who have different points (different colors), read quotations to each other, and both state their current opinion on the issue. (They can also ask questions and prompt for elaboration.) (They can also first meet with a partner with the same quotation to clarify its meaning.) You can use frames such as: - In my opinion, ____ because _____. - Despite the advantages of … - Given the points that I have heard so far, such as … - I think I lean more to the side of ____ because … Should cell phone use be banned in school? Student Model of Opinion Formation Cards My quote says, “In a recent... I agree with it. I think video games are bad cuz they show violence. My quote says…”In a recent…” In my opinion, violent video games should be banned because they show violence that kids copy. For example, in a war video game kids shoot others. My quote says…”In a recent study…” Even though some video games are educational, many are very violent and should be banned. Kids get excited to shoot others and their minds fill with violence. Games might teach to solve problems, but in my opinion kids will be less violent without them. My quote is, “Parents This card says, “Even though… claim…In my opinion, video My card says… “Companies… Even though some games are bad. Likevideo war Ingames my opinion…. kids’ minds games fill show kids howwith to violence, a lotpeople. are shoot other educational. They solve problems and read. Should video games be banned? An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions and why Should students be prohibited from using theme of this shortinstory? American culture this region? the method works. cell phones at school? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions and why What do you think is the most important theme of this shortinstory? American culture this region? the method theme of thisworks. short story? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me Do you the Native Americans were What dofeel you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions and why treated by theme offairly/appropriately/ethically this shortinstory? American culture this region? the method works. the Spanish? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does theto circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how divide fractions and why theme of this short story? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions and why geography influence Native theme of this shortinstory? American culture the method works. this region? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does theto circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how divide fractions and why theme of this shortinstory? American culture works. this region? the method works? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions Why are rules important to haveand in why theme of this shortinstory? American culture the method works. this region? school? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions why What are the importance of theand American theme of this shortinstory? American culture region? the method works. this symbols we learned about? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions and why Why should we get to use the bikes on the theme of this shortinstory? American culture the method works. this region? playground? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions why Why do we learn the sounds of and our theme of this shortinstory? American culture the method works. this region? letters? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions why Why do we have to know whereand we live? theme of this short story? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me Out of do all the civilizations wemost have learned about, What you think isinfluence the important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions and why which do you feel is the best or most important? theme of this short story? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… An Easier “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity: Interview Grid Name Me What do you think isinfluence the most important does the circulatory system work? How did geography Native Explain how to divide fractions why Which character from the noveland theme of this short story? contributed the most to the story? Why? (just two or three key words, if any) 1. 2. 3. Me Even though…. Because a large percentage of students… In order to… Debrief – “Stronger & Clearer Each Turn” Activity 1. What does this type of activity do for learners? 2. How does it connect to the Common Core and the shifts we highlighted at the outset? (speaking with evidence & academic language) 3. How might you use this type of activity in your setting? Oral Output vs. Interaction 1. Output is one-way, one-time communication. Output activities tend to include think-pairshares, answering teacher questions, jigsaws, pro-cons, and oral presentations. 2. Interactions are back-n-forth conversations in which participants build on one another’s Idea ideas to build up and clarify knowledge that wasn’t in their minds before talking. ALDNetwork.org Understanding Language Constructive Conversation Skills (Mini-teachers) Goal: Students collaboratively (but w/o teacher) build an idea (e.g., knowledge, agreement, solution), using the following skills: Create Idea Negotiate Ideas Build Idea Clarify Idea Fortify Idea Hand motions Video – Argument Scale Conversations Context 5th grade Language Arts/ELD class; Advanced and early advanced partners. This Clip student conversation (http://youtu.be/soHXHaPDZgE) • After reading an article on a program that gives pizza as reward for reading, students discuss their opinions on the issue. • Look for supporting opinions, building on ideas, and clarifying Student Task • Based on what you read in the text, do you think cell phones should be allowed in schools? Using the lists provided in the text, write a paragraph arguing why your position is more reasonable than the opposing position. 1. What skills will students need to have in order to complete this task? 2. How are the skills linked to Common Core? Some of the reasons to support cell phones in school are as follows: • Students can take pictures of class projects to e-mail or show to parents. • Students can text-message missed assignments to friends that are absent. • Many cell phones have calculators or Internet access that could be used for assignments. • If students are slow to copy notes from the board, they can take pictures of the missed notes and view them later. • During study halls, students can listen to music through their cell phones. • Parents can get in touch with their children and know where they are at all times. • Students can contact parents in case of emergencies. 37 Some of the reasons to forbid cell phones in school are as follows: • Students might send test answers to friends or use the Internet to cheat during an exam. • Students might record teachers or other students without their knowledge. No one wants to be recorded without giving consent. • Cell phones can interrupt classroom activities. • Cell phones can be used to text during class as a way of passing notes and wasting time. Based on what you read in the text, do you think cell phones should be allowed in schools? Using the lists provided in the text, write a paragraph arguing why your position is more reasonable than the opposing position. “Constructive Conversations” Activity for All 4 Skills: ACTIVITY FOR SUPPORTING IDEAS: ARGUMENT SCALE Argument Balance Scale Reasons & Evidence My responses to opposing points Reasons & Evidence Opposing position My position 2D-Scale 3-D Version Think-Stop • What are you focusing on right now in your classroom? • How could you use variations (i.e. compare/contrast; Pro/Con; cause/effect; for/against; main idea/details; main idea/theme) with these same strategies? • Use a post-it-note and add your ideas to the grid. Commonalities ELA Cognitive Rigor Matrix SBAC Content Specifications for ELA Bloom’s Taxonomy + Webb’s Depthof-Knowledge Levels (Hess, Carlock, Jones, & Walkup, 2009) 42 Maximize Student Learning What’s Your Plan? • What will you work on for session 2? • What kind of evidence/artifact can you bring back with you to share? • Come with gold nuggets and lumps to share and ask questions/clarifications. • 3-2-1 paper (today and bring one back) • Complete survey – exit slip