What are IPs?
advertisement

Business Trends and Design
Methodologies for IP Reuse
Allen C.-H. Wu
Department of Computer Science
Tsing Hua University
Hsinchu, Taiwan, R.O.C
{Email: chunghaw@cs.nthu.edu.tw}
What are IPs?
Soft IP: synthesizable HDL description.
Firm IP: gate-level netlists.
Hard IP: silicon blocks.
Design Reuse
It has been a common practice in software
developments for years.
It has been a common practice in electronic
product developments for years.
What’s new here?
Is it for real or hype???
IPs and Design Reuse in Software
Functions
Procedures
Sub-programs
Soft IP
Source Code
Reuse
Executable Code
Program
Hard IP
Horizontally VS. Vertically Integrated
System Companies
Horizontally integrated system companies
focus on system designs only and
outsourcing many design tasks.
Vertically integrated system companies use a
system-to-silicon in-house model.
In-House Model
System design division
Reuse
In-house core
providers
Semiconductor division
Business Trends
System companies are interested in
designing and manufacturing systems
quickly with low developing costs.
Semiconductor companies are interested in
attracting more customers and increasing the
volume of their production.
INCREASING THEIR REVENUE$$$$$
Why IP Reuse is a Need in Chip and
System Design
Increasing design complexity.
System-on-a-chip technology.
Time-to-Market pressure.
Worldwide designer shortage.
IP-based Model
IP provider
IP provider
System design division
IPs
Reuse
In-house core
providers
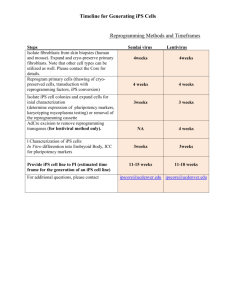
The Factors to Achieve a Successful IP
Business
Customers
Who are the customers?
Market
Where is the market?
YOU
What’s your business model?
Technology
Is the technology ready?
Market for IPs
Soft IPs: too many hurdles need to be
overcome; e.g., legal and security issues.
Firm IPs: some technical issues need to be
resolved; e.g., performance and security
issues.
Hard IPs: may be more realistic which has
been used in many projects.
Who are the Customers?
The system companies who are only
interesting in buying your IPs.
The system companies who are interesting
in both of the IPs and the ASIC design
service.
Obstacles for Commercial IP
Commodity IP isn’t a sustainable business
model
Support costs three times as much as core
development.
Scalable products will survivors, e.g., MIPS
Technology Inc., Advanced RISC Machines
Ltd. And DSP Group Inc.
Business Strategy for IP Vendors
NOW => Provide cell libraries.
NOW => Provide chip layout services.
How to enter IP business and bring in more
revenue?
How to use IPs to sell cell libraries?
How to use design services to sell IPs?
How to use cell libraries and IPs to bring in
more design service revenue?
Considerations for IP Vendors
Definition of suitable cores with high
usability.
Design of these cores with proper set of
parameters to cover a broad segment of the
market.
Packaging those cores with proper interfaces
and documentation for easy use.
Support IP-reuse evaluation and design
methodologies and platform.
Developing business and customer model for
distribution and use of cores.
Requirements for Supporting IP Reuse
Define the sufficient specification to support
IP reuse, such as functionality, electrical,
mechanical, and timing parameters.
Provide multi-level HDL models to support
design verification, simulation, and testing.
Provide test bench and testing scheme.
Provide techniques for generating interfaces
for IP reuse.
IP upgrading for functionality and features.
Design Methodologies supporting IP
Reuse
Netlists
Floorplanning
Place & Route
Verification
Tape out
IPs
Hard &
Firm IPs
Design Methodologies supporting IP
Reuse
Design spec.
Simulation
Environment
IP-based synthesis
IPs
Netlists
Floorplanning
Place & Route
Verification
Tape out
IPs
Functionality
Performance
IP-based Synthesis Method and
Environment
Platform to map a design specification to a
RTL design by reusing IPs.
Platform for design verification and
evaluation.
=> How to convince your customers to use
your IPs?
Business and Customer Model
Marketing strategy.
Accounting .
Customer training in reuse techniques for
different IPs.
Patenting, licensing and royalty collection
from the IP users.
Business Model 1
Buying IPs only: the system companies have
their own system integration methodology
and environment.
Hard IPs: modeling issues.
Firm IPs: modeling and security issues.
Business Model 2
Buying IPs and ASIC design service.
IP-reuse methodology and environment.
Licensing issues when using third-party IPs.
Modeling issues.
Minimal security issues.
Very flexible - provide either hard or firm IPs.
How to include IP-reuse into current design
flow - a IP-reuse driven design flow.
Hurdles Need to be Overcome
Modeling issues.
IP-reuse synthesis methodology and
environment.
An IP-based chip design methodology.
Security issues.
Customer-specific business models.